S17 Cholesterol And Steroids Biosynthesis
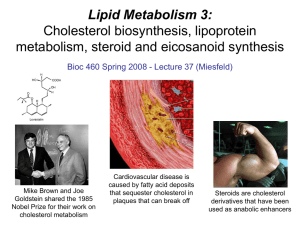
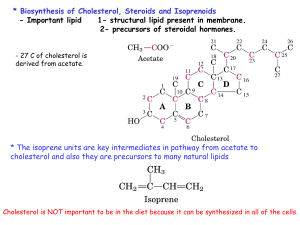
... 1- structural lipid present in membrane. 2- precursors of steroidal hormones. - 27 C of cholesterol is derived from acetate. ...
... 1- structural lipid present in membrane. 2- precursors of steroidal hormones. - 27 C of cholesterol is derived from acetate. ...
Cellular Respiration (Text Book)
... causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space • H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through the ATP synthase Enzyme. • ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP • This is an example of chemiosmosis, the use of energy ...
... causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space • H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through the ATP synthase Enzyme. • ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP • This is an example of chemiosmosis, the use of energy ...
citric acid metabolism in lactic bacteria and
... the microbial ecosystem in the wine during fermentation by imposing selected strains of yeast and bacteria. This prevents contamination due to microfloral spoilage (Renouf et al. 2008a), while ensuring more economical and ecological control of MLF. For example, when the bacteria are active at the hi ...
... the microbial ecosystem in the wine during fermentation by imposing selected strains of yeast and bacteria. This prevents contamination due to microfloral spoilage (Renouf et al. 2008a), while ensuring more economical and ecological control of MLF. For example, when the bacteria are active at the hi ...
A Review on Bio-butyric Acid Production and its Optimization
... acetoacetyl-CoA and butyryl-CoA are formed from pyruvate as key intermediates in the main branch (Jones and Woods, 1986). Butyric acid can be produced consequently in case of presence of high levels of enzymes that are concerned with the pathway of butyryl-CoA to butyrate. During the conversion of a ...
... acetoacetyl-CoA and butyryl-CoA are formed from pyruvate as key intermediates in the main branch (Jones and Woods, 1986). Butyric acid can be produced consequently in case of presence of high levels of enzymes that are concerned with the pathway of butyryl-CoA to butyrate. During the conversion of a ...
Student notes in ppt
... to form the C10 compound geranyl pyrophosphate. The same enzyme adds a second isopentenyl pyrophosphate to generate farnesyl pyrophosphate. Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate are then linked in a head to head arrangement by the enzyme squalene synthase to form squalene (C30) in a reduction reac ...
... to form the C10 compound geranyl pyrophosphate. The same enzyme adds a second isopentenyl pyrophosphate to generate farnesyl pyrophosphate. Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate are then linked in a head to head arrangement by the enzyme squalene synthase to form squalene (C30) in a reduction reac ...
glucuronidation of opioids, carboxylic acid
... suggest that monkey UGT2B9 and human UGT2B7 are functionally similar. ...
... suggest that monkey UGT2B9 and human UGT2B7 are functionally similar. ...
Development of Software Package for Determining Protein
... Asp102 of Chymotrypsin – hydrogen bond with His57 – increases pKa His57 can accepts proton from Ser195 – activates serine protease for cleavage of substrate pKa shift important for each chemical reaction in catalytic mechanism Necessary to donate and abstract protons from neighboring groups Without ...
... Asp102 of Chymotrypsin – hydrogen bond with His57 – increases pKa His57 can accepts proton from Ser195 – activates serine protease for cleavage of substrate pKa shift important for each chemical reaction in catalytic mechanism Necessary to donate and abstract protons from neighboring groups Without ...
BAK1 Gene Variation: the doubts remain
... sequencing of a processed gene on chromosome 20. However, in response, Dr. Gottlieb and coauthors [2010] have argued that “some but not all of the sequence changes present in the BAK1 sequence of our abdominal aorta samples are also present in the chromosome 20 BAK1 sequence. However, all the AAA an ...
... sequencing of a processed gene on chromosome 20. However, in response, Dr. Gottlieb and coauthors [2010] have argued that “some but not all of the sequence changes present in the BAK1 sequence of our abdominal aorta samples are also present in the chromosome 20 BAK1 sequence. However, all the AAA an ...
Ocimum sanctum Induced hepatic damage R.Bhuvaneswari Dr.K.Jegatheesan
... Toxicity of chemicals majorly affects all kinds of plants and animals. Excess of any kind of compounds will be harmful to life [1].Liver plays a major role in detoxification and is generally the major site for intense metabolism[2].It is also a site of biotransformation, of toxic compounds were conv ...
... Toxicity of chemicals majorly affects all kinds of plants and animals. Excess of any kind of compounds will be harmful to life [1].Liver plays a major role in detoxification and is generally the major site for intense metabolism[2].It is also a site of biotransformation, of toxic compounds were conv ...
Metabolomics - Circulation: Cardiovascular Genetics
... Specialized carrier proteins catalyze the transport of nucleotides, amino acids, inorganic ions, fatty acids, keto acids, and cofactors across the impermeable mitochondrial inner membrane. These transport steps are important to maintain a separate inner mitochondrial pool and micromilieu for ATP pro ...
... Specialized carrier proteins catalyze the transport of nucleotides, amino acids, inorganic ions, fatty acids, keto acids, and cofactors across the impermeable mitochondrial inner membrane. These transport steps are important to maintain a separate inner mitochondrial pool and micromilieu for ATP pro ...
Ketone Body Metabolism
... Liver catabolizes fatty acids to meet the energy demand by other tissues Excess of Acetyl CoA is produced, which are destined to form ketone bodies. Ketone bodies are transported by blood to Muscle and Brain. Ketone body formation regenerates free CoA, which is required for β-oxidation. ...
... Liver catabolizes fatty acids to meet the energy demand by other tissues Excess of Acetyl CoA is produced, which are destined to form ketone bodies. Ketone bodies are transported by blood to Muscle and Brain. Ketone body formation regenerates free CoA, which is required for β-oxidation. ...
Modelling of Protein Breakdown During Critical Illness
... Substrate(carbohydrate, fat) −−−−−−→ CO2 + H2 O + energy ...
... Substrate(carbohydrate, fat) −−−−−−→ CO2 + H2 O + energy ...
HIV Protease Inhibitor: Past Endeavors and Future Developments
... mutations, and therefore resistance, in the binding sites of the HIV protease are not of concern since the main interaction takes place through Asp29 and Asp30. This interaction is made possible by the replacement of a THF group by a fused-ring bis-THF moiety in the UIC-94003 compared to previous PI ...
... mutations, and therefore resistance, in the binding sites of the HIV protease are not of concern since the main interaction takes place through Asp29 and Asp30. This interaction is made possible by the replacement of a THF group by a fused-ring bis-THF moiety in the UIC-94003 compared to previous PI ...
structural basis for thermal stability of thermophilic trmd proteins
... The second mechanism used by chaperonins, which contain large cylindrical complexes that create physically isolated compartments designed for the proper folding of polypeptides and misfolded proteins (Nagradova,N.K. 2004) In terms of protein stability under extreme conditions, the literature reveals ...
... The second mechanism used by chaperonins, which contain large cylindrical complexes that create physically isolated compartments designed for the proper folding of polypeptides and misfolded proteins (Nagradova,N.K. 2004) In terms of protein stability under extreme conditions, the literature reveals ...
subunits of succinyl CoA ligase of tomato
... synthesis of succinyl CoA during ketone body formation (Ryan et al., 1997). Recent evidence suggests that the b-subunit is important for conferring nucleotide specificity to the mammalian SCoAL, with relative transcript and polypeptide levels of the GDP and ADP specific ligases differing greatly with ...
... synthesis of succinyl CoA during ketone body formation (Ryan et al., 1997). Recent evidence suggests that the b-subunit is important for conferring nucleotide specificity to the mammalian SCoAL, with relative transcript and polypeptide levels of the GDP and ADP specific ligases differing greatly with ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.