Notes Chapter 3 Biochemistry
... An organic compound contains carbon that is covalently bonded both to other carbon atoms and often to atoms of other elements, including oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen. A carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with other atoms. Carbon atoms can bond with one another to form straight chains, branc ...
... An organic compound contains carbon that is covalently bonded both to other carbon atoms and often to atoms of other elements, including oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen. A carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with other atoms. Carbon atoms can bond with one another to form straight chains, branc ...
PURINE COMPOUNDS Both the pyrimidine bases (uracil, cytosine), and
... Several specific enzymes involved with DNA synthesis are targets for inhibition by F-ara-ATP.20 In particular, F-ara-ATP competes as an alternative substrate with the normal deoxynucleotide, deoxyadenosine 5’-triphosphate (dATP), inhibiting directly the DNA polymerases. Furthermore F-araATP is able ...
... Several specific enzymes involved with DNA synthesis are targets for inhibition by F-ara-ATP.20 In particular, F-ara-ATP competes as an alternative substrate with the normal deoxynucleotide, deoxyadenosine 5’-triphosphate (dATP), inhibiting directly the DNA polymerases. Furthermore F-araATP is able ...
Elements in Cells
... electrons that can bond with other atoms. • When carbon is bonded to hydrogen, which is common in organic molecules, the carbon atom shares an electron with hydrogen, and hydrogen likewise share an electron with carbon. • Carbon-hydrogen molecules are referred to as ...
... electrons that can bond with other atoms. • When carbon is bonded to hydrogen, which is common in organic molecules, the carbon atom shares an electron with hydrogen, and hydrogen likewise share an electron with carbon. • Carbon-hydrogen molecules are referred to as ...
Essential amino acids - Feed-to-Food
... • When steam is used, the temperature of pellets after leaving the die is generally higher • Amino acids were determined with HPLC using the AccQTag method. This method is based on a in comparison with that of the conditioned meal due to the frictional heat in the die derivatizing reagent developed ...
... • When steam is used, the temperature of pellets after leaving the die is generally higher • Amino acids were determined with HPLC using the AccQTag method. This method is based on a in comparison with that of the conditioned meal due to the frictional heat in the die derivatizing reagent developed ...
Generation of Virtual Amino Acid Libraries for Multiple Applications
... The figure above represents the H–reduced formulas of the coded amino acid’s side chains as partially ordered set. This order can be used to describe the set of molecular formulas defined by a fuzzy formula. For instance the fuzzy formula C2−11H5−14N1−4O2−4S includes all molecular formulas f that fu ...
... The figure above represents the H–reduced formulas of the coded amino acid’s side chains as partially ordered set. This order can be used to describe the set of molecular formulas defined by a fuzzy formula. For instance the fuzzy formula C2−11H5−14N1−4O2−4S includes all molecular formulas f that fu ...
Lecture 9
... (1) synthesis of small organic molecules (2) join small molecules (monomers) into big molecules (polymers) (3) aggregrate molecules into droplets which have different properties than their nonliving constituents. (4) origin of heredity, so “droplets” can pass on their molecules to offspring Evolutio ...
... (1) synthesis of small organic molecules (2) join small molecules (monomers) into big molecules (polymers) (3) aggregrate molecules into droplets which have different properties than their nonliving constituents. (4) origin of heredity, so “droplets” can pass on their molecules to offspring Evolutio ...
Amino Acids
... group is protonated and the amino acid is in the cationic form At neutral pH, the carboxyl group is deprotonated but the amino group is protonated. The net charge is zero; such ions are called ...
... group is protonated and the amino acid is in the cationic form At neutral pH, the carboxyl group is deprotonated but the amino group is protonated. The net charge is zero; such ions are called ...
Chemistry of Life
... • Proteins are organic compounds composed mainly of carbon, _____________, oxygen, and nitrogen. • Large molecule built by amino acids • Amino Acids- There are _________ different proteins • Proteins have many different functions such as enzymes, structure, antibodies, hemoglobin(blood flow) ...
... • Proteins are organic compounds composed mainly of carbon, _____________, oxygen, and nitrogen. • Large molecule built by amino acids • Amino Acids- There are _________ different proteins • Proteins have many different functions such as enzymes, structure, antibodies, hemoglobin(blood flow) ...
AP Biology Objectives
... 10. Describe the structure and function of tRNA, and ribosomes. 11. Describe initiation, elongation, and termination of translation, AND explain which enzymes, protein factors, and energy sources are needed for each stage. 12. Explain what determines the primary structure of a protein and describe h ...
... 10. Describe the structure and function of tRNA, and ribosomes. 11. Describe initiation, elongation, and termination of translation, AND explain which enzymes, protein factors, and energy sources are needed for each stage. 12. Explain what determines the primary structure of a protein and describe h ...
Answers to chapter 7 questions Mastering Concepts 7.1 1. How did
... e. No, because the last codon would be a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) f. The peptide would fold into its proper shape and then either begin performing its function in the cell or be exported to the cell’s exterior. g. The figure depicts a prokaryotic cell. In eukaryotes, the mRNA is fully synthesiz ...
... e. No, because the last codon would be a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) f. The peptide would fold into its proper shape and then either begin performing its function in the cell or be exported to the cell’s exterior. g. The figure depicts a prokaryotic cell. In eukaryotes, the mRNA is fully synthesiz ...
What are the major types of organic molecules?
... A. carbohydrates contain only the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen B. the ratio works out so that carbohydrates are typically (CH2O)n C. carbohydrates are the main molecules in biological systems created for energy storage and consumed for energy production; some are also used as building mater ...
... A. carbohydrates contain only the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen B. the ratio works out so that carbohydrates are typically (CH2O)n C. carbohydrates are the main molecules in biological systems created for energy storage and consumed for energy production; some are also used as building mater ...
Biological Molecules continued
... The monomer building blocks of proteins are called amino acids. Most of these amino acids share a common structure. Two amino acids can bond to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. These amino acids can bond to each other in a long chain to form what is commonly called a polypeptide. These ...
... The monomer building blocks of proteins are called amino acids. Most of these amino acids share a common structure. Two amino acids can bond to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. These amino acids can bond to each other in a long chain to form what is commonly called a polypeptide. These ...
CH 3: The Molecules of Life
... covalent bonds called alpha glycosidic bonds • Molecules are either coiled or branched – depending on type of starch ...
... covalent bonds called alpha glycosidic bonds • Molecules are either coiled or branched – depending on type of starch ...
A plant has stunted growth and yellowing leaves because it is
... but does not understand that a hydrogen atom is removed from one amino acid and a hydroxyl group is removed from the other, and that the hydrogen atom and the hydroxyl group form a water molecule, which is released to the environment. Aligned to: LO 2.9 CA 2.9: Represent & Model Matter Exchange ...
... but does not understand that a hydrogen atom is removed from one amino acid and a hydroxyl group is removed from the other, and that the hydrogen atom and the hydroxyl group form a water molecule, which is released to the environment. Aligned to: LO 2.9 CA 2.9: Represent & Model Matter Exchange ...
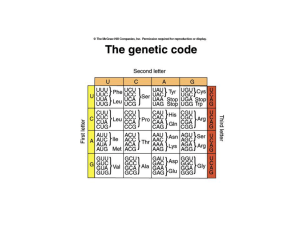
Features of the genetic code
... methyl thransferase adds methyl groups (-CH3) to the G and one or more of the first few bases of the RNA transcript. Capping and methylation is believed to be critical for efficient translation. • Addition of a poly A tail (100-200 As) at the 3’ end of the primary transcript by a poly-A-polymerase. ...
... methyl thransferase adds methyl groups (-CH3) to the G and one or more of the first few bases of the RNA transcript. Capping and methylation is believed to be critical for efficient translation. • Addition of a poly A tail (100-200 As) at the 3’ end of the primary transcript by a poly-A-polymerase. ...
The Organic Molecules of Life
... the process in which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy (sugar molecules) Organelle containing chlorophyll. Photosynthesis (energy from sunlight is converted into chemical energyfood) takes place here. most common lipid in our diet; A lipid made ...
... the process in which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy (sugar molecules) Organelle containing chlorophyll. Photosynthesis (energy from sunlight is converted into chemical energyfood) takes place here. most common lipid in our diet; A lipid made ...
CATALYSIS OF BIOCHEMICAL REACTIONS
... 1. A and B together have some potential energy (in chemical bonds) and kinetic energy (in motion). 2. A and B collide; collision distorts or stresses bonds to the point where they can rearrange electrons; generally, this requires more potential energy (since without stress, one expects electrons to ...
... 1. A and B together have some potential energy (in chemical bonds) and kinetic energy (in motion). 2. A and B collide; collision distorts or stresses bonds to the point where they can rearrange electrons; generally, this requires more potential energy (since without stress, one expects electrons to ...
Exam 1
... 4. A mutant form of hemoglobin called Hb Ohio has a 142AlaAsp mutation which causes a change in alpha helix structure, which in turn disrupts salt bridges in the central cavity of Hb Ohio. What effect does this mutation have on the oxygen binding affinity of Hb Ohio compared to normal hemoglobin (H ...
... 4. A mutant form of hemoglobin called Hb Ohio has a 142AlaAsp mutation which causes a change in alpha helix structure, which in turn disrupts salt bridges in the central cavity of Hb Ohio. What effect does this mutation have on the oxygen binding affinity of Hb Ohio compared to normal hemoglobin (H ...
- Applied Science University
... After studying this course the student should be able to: Successful completion of this course should lead to the following learning outcomes : 1- Students should be able to follow the saftey procedures and lab instruction. 2- Student should be able to identify and effeciently use the glasswares and ...
... After studying this course the student should be able to: Successful completion of this course should lead to the following learning outcomes : 1- Students should be able to follow the saftey procedures and lab instruction. 2- Student should be able to identify and effeciently use the glasswares and ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.