You Light Up My Life
... • DNA is two nucleotide strands held together by hydrogen bonds • Hydrogen bonds between two strands are easily broken ...
... • DNA is two nucleotide strands held together by hydrogen bonds • Hydrogen bonds between two strands are easily broken ...
RNA
... Step 1: RNA polymerase (enzyme) binds to DNA at the promoter region (a DNA sequence that signals the start of the gene and marks the start of transcription.) Step 2: RNA polymerase breaks the hydrogen bonds, unwinding the DNA double helix. Step 3: RNA polymerase reads the DNA, building a new RNA str ...
... Step 1: RNA polymerase (enzyme) binds to DNA at the promoter region (a DNA sequence that signals the start of the gene and marks the start of transcription.) Step 2: RNA polymerase breaks the hydrogen bonds, unwinding the DNA double helix. Step 3: RNA polymerase reads the DNA, building a new RNA str ...
Reading GuideChapter6_Tues
... Which of these three methods is how cells make ATP within a metabolic pathway such as glycolysis by the transfer of a phosphate group from an organic compound to ADP? Which process is the generation of ATP through oxidation/reduction reactions in the electron transport chain? Another key concept for ...
... Which of these three methods is how cells make ATP within a metabolic pathway such as glycolysis by the transfer of a phosphate group from an organic compound to ADP? Which process is the generation of ATP through oxidation/reduction reactions in the electron transport chain? Another key concept for ...
DNA
... DNA replication • DNA replication begins when enzyme helicase unwinds a segment of the DNA and breaks the hydrogen bonds between the two complementary strands of DNA. • Replication fork - the junction where the double-stranded DNA splits apart into 2 single strands • DNA is copied by enzyme DNA pol ...
... DNA replication • DNA replication begins when enzyme helicase unwinds a segment of the DNA and breaks the hydrogen bonds between the two complementary strands of DNA. • Replication fork - the junction where the double-stranded DNA splits apart into 2 single strands • DNA is copied by enzyme DNA pol ...
Genetics - LLI Manassas
... in our body. Making them requires enzymes, which are themselves proteins, and proteins such as RNA polymerase (pəˈliməˌrās) and the ribosome (rībəˌsōm) described below, etc. are needed to fabricate all these. There are over 100,000 unique types, including ATP synthase (sĭn′thās′). These and many/mo ...
... in our body. Making them requires enzymes, which are themselves proteins, and proteins such as RNA polymerase (pəˈliməˌrās) and the ribosome (rībəˌsōm) described below, etc. are needed to fabricate all these. There are over 100,000 unique types, including ATP synthase (sĭn′thās′). These and many/mo ...
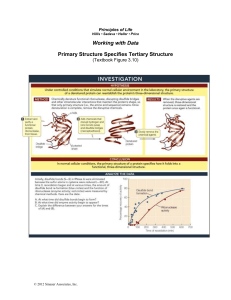
Principles of Life
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
PHAR2811 Dale`s lecture 6 Telomerases as drug targets
... occur after replication. • An example. There are 3.2 X 109 purine nucleotides in the human genome. Each day ~10 000 glycosidic bonds are cleaved from these purines in a given cell under physiological conditions. • The conclusion: your cells contain some nasty little compounds. There are 130 genes wh ...
... occur after replication. • An example. There are 3.2 X 109 purine nucleotides in the human genome. Each day ~10 000 glycosidic bonds are cleaved from these purines in a given cell under physiological conditions. • The conclusion: your cells contain some nasty little compounds. There are 130 genes wh ...
transcription - Geneticskippnyc
... • In transcription, the DNA helix unzips – RNA nucleotides line up along one strand of the DNA following the base-pairing rules – The single-stranded messenger RNA peels away and the DNA strands rejoin ...
... • In transcription, the DNA helix unzips – RNA nucleotides line up along one strand of the DNA following the base-pairing rules – The single-stranded messenger RNA peels away and the DNA strands rejoin ...
Document
... – Carboxyl – in amino acids, fatty acids; acts as an acid and releases H+ – Amino – in amino acids; acts as a weak base – Sulfhydryl – in amino acid cysteine; helps stabilize protein structure ...
... – Carboxyl – in amino acids, fatty acids; acts as an acid and releases H+ – Amino – in amino acids; acts as a weak base – Sulfhydryl – in amino acid cysteine; helps stabilize protein structure ...
Biomolecule Discussion Guide KEY
... a. How are polymers formed? Polymers are formed through a process called dehydration synthesis or condensation. During this process, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom are removed from the monomers to form water, and then, the two monomers are joined together. (Students may wish to draw a diagra ...
... a. How are polymers formed? Polymers are formed through a process called dehydration synthesis or condensation. During this process, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom are removed from the monomers to form water, and then, the two monomers are joined together. (Students may wish to draw a diagra ...
AMINO ACIDS IN PROTEINS
... structures (-helix and -sheet structure) For example: keratin, collagen (-helix), silk fibrin (-sheet structure) ...
... structures (-helix and -sheet structure) For example: keratin, collagen (-helix), silk fibrin (-sheet structure) ...
Proleins: Chem[siry And
... 2. (a) How many amino ands are there? (b) How are amino acids used by living things? 3. List several of your body parts that are protein. ...
... 2. (a) How many amino ands are there? (b) How are amino acids used by living things? 3. List several of your body parts that are protein. ...
PowerPoint Presentation Materials to accompany
... Therefore, the alteration of an amino acid already attached to tRNA should cause that altered amino acid to be incorporated into the polypeptide instead of the normal amino acid Example: Cysteine on a tRNAcys is changed to alanine cys will add alanine instead of the Therefore, the tRNA ...
... Therefore, the alteration of an amino acid already attached to tRNA should cause that altered amino acid to be incorporated into the polypeptide instead of the normal amino acid Example: Cysteine on a tRNAcys is changed to alanine cys will add alanine instead of the Therefore, the tRNA ...
Document
... • Cooperativity is caused by conformational changes in the first protein subunit which lead to conformational and binding rate changes in neighboring subunits • Regulatory molecules usually change conformation and therefore properties of protein • This is the basis of physiological regulation of pro ...
... • Cooperativity is caused by conformational changes in the first protein subunit which lead to conformational and binding rate changes in neighboring subunits • Regulatory molecules usually change conformation and therefore properties of protein • This is the basis of physiological regulation of pro ...
Outline05 Enzymes - Napa Valley College
... total of all chemical reactions in the body catabolic reactions - break down large molecules into smaller ones anabolic reactions - build larger molecules from smaller ones (synthesis) exergonic reactions release energy endergonic reactions require energy Major classes of metabolic reactions: 1. H ...
... total of all chemical reactions in the body catabolic reactions - break down large molecules into smaller ones anabolic reactions - build larger molecules from smaller ones (synthesis) exergonic reactions release energy endergonic reactions require energy Major classes of metabolic reactions: 1. H ...
Chapter 5 - My Teacher Site
... • Lipids are not true polymers and they are generally not big enough to be called macromolecules – They are grouped together because they all mix poorly, if at all, with water due to their structure • Although some may contain polar bonds associated with oxygen, they consist mostly of hydrocarbon r ...
... • Lipids are not true polymers and they are generally not big enough to be called macromolecules – They are grouped together because they all mix poorly, if at all, with water due to their structure • Although some may contain polar bonds associated with oxygen, they consist mostly of hydrocarbon r ...
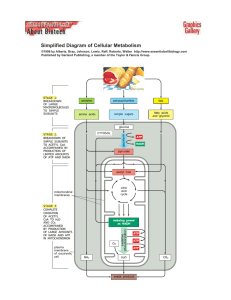
Cellular Metabolism and Nutrition notes
... • The process that releases energy from molecules of glucose and makes it available for cellular use. (In the form of ATP). • Includes 2 pathways – Aerobic - requires oxygen. – Anaerobic - no oxygen required. ...
... • The process that releases energy from molecules of glucose and makes it available for cellular use. (In the form of ATP). • Includes 2 pathways – Aerobic - requires oxygen. – Anaerobic - no oxygen required. ...
study guide RNA DNA Protine syn Key
... which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. The two can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, RNA strand. Transcription proceeds in the ...
... which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. The two can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, RNA strand. Transcription proceeds in the ...
Fatty Acid oxidation
... β-oxidation Pathway Oxidation of fatty acids takes place in mitochondria where the various enzymes for fatty acid oxidation are present close to the enzymes of the electron transport chain. Fatty acid oxidation is a major source of cell ATP Oxidation of FAs occur at the β-carbon atom resultin ...
... β-oxidation Pathway Oxidation of fatty acids takes place in mitochondria where the various enzymes for fatty acid oxidation are present close to the enzymes of the electron transport chain. Fatty acid oxidation is a major source of cell ATP Oxidation of FAs occur at the β-carbon atom resultin ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.