EXAM OF SCIENTIFIC CULTURE CHEMISTRY PROBLEM 1
... 3.2.1 Propose the hybridization state of the four nitrogen atoms of FAD and indicate the nature of the orbital containing the non-bonding electron pair. 3.2.2 FAD is an aromatic compound. Justify this character by showing, among other possibilities, the number of electrons involved in the aromaticit ...
... 3.2.1 Propose the hybridization state of the four nitrogen atoms of FAD and indicate the nature of the orbital containing the non-bonding electron pair. 3.2.2 FAD is an aromatic compound. Justify this character by showing, among other possibilities, the number of electrons involved in the aromaticit ...
Transcription Student Handout
... DNA carries all of the instructions for making the proteins found in our bodies. In fact, DNA is the universal code for the characteristics of simple organisms such as bacteria, and for complex organisms such as plants or animals. DNA codes for the characteristics of all living things! In this lesso ...
... DNA carries all of the instructions for making the proteins found in our bodies. In fact, DNA is the universal code for the characteristics of simple organisms such as bacteria, and for complex organisms such as plants or animals. DNA codes for the characteristics of all living things! In this lesso ...
Nitrogen Acquisition and Amino Acid Metabolism
... b. We (eukaryotes) can’t take inorganic forms of nitrogen and put it in the reduced form we need to make amino acids. c. Prevalent forms of nitrogen i. atomospheric nitrogen (78% of atmosphere) ii. nitrate anions (NO3-) iii. These are oxidized forms of nitrogen. iv. We have to have reduced form. d. ...
... b. We (eukaryotes) can’t take inorganic forms of nitrogen and put it in the reduced form we need to make amino acids. c. Prevalent forms of nitrogen i. atomospheric nitrogen (78% of atmosphere) ii. nitrate anions (NO3-) iii. These are oxidized forms of nitrogen. iv. We have to have reduced form. d. ...
RNA-catalysed nucleotide synthesis
... Ribozymes of RNA world need to promote reactions involving small organic molecules. Uracil is significantly smaller than the smallest known ribozyme substrate Found catalytic RNA can specifically recognize and utilize 4SUra and can ...
... Ribozymes of RNA world need to promote reactions involving small organic molecules. Uracil is significantly smaller than the smallest known ribozyme substrate Found catalytic RNA can specifically recognize and utilize 4SUra and can ...
Parenteral Alimentation in Surgery
... Too frequently it is considered an enemy rather than an essential to normal metabolism. For example, it is a precursor to bile acids, a precursor to steroid hormones, a regulator of cell permeability, an insulator for axons, and perhaps has other important functions. Just why chole terol is found wi ...
... Too frequently it is considered an enemy rather than an essential to normal metabolism. For example, it is a precursor to bile acids, a precursor to steroid hormones, a regulator of cell permeability, an insulator for axons, and perhaps has other important functions. Just why chole terol is found wi ...
glossary of technical terms
... technologies. Millions or billions of DNAs can be sequenced in parallel, yielding substantially more throughput for genome sequencing ...
... technologies. Millions or billions of DNAs can be sequenced in parallel, yielding substantially more throughput for genome sequencing ...
breakfast proteins
... Write out a template for the cereal chain using letters to correspond to the different colors of the cereal (ie. YOPPRRGYYOP). Tape this down somewhere in the corner of the room and section off this area with some string. Put some scrap paper and things to write with next to the template. To do and ...
... Write out a template for the cereal chain using letters to correspond to the different colors of the cereal (ie. YOPPRRGYYOP). Tape this down somewhere in the corner of the room and section off this area with some string. Put some scrap paper and things to write with next to the template. To do and ...
Biology-1 Exam Two Sample Questions Substrates bind to an
... b. Enzymes are very specific for certain substrates. c. Enzymes are used up in chemical reactions. d. Enzymes emerge unchanged from the reactions they catalyze. e. An enzyme binds to its substrate at the enzyme's active site. 3. Which of the following statements about the ATP molecule is true? a. It ...
... b. Enzymes are very specific for certain substrates. c. Enzymes are used up in chemical reactions. d. Enzymes emerge unchanged from the reactions they catalyze. e. An enzyme binds to its substrate at the enzyme's active site. 3. Which of the following statements about the ATP molecule is true? a. It ...
Energy Production II - University of Massachusetts Amherst
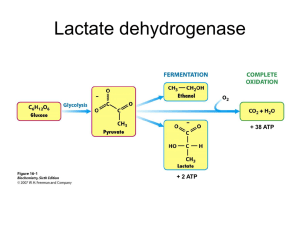
... lactate), replaces blood glucose being used to maintain normal blood glucose levels. ...
... lactate), replaces blood glucose being used to maintain normal blood glucose levels. ...
Flexibility of a polypeptide chain
... but in proteins, rigidity of peptide units and the restricted set of allowed phi and psi values actually limit the number of possible structures and it is overcome by interactions that favor the folded form e.g. hydrophobic interactions among apolar side-chains (rather than being exposed to polar wa ...
... but in proteins, rigidity of peptide units and the restricted set of allowed phi and psi values actually limit the number of possible structures and it is overcome by interactions that favor the folded form e.g. hydrophobic interactions among apolar side-chains (rather than being exposed to polar wa ...
Picture Guide to Chapter 4
... Each atom of carbon has four electrons in its outer energy level, which makes it possible for each carbon atom to form four bonds with other atoms. As a result, carbon atoms can form long chains. A huge number of different carbon compounds exist. Each compound has a different structure. Fo ...
... Each atom of carbon has four electrons in its outer energy level, which makes it possible for each carbon atom to form four bonds with other atoms. As a result, carbon atoms can form long chains. A huge number of different carbon compounds exist. Each compound has a different structure. Fo ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... (ii) Increasing tyrosyl –tRNA synthetase activity by protein engineering (28) Discuss the following: (i) Enzyme replacement therapy for cancer (ii) Enzymes used in the alcohol and starch industry (29) Explain the following: (i) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (ii) Enzymes in the diagnos ...
... (ii) Increasing tyrosyl –tRNA synthetase activity by protein engineering (28) Discuss the following: (i) Enzyme replacement therapy for cancer (ii) Enzymes used in the alcohol and starch industry (29) Explain the following: (i) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (ii) Enzymes in the diagnos ...
Herbicide Mode of Action - Montana State University
... Specific biochemical change responsible for killing plant is not known (probably several processes) Grasses are not susceptible (may be due to differences in vascular tissue structure or differences in translocation or metabolism) ...
... Specific biochemical change responsible for killing plant is not known (probably several processes) Grasses are not susceptible (may be due to differences in vascular tissue structure or differences in translocation or metabolism) ...
Lecture 6A/ Chapter 6 Protein
... • A protein is a compound composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N) atoms. • Proteins are like carbohydrates (CHO) and lipids. BUT • Proteins also contain a N atom. • Amino acids: the building blocks of proteins. • Amino group • Acid group • H atom • Distinctive side group ...
... • A protein is a compound composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N) atoms. • Proteins are like carbohydrates (CHO) and lipids. BUT • Proteins also contain a N atom. • Amino acids: the building blocks of proteins. • Amino group • Acid group • H atom • Distinctive side group ...
Metabolic Pathways
... • Induced fit and the role of the active site of enzymes including shape and substrate affinity. • How enzymes affect activation energy. • The effects of substrate and end product concentration on the direction and rate of enzyme reactions. • Enzymes often act in groups or as multi-enzyme ...
... • Induced fit and the role of the active site of enzymes including shape and substrate affinity. • How enzymes affect activation energy. • The effects of substrate and end product concentration on the direction and rate of enzyme reactions. • Enzymes often act in groups or as multi-enzyme ...
Biological Building Blocks II
... • Gas: molecules have enough energy to break free from each other ...
... • Gas: molecules have enough energy to break free from each other ...
Chapter 3: Energy, Catalysis, and Biosynthesis
... phosphorylating it at the same time so that it can be fed unchanged into the glycolytic pathway. 13-41 In the final stage of the oxidation of food molecules, a gradient of protons is formed across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which is normally impermeable to protons. If cells were exposed to an ...
... phosphorylating it at the same time so that it can be fed unchanged into the glycolytic pathway. 13-41 In the final stage of the oxidation of food molecules, a gradient of protons is formed across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which is normally impermeable to protons. If cells were exposed to an ...
PURINE & PYRIMIDINE METABOLISM
... purine synthesis. IMP is synthesized and could make AMP or GMP. It happens in almost most cells’ cytosol except human brain,polymorphonuclear leukocytes and ...
... purine synthesis. IMP is synthesized and could make AMP or GMP. It happens in almost most cells’ cytosol except human brain,polymorphonuclear leukocytes and ...
Biology Review Test
... 20. What are disease-causing organisms called? a. microorganisms b. pathogens c. viruses d. parasites ...
... 20. What are disease-causing organisms called? a. microorganisms b. pathogens c. viruses d. parasites ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.