Molecular Sequence Programs
... is perfectly legal, assuming that the species name has gone before, and is filled out to full length by blanks. The above digits and blanks will be ignored, the sequence being taken as starting at the first base symbol (in this case an A). This should enable you to use output from many multipleseque ...
... is perfectly legal, assuming that the species name has gone before, and is filled out to full length by blanks. The above digits and blanks will be ignored, the sequence being taken as starting at the first base symbol (in this case an A). This should enable you to use output from many multipleseque ...
ENZYMES
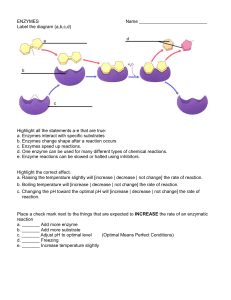
... a. Raising the temperature slightly will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. b. Boiling temperature will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. c. Changing the pH toward the optimal pH will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. ...
... a. Raising the temperature slightly will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. b. Boiling temperature will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. c. Changing the pH toward the optimal pH will [increase | decrease | not change] the rate of reaction. ...
Document
... In other words, these universal genes appear to be younger than the taxonomic groups in which they are found today “ That is to say, there was a time when Archaea, Bacteria and Eukaryotes existed but that they lacked the amino acids arginine and tryptophan. If so, then LUCA, if it ever existed, coul ...
... In other words, these universal genes appear to be younger than the taxonomic groups in which they are found today “ That is to say, there was a time when Archaea, Bacteria and Eukaryotes existed but that they lacked the amino acids arginine and tryptophan. If so, then LUCA, if it ever existed, coul ...
Updated - PeproTech Posters
... Protein transduction using TAT fusion proteins represents an alternative methodology for introducing transcription factors and other intracellular proteins into primary as well as transformed cells. Recombinant human TIGAR-TAT expressed in E.coli is a 36 kDa protein containing 284 amino-acid residue ...
... Protein transduction using TAT fusion proteins represents an alternative methodology for introducing transcription factors and other intracellular proteins into primary as well as transformed cells. Recombinant human TIGAR-TAT expressed in E.coli is a 36 kDa protein containing 284 amino-acid residue ...
Today`s Plan: 1/5/09
... a glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains Main component of phospholipids, which form micells in water and are responsible for? Saturated fats contain all single bonds on the main hydrocarbon chain, while unsaturated fats contain double or triple bonds. What’s a trans-fat? ...
... a glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains Main component of phospholipids, which form micells in water and are responsible for? Saturated fats contain all single bonds on the main hydrocarbon chain, while unsaturated fats contain double or triple bonds. What’s a trans-fat? ...
EF-Tu (elongation factor thermo unstable)
... The central dogma of biology is the pathway that starts from a DNA sequence and leads to the formation of a protein; therefore, DNA directs the synthesis of proteins. The process of protein synthesis, also known as translation, can be divided into three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination ...
... The central dogma of biology is the pathway that starts from a DNA sequence and leads to the formation of a protein; therefore, DNA directs the synthesis of proteins. The process of protein synthesis, also known as translation, can be divided into three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination ...
Chemistry: Biological Molecules (GPC)
... of cellulose, which provides structural support to the cell. Wood and paper are mostly cellulosic in nature. Cellulose is made up of glucose monomers that are linked by bonds between particular carbon atoms in the glucose molecule. Every other glucose monomer in cellulose is ipped over and packed t ...
... of cellulose, which provides structural support to the cell. Wood and paper are mostly cellulosic in nature. Cellulose is made up of glucose monomers that are linked by bonds between particular carbon atoms in the glucose molecule. Every other glucose monomer in cellulose is ipped over and packed t ...
Gene Duplication in the Mo-Fe Protein of Nitrogenase
... • catalyzes the conversion of molecular nitrogen (N2) from the air into ammonia (NH3). • It is found in a variety of bacteria, some of them symbiotic with plants. ...
... • catalyzes the conversion of molecular nitrogen (N2) from the air into ammonia (NH3). • It is found in a variety of bacteria, some of them symbiotic with plants. ...
aminoacyl-tRNA
... using artificial mRNA templates of various base composition (and triplets), in vitro protein synthesis and filter binding assays. • A tRNA molecule can recognize one to three codons depending what the first (wobble) nucleotide of the anticodon is (C and A for one, U and G for two, I for three). • In ...
... using artificial mRNA templates of various base composition (and triplets), in vitro protein synthesis and filter binding assays. • A tRNA molecule can recognize one to three codons depending what the first (wobble) nucleotide of the anticodon is (C and A for one, U and G for two, I for three). • In ...
Amino Acid Synthesis Inhibitors-Group 2 Mode of
... Site of Action – Light causes the formation of free radicals. These radicals rupture plant cell membranes resulting in a rapid browning of tissue Translocation – None or very limited, necrotic spots Uses / Notes – Mostly foliar-applied - uptake into leaves – Some soil-applied - root and shoot uptake ...
... Site of Action – Light causes the formation of free radicals. These radicals rupture plant cell membranes resulting in a rapid browning of tissue Translocation – None or very limited, necrotic spots Uses / Notes – Mostly foliar-applied - uptake into leaves – Some soil-applied - root and shoot uptake ...
organic compounds
... • Insulin resistance occurs when the body becomes less sensitive to insulin. Insulin resistance occurs when insulin levels are sufficiently high over a prolonged period of time causing the body’s own sensitivity to the hormone to be reduced. • Once the body starts to get resistant to insulin, it can ...
... • Insulin resistance occurs when the body becomes less sensitive to insulin. Insulin resistance occurs when insulin levels are sufficiently high over a prolonged period of time causing the body’s own sensitivity to the hormone to be reduced. • Once the body starts to get resistant to insulin, it can ...
No Slide Title
... – hundreds of glucose molecules combined to form glycogen for storage in liver & skeletal muscles • Lipogenesis (triglyceride synthesis) – converted to glycerol & fatty acids within liver & sent to fat cells ...
... – hundreds of glucose molecules combined to form glycogen for storage in liver & skeletal muscles • Lipogenesis (triglyceride synthesis) – converted to glycerol & fatty acids within liver & sent to fat cells ...
Student PPT Notes
... with a carboxyl group – __________ on 1 end) attached to a ____________(3C backbone) * uses primarily as ________________________ molecules * contain ____ as many _______/gram than Carbs & Proteins ...
... with a carboxyl group – __________ on 1 end) attached to a ____________(3C backbone) * uses primarily as ________________________ molecules * contain ____ as many _______/gram than Carbs & Proteins ...
Document
... – DNA and RNA are responsible for storage and transmission of genetic information. – They determine how genetic information is transferred from one cell to another and how genetic traits are transferred from parents to offspring. – The major function of DNA is control and direction or protein synthe ...
... – DNA and RNA are responsible for storage and transmission of genetic information. – They determine how genetic information is transferred from one cell to another and how genetic traits are transferred from parents to offspring. – The major function of DNA is control and direction or protein synthe ...
review powerpoint
... A. in the presence of catalysts B. at higher concentrations of reactants C. when reactants are toxic chemicals D. in the absence of catalysts ...
... A. in the presence of catalysts B. at higher concentrations of reactants C. when reactants are toxic chemicals D. in the absence of catalysts ...
Lecture PPT
... isotopically enriched (for example, containing 15N salts, or 13C-labelled amino acids) or isotopically depleted. b, Proteins are labelled at specific sites with isotopically encoded reagents. The reagents can also contain affinity tags, allowing for the selective isolation of the labelled peptides a ...
... isotopically enriched (for example, containing 15N salts, or 13C-labelled amino acids) or isotopically depleted. b, Proteins are labelled at specific sites with isotopically encoded reagents. The reagents can also contain affinity tags, allowing for the selective isolation of the labelled peptides a ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.