* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Review - Renton School District
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
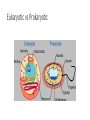
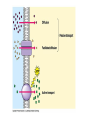
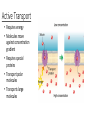
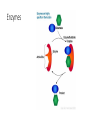
Biology Review Mid-Term Final Exam Carbon and CarbonTime • Carbon is the element for Life • Atoms last forever • All matter is made up of atoms • Energy lasts forever Molecules vs Atoms Atoms Molecules • Single element • 2 or more elements together • • • • Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen • Water (H20) • Carbon dioxide (CO2) • Methane (CH4) High energy bonds • Carbon to carbon • Carbon to hydrogen Reactants and products BTB = measures what? • Presence of carbon dioxide • Changes yellow • Movement of carbon dioxide or carbon molecules Forms of energy • Chemical • Heat • Light • Motion Biosynthesis: Building Cow Muscles Build PROTEIN molecules by taping 4 amino acid monomers together. Notice you will need to remove an –H and –OH from each amino acid. Tape these back together to make water. Chemical change 8 Digestion Cellular Respiration SUGAR + OXYGEN CARBON DIOXIDE + WATER + ENERGY C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + ATP • What happens to atoms and energy in cellular respiration? Carbon Dioxide Glucose Reactants Chemical change Water Products Oxygen Heat and motion energy 11 Biomolecules (Macromolecules) Biomolecule (polymer) Subunit (monomer) Example: food source Carbohydrates Glucose (simple sugar) Starch: potato, rice, bread Cellulose: plants Lipids (fats) Fatty lipids Oils, butter Proteins Amino acids Meat, eggs, nuts Biomolecular Processes Process Chemical Input Chemical Output Energy form before Energy form after Digestion Carbs, O2, H2O polymer CO2, feces, urine monomer chemical Chemical, heat, movement Biosynthesis Monomer Amino acid Polymer, H2O protein chemical Chemical, heat C-C, C-H Cellular Respiration O2, Sugar (C6H12O6) CO2, H20 Chemical C-C, C-H ATP, heat, movement (growth) Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic Plant vs Animal Cells Diffusion: Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration Simple • No energy required • High to low movement across membrane • Small molecules • random Facilitated • No energy require • High to low • Small and large molecules • random Active Transport • Requires energy • Molecules move against concentration gradient • Requires special proteins • Transport polar molecules • Transports large molecules Organelle Organelles of the cell Function Prok Animal Plant Nucleus Control center X X Mitochondria Energy (power house) X X chloroplast photosynthesis Lysosome Break things down (enzymes) Cell membrane Gate keeper, structure Cell wall Structure, support, protection ribosomes Makes proteins X X X DNA/chromomso mes Instruction manual X X X Golgi App Packaging and shipping X X Endoplasmic Reticulum transportation X X X X X X X X Enzymes Photosynthesis