File
... - COX-1 is a constitutive enzyme which is present in platelets and other cells. - COX-2 is an inducible form, which is produced in response to cytokine stimulation in areas of ...
... - COX-1 is a constitutive enzyme which is present in platelets and other cells. - COX-2 is an inducible form, which is produced in response to cytokine stimulation in areas of ...
Anabolism
... The figure shows 2 ATP, resulting directly from 2 turns of the cycle per glucose molecule that enters glycolysis. ...
... The figure shows 2 ATP, resulting directly from 2 turns of the cycle per glucose molecule that enters glycolysis. ...
Enzymes
... Enzymes We've been talking about various biological molecules and that they are needed for reactions in the body (DNA, Protein synthesis, Cellular respiration etc.) and how molecules can change. You should know that it doesn't happen on its own. If you leave a blob of protein in a petri dish will it ...
... Enzymes We've been talking about various biological molecules and that they are needed for reactions in the body (DNA, Protein synthesis, Cellular respiration etc.) and how molecules can change. You should know that it doesn't happen on its own. If you leave a blob of protein in a petri dish will it ...
How do proteins recognize DNA
... Repressor protein stimulates transcription of Repressor and blocks transcription of Cro, and maintains the lysogenic state. Cro protein, does the opposite. It stimulates transcription of Cro and blocks transcription of Repressor and turns the switch to the lytic state. The operator region contains t ...
... Repressor protein stimulates transcription of Repressor and blocks transcription of Cro, and maintains the lysogenic state. Cro protein, does the opposite. It stimulates transcription of Cro and blocks transcription of Repressor and turns the switch to the lytic state. The operator region contains t ...
Enzymes
... (steady) internal balance. • In living things, homeostasis shares a close relationship with enzyme function. • Enzymes can destroy harmful substances that might disrupt homeostasis. – And homeostasis maintains conditions necessary for enzymes to function. ...
... (steady) internal balance. • In living things, homeostasis shares a close relationship with enzyme function. • Enzymes can destroy harmful substances that might disrupt homeostasis. – And homeostasis maintains conditions necessary for enzymes to function. ...
CAD_issue_#3 - University of Illinois Archives
... implications of the notion transcend translation per se; going into the dynamic of the mechanism's evolution; beyond that into the evolution of (all or most) biological macromolecules; then to the evolution of biological entities (and processes?) at all its organizational levels; and (see CAD issue ...
... implications of the notion transcend translation per se; going into the dynamic of the mechanism's evolution; beyond that into the evolution of (all or most) biological macromolecules; then to the evolution of biological entities (and processes?) at all its organizational levels; and (see CAD issue ...
Purine & Pyrimidine Disorders: Clinical Aspects
... Methionine and cystine restriction diet 3.0 g/kg/day protein 1-1.7 g/kg/day restricted natural protein ...
... Methionine and cystine restriction diet 3.0 g/kg/day protein 1-1.7 g/kg/day restricted natural protein ...
Lecture 1001
... Isotope forms of elements are important in science and medicine Look for application of isotope form of an element used in science and medicine Describe the kind of application Determine the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons Draw a planetary description of the isotopic element ...
... Isotope forms of elements are important in science and medicine Look for application of isotope form of an element used in science and medicine Describe the kind of application Determine the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons Draw a planetary description of the isotopic element ...
Metabolism Fact Sheet - Barth Syndrome Foundation
... sequence called acyltransferases. Acyl- means fatty acid or fat. Transferase does mean to transfer this fatty acuid from one thing or molecule o another. Acyltransferases are enzymes that remodel phospholipids In Barth syndrome, cells cannot add the unsaturated fatty acids to the premature form of c ...
... sequence called acyltransferases. Acyl- means fatty acid or fat. Transferase does mean to transfer this fatty acuid from one thing or molecule o another. Acyltransferases are enzymes that remodel phospholipids In Barth syndrome, cells cannot add the unsaturated fatty acids to the premature form of c ...
Biochemisty
... – phospholipids (also known as glycerophospholipids) - lipids which are made of fatty acids, glycerol, a phosphoryl group and an alcohol. Many also contain nitrogen – glycolipids (also known as glycosphingolipids): Lipids which have a spingosine and different backbone than the phospholipids ...
... – phospholipids (also known as glycerophospholipids) - lipids which are made of fatty acids, glycerol, a phosphoryl group and an alcohol. Many also contain nitrogen – glycolipids (also known as glycosphingolipids): Lipids which have a spingosine and different backbone than the phospholipids ...
ENERGY METABOLISM
... The surplus amino acids ARE NOT STORED, but are either: a. released into the blood for all tissues to use in protein synthesis, b. they are with the resulting carbon skeletons being degraded by the liver pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or TCA cycle intermediates, these metabolites can be oxidized for energy o ...
... The surplus amino acids ARE NOT STORED, but are either: a. released into the blood for all tissues to use in protein synthesis, b. they are with the resulting carbon skeletons being degraded by the liver pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or TCA cycle intermediates, these metabolites can be oxidized for energy o ...
Kofaktörler - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Coenzymes Cosubstrates- altered in rxn and regenerated to original structure in subsequent rxn - disassociated from active site - shuttle chemical groups among different enzyme rxns. Prosthetic groups- remains bound to enzyme - must return to original form Both cosubstrates and prosthetic groups su ...
... Coenzymes Cosubstrates- altered in rxn and regenerated to original structure in subsequent rxn - disassociated from active site - shuttle chemical groups among different enzyme rxns. Prosthetic groups- remains bound to enzyme - must return to original form Both cosubstrates and prosthetic groups su ...
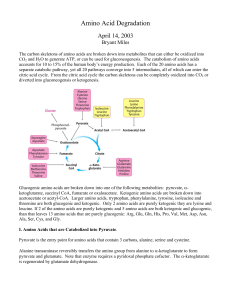
Amino Acid Degradation
... Branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase is a huge multienzyme complex homologous to pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. This enzyme contains a thiamine pyrophosphate cofactor, a lipoamide cofactor, a FAD prosthetic group. The chemistry, mechanism and structure of these enzymes ...
... Branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase is a huge multienzyme complex homologous to pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. This enzyme contains a thiamine pyrophosphate cofactor, a lipoamide cofactor, a FAD prosthetic group. The chemistry, mechanism and structure of these enzymes ...
OC 27 Amino Acids
... • N-H groups of all peptide bonds point in the same direction, which is roughly parallel to the axis of the helix • C=O groups of all peptide bonds point in the opposite direction, and also parallel to the axis of the helix • the C=O group of each peptide bond is hydrogen bonded to the N-H group of ...
... • N-H groups of all peptide bonds point in the same direction, which is roughly parallel to the axis of the helix • C=O groups of all peptide bonds point in the opposite direction, and also parallel to the axis of the helix • the C=O group of each peptide bond is hydrogen bonded to the N-H group of ...
Document
... Primary source of energy for cells, some can be structural. Glucose is the main source of energy for cells Disaccharides – two sugar units. Nutritional molecules for plants and in milk for offspring. Sucrose is the main source of nutrients for all parts of a plant Polysaccharides – Multiple sugar un ...
... Primary source of energy for cells, some can be structural. Glucose is the main source of energy for cells Disaccharides – two sugar units. Nutritional molecules for plants and in milk for offspring. Sucrose is the main source of nutrients for all parts of a plant Polysaccharides – Multiple sugar un ...
Solutions to 7.014 Quiz I
... e) Where in that molecule is the energy that is used to perform work stored? Be specific. In ATP, the energy used to do work is stored in the phosphate bonds. Breakdown of the molecule (in d) is often coupled with other reactions in the cell, making the new, coupled, reaction proceed at an appreciab ...
... e) Where in that molecule is the energy that is used to perform work stored? Be specific. In ATP, the energy used to do work is stored in the phosphate bonds. Breakdown of the molecule (in d) is often coupled with other reactions in the cell, making the new, coupled, reaction proceed at an appreciab ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.