05- macromolecules
... – Are lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings – Differ in functional groups attached to rings ...
... – Are lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings – Differ in functional groups attached to rings ...
End of Chapter 18 Questions
... a. Thiamine (Vitamin B1)—part of the coenzyme needed for oxidation of carbohydrates and in a coenzyme needed in synthesis of ribose. b. Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)—part of enzymes and coenzymes such as FAD, needed for oxidation of glucose and fatty acids as well as needed for cellular growth. c. Niacin ...
... a. Thiamine (Vitamin B1)—part of the coenzyme needed for oxidation of carbohydrates and in a coenzyme needed in synthesis of ribose. b. Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)—part of enzymes and coenzymes such as FAD, needed for oxidation of glucose and fatty acids as well as needed for cellular growth. c. Niacin ...
Energy Releasing Pathway
... How many CO2 are liberated per acetic acid? Per glucose? As H+’s are removed then a P jumps on only to be removed to form ATP. ...
... How many CO2 are liberated per acetic acid? Per glucose? As H+’s are removed then a P jumps on only to be removed to form ATP. ...
Food Safety & Toxicology (3) - Share My Knowledge & Experience
... • Reduction: Consumption of foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products and seafood, and enhanced vitamin D intake ...
... • Reduction: Consumption of foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products and seafood, and enhanced vitamin D intake ...
Complete nucleotide sequence and genome organization of a
... a stable hairpin structure (Fig. 2A) located just upstream of the UAA termination codon of the 29K gene. Fig. 2B shows an alternative RNA folding with pseudoknot formation in this region (stems I and II have free energy -5,5 and -4,0 kcallmol, respectively). Both tentative folding have similar calcu ...
... a stable hairpin structure (Fig. 2A) located just upstream of the UAA termination codon of the 29K gene. Fig. 2B shows an alternative RNA folding with pseudoknot formation in this region (stems I and II have free energy -5,5 and -4,0 kcallmol, respectively). Both tentative folding have similar calcu ...
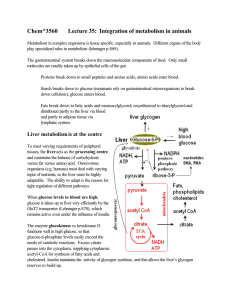
Chem*3560 Lecture 35: Integration of metabolism in animals
... ← direction during intense bursts of activity There is constant physical damage and repair of muscle fibres especially during vigorous activity. Repair enlarges and generates stronger muscles, and is the basis of body building. Because this involves very active protein degradation and resynthesis, q ...
... ← direction during intense bursts of activity There is constant physical damage and repair of muscle fibres especially during vigorous activity. Repair enlarges and generates stronger muscles, and is the basis of body building. Because this involves very active protein degradation and resynthesis, q ...
Deciphering the Genetic Code commemorative booklet
... to determine how RNA works free of the complicated biological processes that could shroud molecular activity. Nirenberg and Matthaei selected E. coli bacteria cells as their source of cytoplasm. They added the E. coli extract to 20 test tubes, each containing a mixture of all 20 amino acids. In each ...
... to determine how RNA works free of the complicated biological processes that could shroud molecular activity. Nirenberg and Matthaei selected E. coli bacteria cells as their source of cytoplasm. They added the E. coli extract to 20 test tubes, each containing a mixture of all 20 amino acids. In each ...
Secondary metabolism is a term for pathways and products
... Fig 7: Interrelationship of biosynthetic pathways leading to secondary constituents. Biosynthesis of Aromatic Compounds Shikimic Acid Pathway: The shikmic acid pathway is a key intermediate from carbohydrate for the biosynthesis of C6-C3 units (phenyl propane derivative). Besides serving as precurso ...
... Fig 7: Interrelationship of biosynthetic pathways leading to secondary constituents. Biosynthesis of Aromatic Compounds Shikimic Acid Pathway: The shikmic acid pathway is a key intermediate from carbohydrate for the biosynthesis of C6-C3 units (phenyl propane derivative). Besides serving as precurso ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... b. Explain the absolute and group specificity of enzyme calalyzed reaction. c. What is role of humus in the fertility of soil? ...
... b. Explain the absolute and group specificity of enzyme calalyzed reaction. c. What is role of humus in the fertility of soil? ...
Lecture 24 (4/29/13) "The Food You Eat
... oxidation of sugar in a cell, compared with ordinary burning (A) In the cell, enzymes catalyze oxidation via a series of small steps in which free energy is transferred in conveniently sized packets to carrier molecules—most often ATP and NADH. At each step, an enzyme controls the reaction by reduci ...
... oxidation of sugar in a cell, compared with ordinary burning (A) In the cell, enzymes catalyze oxidation via a series of small steps in which free energy is transferred in conveniently sized packets to carrier molecules—most often ATP and NADH. At each step, an enzyme controls the reaction by reduci ...
1 1 2 bez pyt lecture chemistryofaminoacids 7 fin
... There Are Four Levels of Protein Structure •Primary structure - amino acid linear sequence •Secondary structure – the type and the shape of the peptide chain, such as a-helices and b-sheets •Tertiary structure - describes the shape of the fully folded polypeptide chain in space •Quaternary structure ...
... There Are Four Levels of Protein Structure •Primary structure - amino acid linear sequence •Secondary structure – the type and the shape of the peptide chain, such as a-helices and b-sheets •Tertiary structure - describes the shape of the fully folded polypeptide chain in space •Quaternary structure ...
Document
... – This gives another excellent genetic clock – Identify the same ERV in to species and count the differences – More differences = longer since last common ancestor © Colin Frayn, 2008-2011 www.frayn.net ...
... – This gives another excellent genetic clock – Identify the same ERV in to species and count the differences – More differences = longer since last common ancestor © Colin Frayn, 2008-2011 www.frayn.net ...
Class I tRNA
... RNA is concentrated at the interface with the 50S subunit. Both 30S and 50S subunits are self-assembled in vitro. In 30S subunit, S4 and S8 bind to 16S rRNA first, other proteins then join sequentially and cooperatively. ...
... RNA is concentrated at the interface with the 50S subunit. Both 30S and 50S subunits are self-assembled in vitro. In 30S subunit, S4 and S8 bind to 16S rRNA first, other proteins then join sequentially and cooperatively. ...
bioc-2200-a-biol-2200-a-mock-final-exam
... a. the formation of α-ketoglutarate b. the formation of succinate c. the formation of isocitrate d. the formation of oxaloacetate 8. In a newly discovered fungus, am unknown protein is isolated that is localized in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Upon removal of the protein, the cell appears to be ...
... a. the formation of α-ketoglutarate b. the formation of succinate c. the formation of isocitrate d. the formation of oxaloacetate 8. In a newly discovered fungus, am unknown protein is isolated that is localized in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Upon removal of the protein, the cell appears to be ...
peran serta masyarakat dalam plh
... dipertimbangkan menjadi dasar spesifitas enzim Cofactor the additional chemical groups appearing in those enzymes that are conjugated proteins. ...
... dipertimbangkan menjadi dasar spesifitas enzim Cofactor the additional chemical groups appearing in those enzymes that are conjugated proteins. ...
gene to protein webquest.indd
... • The Living Environment: Heredity - the information passed from parents to offspring is coded in DNA molecules. • The Living Environment: Cells - within every cell are specialized parts for the transport of materials, energy transfer, protein building, waste disposal, information feedback, and even ...
... • The Living Environment: Heredity - the information passed from parents to offspring is coded in DNA molecules. • The Living Environment: Cells - within every cell are specialized parts for the transport of materials, energy transfer, protein building, waste disposal, information feedback, and even ...
Peroxisomal oxidation of fatty acids
... carnitine by Carnityl acyl transferase I (CAT-I), then the fatty acyl-Carnitine ester is transported in the mitochondra. 2. In mitochondria, FA is transferred to mitochondral CoA by CAT-II, and the Fatty acyl-CoA thus formed is ready for oxidation pathway. Cytosolic and mitochondrial CoA pools have ...
... carnitine by Carnityl acyl transferase I (CAT-I), then the fatty acyl-Carnitine ester is transported in the mitochondra. 2. In mitochondria, FA is transferred to mitochondral CoA by CAT-II, and the Fatty acyl-CoA thus formed is ready for oxidation pathway. Cytosolic and mitochondrial CoA pools have ...
Acids and Bases
... • So NaCl in water dissociates into Na+ and Cl• So H3PO4 dissociates into 3H+ and PO4-3 • Remembers ionic compounds are formed by metals and nonmetals or by metals and polyatomic ions ...
... • So NaCl in water dissociates into Na+ and Cl• So H3PO4 dissociates into 3H+ and PO4-3 • Remembers ionic compounds are formed by metals and nonmetals or by metals and polyatomic ions ...
Amino Acid Analysis Quick Reference Card For Hydrolysate
... This document supports amino acid analysis for hydrolysate samples using iTRAQ™ Reagents and the AB SCIEX Amino Acid 20/20 Analyzer. The labeling protocol labels a peptide hydrolysate, protein hydrolysate, or a hydrolysate from animal feed sample (dry ≈ 10 nmol amino acid) with iTRAQ Reagent 117. An ...
... This document supports amino acid analysis for hydrolysate samples using iTRAQ™ Reagents and the AB SCIEX Amino Acid 20/20 Analyzer. The labeling protocol labels a peptide hydrolysate, protein hydrolysate, or a hydrolysate from animal feed sample (dry ≈ 10 nmol amino acid) with iTRAQ Reagent 117. An ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.