Fermentation and Cellular Respiration 1. Define: Glycolysis
... Glycolysis – Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway allowing for the partial catabolism of glucose. During glycolysis, each glucose molecule is split into two pyruvic acid molecules with the associated production of two molecules of ATP and the reduction of two molecules of NAD to form NADH + H+ (also kn ...
... Glycolysis – Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway allowing for the partial catabolism of glucose. During glycolysis, each glucose molecule is split into two pyruvic acid molecules with the associated production of two molecules of ATP and the reduction of two molecules of NAD to form NADH + H+ (also kn ...
Polymer - Deans Community High School
... All proteins contain the elements C,N,O,H. They are condensation polymers, made by amino acids linking together. An amine group of one molecule links to the carboxyl group of another molecule to form an amide or peptide bond. The body makes specific proteins it needs, but cannot make all the amino a ...
... All proteins contain the elements C,N,O,H. They are condensation polymers, made by amino acids linking together. An amine group of one molecule links to the carboxyl group of another molecule to form an amide or peptide bond. The body makes specific proteins it needs, but cannot make all the amino a ...
Lec 01 - History of Microbiology True or False 1. Robert Koch is the
... The formation of ATP during the transport of electrons and hydrogen to oxygen is called _______________. (oxidative phosphorylation) Energy is released when electrons travel from a more ____________ source to a more ____________ substance. (negative) (positive) Hydrocarbons such as alkanes are ultim ...
... The formation of ATP during the transport of electrons and hydrogen to oxygen is called _______________. (oxidative phosphorylation) Energy is released when electrons travel from a more ____________ source to a more ____________ substance. (negative) (positive) Hydrocarbons such as alkanes are ultim ...
Metabolism
... Fatty acid synthesis Protein synthesis High energy compounds Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Guanosine triphosphate (GTP) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) – Both NADH and NADPH contain niacin Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADH2) – Contains ribo ...
... Fatty acid synthesis Protein synthesis High energy compounds Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Guanosine triphosphate (GTP) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) – Both NADH and NADPH contain niacin Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADH2) – Contains ribo ...
Chemistry - cloudfront.net
... polypeptide, or peptide. One protein differs from another by the number and arrangement of the twenty different amino acids. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon bonded to an amino group (–NH2), a carboxyl group (–COOH), and a hydrogen atom. The fourth bond of the central carbon is shown wit ...
... polypeptide, or peptide. One protein differs from another by the number and arrangement of the twenty different amino acids. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon bonded to an amino group (–NH2), a carboxyl group (–COOH), and a hydrogen atom. The fourth bond of the central carbon is shown wit ...
Chapter 9 – Catalytic Strategies (So we`ve talked about enzymes
... (But by and large Proteases are enzymes that degrade proteins by cleaving peptide bonds … like collagen in jello for example! There are a ton of these in our bodies, but why are they so abundant?) (Mainly for digestion but it also allows us to get rid of proteins that are no longer needed or are dam ...
... (But by and large Proteases are enzymes that degrade proteins by cleaving peptide bonds … like collagen in jello for example! There are a ton of these in our bodies, but why are they so abundant?) (Mainly for digestion but it also allows us to get rid of proteins that are no longer needed or are dam ...
297 special transport and neurological significance of two amino
... mediated transport of ordinary dipolar L-amino acids over that of their D-isomers are quite usual in mammalian tissue (Oxender and Christensen, 1963). No basis has been noted for suspecting that the two enantiomorphs are transported by different means. Our conclusion that the yeast transport system ...
... mediated transport of ordinary dipolar L-amino acids over that of their D-isomers are quite usual in mammalian tissue (Oxender and Christensen, 1963). No basis has been noted for suspecting that the two enantiomorphs are transported by different means. Our conclusion that the yeast transport system ...
Slides - Websupport1
... Glucose 6 phosphate goes through the second phosphorylation reaction and a phosphate is added to carbonenumber 1. The new molecule produced as a result is ...
... Glucose 6 phosphate goes through the second phosphorylation reaction and a phosphate is added to carbonenumber 1. The new molecule produced as a result is ...
Introduction to Structure Biology
... • As a result, in general, hydrophobic sidechains are located in the interior of protein, forming the hydrophobic core • Polar and charged amino acids usually are located on the surface of the protein • Polar and charged residues also can make hydrophobic contacts with their aliphatic carbon atoms • ...
... • As a result, in general, hydrophobic sidechains are located in the interior of protein, forming the hydrophobic core • Polar and charged amino acids usually are located on the surface of the protein • Polar and charged residues also can make hydrophobic contacts with their aliphatic carbon atoms • ...
1 - contentextra
... Glycolysis allows a net gain of two ATPs, two molecules of NADH, and two molecules of pyruvate. This metabolic process is controlled by enzymes. If ATP levels are high in the cell, feedback inhibition blocks the first enzyme of the pathway. This slows or stops the process. ...
... Glycolysis allows a net gain of two ATPs, two molecules of NADH, and two molecules of pyruvate. This metabolic process is controlled by enzymes. If ATP levels are high in the cell, feedback inhibition blocks the first enzyme of the pathway. This slows or stops the process. ...
DNA sequencing by the Sanger method
... The standard DNA sequencing technique is the Sanger method, named for its developer, Frederick Sanger, who shared the 1980 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. This method begins with the use of special enzymes to synthesize fragments of DNA that terminate when a selected base appears in the stretch of DNA bei ...
... The standard DNA sequencing technique is the Sanger method, named for its developer, Frederick Sanger, who shared the 1980 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. This method begins with the use of special enzymes to synthesize fragments of DNA that terminate when a selected base appears in the stretch of DNA bei ...
Document
... should be amino acids with hydrophobic side chains, 7. tryptophan__________ and the even numbered amino acids, sticking out on the 8. arginine_____________ inside, which is an aqueous environment, are most 9. valine _______________ likely to be hydrophilic side chains, i.e., charged or 10.glutamine_ ...
... should be amino acids with hydrophobic side chains, 7. tryptophan__________ and the even numbered amino acids, sticking out on the 8. arginine_____________ inside, which is an aqueous environment, are most 9. valine _______________ likely to be hydrophilic side chains, i.e., charged or 10.glutamine_ ...
7.5 Proteins - HS Biology IB
... primary structure is sequence / number of amino acids; determined by base sequence in the gene; (largely) determines higher level structures/secondary structure/tertiary structure; secondary structure is regular repeating patterns; such as alpha/α helix and beta/β (pleated) sheet; determined by H bo ...
... primary structure is sequence / number of amino acids; determined by base sequence in the gene; (largely) determines higher level structures/secondary structure/tertiary structure; secondary structure is regular repeating patterns; such as alpha/α helix and beta/β (pleated) sheet; determined by H bo ...
Chapter 18
... a. Thiamine (Vitamin B1)—part of the coenzyme needed for oxidation of carbohydrates and in a coenzyme needed in synthesis of ribose. b. Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)—part of enzymes and coenzymes such as FAD, needed for oxidation of glucose and fatty acids as well as needed for cellular growth. c. Niacin ...
... a. Thiamine (Vitamin B1)—part of the coenzyme needed for oxidation of carbohydrates and in a coenzyme needed in synthesis of ribose. b. Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)—part of enzymes and coenzymes such as FAD, needed for oxidation of glucose and fatty acids as well as needed for cellular growth. c. Niacin ...
Protein Function Follows Form: Small Changes may Cause Big
... Group Activity: Amino Acid Sorting • Students will work in groups with notecards that each have an amino acid structure, with its name and abbreviation(s). • Students will sort the amino acids according to the chemical properties (polarity, size, charge) of their side chains. • This formative asses ...
... Group Activity: Amino Acid Sorting • Students will work in groups with notecards that each have an amino acid structure, with its name and abbreviation(s). • Students will sort the amino acids according to the chemical properties (polarity, size, charge) of their side chains. • This formative asses ...
Document
... Lack of ADA causes accumulation of deoxyadenosine. Immune cells, which have potent salvage pathways, accumulate dATP, which blocks production of other dNTPs by its action on ribonucleotide reductase. Immune cells can’t replicate their DNA, and thus can’t mount an immune response. ...
... Lack of ADA causes accumulation of deoxyadenosine. Immune cells, which have potent salvage pathways, accumulate dATP, which blocks production of other dNTPs by its action on ribonucleotide reductase. Immune cells can’t replicate their DNA, and thus can’t mount an immune response. ...
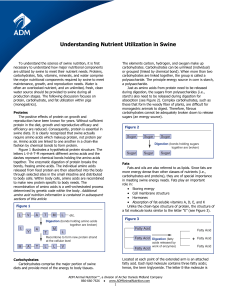
Nutrient Utilization in Swine
... Most information normally discusses excess nitrogen excretion as a result of overfeeding protein. However, deficiencies in one or more essential amino acids can also result in excess nitrogen excretion. To understand this process, one needs to have a basic understanding of how protein is formed. The ...
... Most information normally discusses excess nitrogen excretion as a result of overfeeding protein. However, deficiencies in one or more essential amino acids can also result in excess nitrogen excretion. To understand this process, one needs to have a basic understanding of how protein is formed. The ...
Final Exam - UC Davis Plant Sciences
... This exam consists of 8 questions. A maximum of 100 points can be earned. Partial credit will be given. There are a total of 12 pages, including the cover page and one blank sheet at the end for notes. However, do not use the blank sheet for your final answers. If you need more space, use the back o ...
... This exam consists of 8 questions. A maximum of 100 points can be earned. Partial credit will be given. There are a total of 12 pages, including the cover page and one blank sheet at the end for notes. However, do not use the blank sheet for your final answers. If you need more space, use the back o ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.