Review of Advanced DNA Structure and Function PPT
... • DNA polymerase can traverse through parental nucleosomes without displacing them • Old Histones are distributed to daughter strands • More Histones must be synthesized • Occurs specifically in S phase • Histones loaded by chaperone proteins • Nucleosome assembly protein • Chromatin assembly factor ...
... • DNA polymerase can traverse through parental nucleosomes without displacing them • Old Histones are distributed to daughter strands • More Histones must be synthesized • Occurs specifically in S phase • Histones loaded by chaperone proteins • Nucleosome assembly protein • Chromatin assembly factor ...
CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF MACROMOLECULES
... Breaking Down Polymers • The covalent bonds connecting monomers in a polymer are disassembled by hydrolysis. – In hydrolysis as the covalent bond is broken a hydrogen atom and hydroxyl group from a split water molecule attaches where the covalent bond used to be. ...
... Breaking Down Polymers • The covalent bonds connecting monomers in a polymer are disassembled by hydrolysis. – In hydrolysis as the covalent bond is broken a hydrogen atom and hydroxyl group from a split water molecule attaches where the covalent bond used to be. ...
AccessMedicine | Print: Cha
... Synthetic derivatives of nucleoside triphosphates incapable of undergoing hydrolytic release of the terminal phosphoryl group. (Pu/Py, a purine or pyrimidine base; R, ribose or deoxyribose.) Shown are the parent (hydrolyzable) nucleoside triphosphate (top) and the unhydrolyzable -methylene (center) ...
... Synthetic derivatives of nucleoside triphosphates incapable of undergoing hydrolytic release of the terminal phosphoryl group. (Pu/Py, a purine or pyrimidine base; R, ribose or deoxyribose.) Shown are the parent (hydrolyzable) nucleoside triphosphate (top) and the unhydrolyzable -methylene (center) ...
Prescott`s Microbiology, 9th Edition Chapter 10 –Introduction to
... this case, because the equation G0’ = -nF . E’0 has a negative on the right side, the values must be inversely related) to delta E, this reaction would have a positive delta G, and thus not be spontaneous, and require energy input to drive forward. Figure 10.7 Refer to figure 10.6 and determine th ...
... this case, because the equation G0’ = -nF . E’0 has a negative on the right side, the values must be inversely related) to delta E, this reaction would have a positive delta G, and thus not be spontaneous, and require energy input to drive forward. Figure 10.7 Refer to figure 10.6 and determine th ...
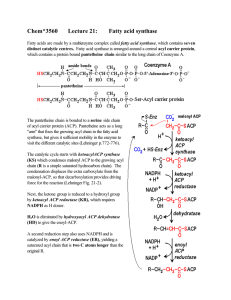
Chem*3560 Lecture 21: Fatty acid synthase
... acyl-S-ACP (the product of enoyl ACP reductase), acyl transferase transfers the saturated acyl from ACP to the auxilary HS-Enz site (right). This allows for another cycle of elongation of an existing chain, and makes HS-ACP available for the next reaction. The enzyme malonyl CoA-ACP transferase (MT) ...
... acyl-S-ACP (the product of enoyl ACP reductase), acyl transferase transfers the saturated acyl from ACP to the auxilary HS-Enz site (right). This allows for another cycle of elongation of an existing chain, and makes HS-ACP available for the next reaction. The enzyme malonyl CoA-ACP transferase (MT) ...
Enzyme specificity
... person in class to recap what was talked about/learned in the last lesson Warning! Be on your guard it may be your turn next!! ...
... person in class to recap what was talked about/learned in the last lesson Warning! Be on your guard it may be your turn next!! ...
8/18/2015 1 BCMB 3100
... hydrophobicity of ligands (e.g. alkyl groups) covalently attached to a gel matrix. In RPC, proteins can bind very strongly to the gel and require non-polar solvents for their elution. In HIC protein binding is promoted by inclusion of salt in the solvent and elution of proteins is caused by decreasi ...
... hydrophobicity of ligands (e.g. alkyl groups) covalently attached to a gel matrix. In RPC, proteins can bind very strongly to the gel and require non-polar solvents for their elution. In HIC protein binding is promoted by inclusion of salt in the solvent and elution of proteins is caused by decreasi ...
BICH 303 Exam #1 Fall 2005 1. Amphiphilic or amphipathic
... E. favors the binding of Bohr protons. 25. The trigger for the conformational change in quaternary structure of hemoglobin is: A. oxygen binding to the distal histidine B. oxygen binding to the Fe(II) C. oxygen binding to the proximal histidine D. the loss of Bohr protons E. the loss of 2,3- bispho ...
... E. favors the binding of Bohr protons. 25. The trigger for the conformational change in quaternary structure of hemoglobin is: A. oxygen binding to the distal histidine B. oxygen binding to the Fe(II) C. oxygen binding to the proximal histidine D. the loss of Bohr protons E. the loss of 2,3- bispho ...
Free Response – due Friday, Oct 2 – typed – single
... properties of carbon atoms allow carbon to form many different types of molecules with many different functions. In your answer: • define covalent bond • explain how carbon-based rings and chains can form very large molecules • name the four main types of carbon-based molecules in organisms and disc ...
... properties of carbon atoms allow carbon to form many different types of molecules with many different functions. In your answer: • define covalent bond • explain how carbon-based rings and chains can form very large molecules • name the four main types of carbon-based molecules in organisms and disc ...
Restriction Maps
... compatible sticky ends and seal up the molecule. Restriction enzymes and ligase can be used as cut and paste tools for genetic engineering to join together different pieces of DNA to create “recombinant” molecules. ...
... compatible sticky ends and seal up the molecule. Restriction enzymes and ligase can be used as cut and paste tools for genetic engineering to join together different pieces of DNA to create “recombinant” molecules. ...
Final Examination
... any protein that participates in an oxidoreductase reaction any protein that participates in an oxidoreductase reaction but does not contain a flavin coenzyme any protein that participates in an oxidase reaction and also contains heme any molecule found in cells that is colored (in the visib ...
... any protein that participates in an oxidoreductase reaction any protein that participates in an oxidoreductase reaction but does not contain a flavin coenzyme any protein that participates in an oxidase reaction and also contains heme any molecule found in cells that is colored (in the visib ...
Medical Biochemistry. Human Metabolism in Health and Disease Brochure
... metabolic pathways and reactions are connected to human health and disease. Rather than cover all the reactions that human cells and tissues are capable of executing, this text better enables readers to learn core concepts by emphasizing select examples that illustrate the physiologic and pathophysi ...
... metabolic pathways and reactions are connected to human health and disease. Rather than cover all the reactions that human cells and tissues are capable of executing, this text better enables readers to learn core concepts by emphasizing select examples that illustrate the physiologic and pathophysi ...
oL-Amylase of Clostridium thermosulfurogenes EMi:
... the majority of E. coli proteins. The thermostable C. thermosulfurogenes EM1 cx-amylase remained soluble under these conditions. After centrifugation (15,000 x g, 15 min, 4°C) 3.2 U of ox-amylase was obtained in 20 ml (800 mg of total protein). This solution was loaded on a Q-Sepharose Fast flow col ...
... the majority of E. coli proteins. The thermostable C. thermosulfurogenes EM1 cx-amylase remained soluble under these conditions. After centrifugation (15,000 x g, 15 min, 4°C) 3.2 U of ox-amylase was obtained in 20 ml (800 mg of total protein). This solution was loaded on a Q-Sepharose Fast flow col ...
amino acids M
... 2o : Local structures which include, folds, turns, helices and b -sheets held in place by hydrogen bonds. 3o : 3-D arrangement of all atoms in a single polypeptide chain. 4o : Arrangement of polypeptide chains into a functional protein, eg. hemoglobin. ...
... 2o : Local structures which include, folds, turns, helices and b -sheets held in place by hydrogen bonds. 3o : 3-D arrangement of all atoms in a single polypeptide chain. 4o : Arrangement of polypeptide chains into a functional protein, eg. hemoglobin. ...
Chapter 10: DNA-RNA and Protein Synthesis PPT
... promoter which has the start codon AUG to code for the amino acid methionine 3.Promoters mark the beginning of a DNA chain in prokaryotes, but mark the beginning of 1 to several related genes in eukaryotes 4.The 2 DNA strands separate, but only one will serve as the template & be copied 5.Free nucle ...
... promoter which has the start codon AUG to code for the amino acid methionine 3.Promoters mark the beginning of a DNA chain in prokaryotes, but mark the beginning of 1 to several related genes in eukaryotes 4.The 2 DNA strands separate, but only one will serve as the template & be copied 5.Free nucle ...
8.4 Transcription
... – RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. – The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed. DNA ...
... – RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. – The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed. DNA ...
What are proteins?
... Structural features of proteins are usually described at four levels of complexity: ...
... Structural features of proteins are usually described at four levels of complexity: ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Foundations of Biology
... The central dogma states that once “information” has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is impossible. Inf ...
... The central dogma states that once “information” has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is impossible. Inf ...
8.4 Transcription KEY CONCEPT Transcription converts a gene into a single-stranded RNA molecule.
... – RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. – The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed. DNA ...
... – RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. – The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed. DNA ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.