1 A
... The following basic conclusions can be drawn from the data in the above Table: (i) a decrease in the redox potential means stabilisation of the FeIII state as compared to FeII. That is, in the presence of hydroxide, cyanide, or oxalate ions FeII can be oxidised to FeIII or FeIII can hardly be reduce ...
... The following basic conclusions can be drawn from the data in the above Table: (i) a decrease in the redox potential means stabilisation of the FeIII state as compared to FeII. That is, in the presence of hydroxide, cyanide, or oxalate ions FeII can be oxidised to FeIII or FeIII can hardly be reduce ...
KEY
... of N2 that it reduces to ammonia. Yet even this large input underestimates the total energetic investment in nitrogen fixation. Briefly explain why merely counting the ATPs consumed underestimates the overall energetic cost of nitrogen fixation. The 8 electrons used to reduce N2 (and H+) are derived ...
... of N2 that it reduces to ammonia. Yet even this large input underestimates the total energetic investment in nitrogen fixation. Briefly explain why merely counting the ATPs consumed underestimates the overall energetic cost of nitrogen fixation. The 8 electrons used to reduce N2 (and H+) are derived ...
Chapter 14: History of Life
... – Miller-Urey Apparatus tested Oparin’s hypothesis – Treated compounds with heat & electricity – Produced amino acids; later ATP & nucleotides too ...
... – Miller-Urey Apparatus tested Oparin’s hypothesis – Treated compounds with heat & electricity – Produced amino acids; later ATP & nucleotides too ...
No Slide Title
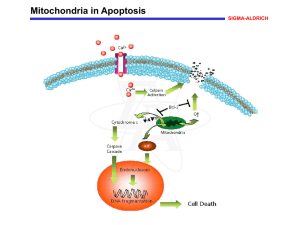
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
Name
... function of this carbohydrate? A) This carbohydrate is an energy source. B) This carbohydrate is a cofactor for an enzyme that is involved in cell transport. C) This carbohydrate is acting as some sort of signal to other cells. D) This carbohydrate is helping to anchor some protein to the cell membr ...
... function of this carbohydrate? A) This carbohydrate is an energy source. B) This carbohydrate is a cofactor for an enzyme that is involved in cell transport. C) This carbohydrate is acting as some sort of signal to other cells. D) This carbohydrate is helping to anchor some protein to the cell membr ...
basic chemistry of atoms and molecules
... called monomers. Monomers are the basic building blocks used to create even larger molecules called polymers. Some common monomers are glucose, glycerol and fatty acids, amino acids, and nucleotides. These monomers can be used to build the four biologically important polymers, which are carbohydrate ...
... called monomers. Monomers are the basic building blocks used to create even larger molecules called polymers. Some common monomers are glucose, glycerol and fatty acids, amino acids, and nucleotides. These monomers can be used to build the four biologically important polymers, which are carbohydrate ...
Enzymes
... permanently دائماto the enzyme and include two types:a)- Inorganic cofactors, include zinc, iron, and copper. b)- Organic cofactors, include vitamins or molecules derived from vitamins. ...
... permanently دائماto the enzyme and include two types:a)- Inorganic cofactors, include zinc, iron, and copper. b)- Organic cofactors, include vitamins or molecules derived from vitamins. ...
24_Test - Ventura College
... Which of the following is not true of metal-ion catalysis? A. It can make a reaction center more susceptible to receiving electrons B. It can make a leaving group a weaker base, and therefore a better leaving group C. It can increase the rate of a hydrolysis reaction by increasing the nucleophilicit ...
... Which of the following is not true of metal-ion catalysis? A. It can make a reaction center more susceptible to receiving electrons B. It can make a leaving group a weaker base, and therefore a better leaving group C. It can increase the rate of a hydrolysis reaction by increasing the nucleophilicit ...
ENZYMES AS CATALYSTS ROLE OF COENZYMES AND METALS
... A few principles explain the catalytic power and specificity of enzymes A. The rearrangements of covalent bonds during an enzyme-catalyzed reaction • Catalytic functional groups on an enzyme may form a transient covalent bond with a substrate. • These interactions lower the activation energy by pro ...
... A few principles explain the catalytic power and specificity of enzymes A. The rearrangements of covalent bonds during an enzyme-catalyzed reaction • Catalytic functional groups on an enzyme may form a transient covalent bond with a substrate. • These interactions lower the activation energy by pro ...
DNA Replication
... The leading strand template for the right fork is the lagging strand template for the left fork... …and vice versa. ...
... The leading strand template for the right fork is the lagging strand template for the left fork... …and vice versa. ...
A Comparative Genomic Method for Computational
... cellular and molecular biology, F. Neidhardt, et al., Editors.1996, American Society for Microbiology: Washington DC. p. 615. ...
... cellular and molecular biology, F. Neidhardt, et al., Editors.1996, American Society for Microbiology: Washington DC. p. 615. ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.