PAGES 1-41 INCL. 1. Overview (a) discovery of enzymes (b
... - specificity relates to binding of substrate to enzyme - group specific enzymes can use a variety of substrates, each containing a certain functional group which is modified - absolute specificity utilize only one substrate (or specific pair) in one reaction 2.(a) What is a catalyst? - any molecule ...
... - specificity relates to binding of substrate to enzyme - group specific enzymes can use a variety of substrates, each containing a certain functional group which is modified - absolute specificity utilize only one substrate (or specific pair) in one reaction 2.(a) What is a catalyst? - any molecule ...
Hydrophobic-Hydrophilic Forces and their Effects on Protein
... A protein is made up of a collection of amino acids, which are molecules that have both carboxyl and amino groups. An amino acid contains a carbon atom (Cα), and has four different connections, these include an amino group, carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (this differs depending on ...
... A protein is made up of a collection of amino acids, which are molecules that have both carboxyl and amino groups. An amino acid contains a carbon atom (Cα), and has four different connections, these include an amino group, carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (this differs depending on ...
Fate of pyruvate
... Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is composed of three enzymes & five coenzymes ...
... Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is composed of three enzymes & five coenzymes ...
Multiple choice questions
... Muscle and liver glycogen stores in a well nourished athlete would be sufficient to sustain approximately how many minutes of submaximal exercise (if this were the only energy source used)? The exercise is club level marathon pace. ...
... Muscle and liver glycogen stores in a well nourished athlete would be sufficient to sustain approximately how many minutes of submaximal exercise (if this were the only energy source used)? The exercise is club level marathon pace. ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... • Enzymes are protein catalysts that increase the velocity of a chemical reaction, and are not consumed during the reaction they catalyze. [Note: Some types of RNA can act like enzymes, usually catalyzing the cleavage and synthesis of phosphodiester bonds. RNAs with catalytic activity are called rib ...
... • Enzymes are protein catalysts that increase the velocity of a chemical reaction, and are not consumed during the reaction they catalyze. [Note: Some types of RNA can act like enzymes, usually catalyzing the cleavage and synthesis of phosphodiester bonds. RNAs with catalytic activity are called rib ...
- TestbankU
... basic chemical knowledge. A foundation is provided by presenting the structure of the atom and discussing the important features of chemical bonding and reactions. Because water is one of the fundamental molecules in living systems, a thorough analysis of this marvelous substance is provided along w ...
... basic chemical knowledge. A foundation is provided by presenting the structure of the atom and discussing the important features of chemical bonding and reactions. Because water is one of the fundamental molecules in living systems, a thorough analysis of this marvelous substance is provided along w ...
ALE 8 - Biol 100
... Hemoglobin is a protein in your red blood cells that is responsible for carrying oxygen. A mutation in the gene that codes for hemoglobin leads to a disease called sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell hemoglobin is unable to carry oxygen effectively, resulting in weakness in individuals who inherit one c ...
... Hemoglobin is a protein in your red blood cells that is responsible for carrying oxygen. A mutation in the gene that codes for hemoglobin leads to a disease called sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell hemoglobin is unable to carry oxygen effectively, resulting in weakness in individuals who inherit one c ...
Lecture 1 - Columbus Labs
... introduces the components of biological macromolecules and the principles behind their observed structures. The structure, properties, and functions of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates will be the focus of the course with an additional emphasis on large cellular assemblies such as ...
... introduces the components of biological macromolecules and the principles behind their observed structures. The structure, properties, and functions of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates will be the focus of the course with an additional emphasis on large cellular assemblies such as ...
Importance of Amino Acid Side Groups for Biologic
... alanyl-7-peptide has a different conformation from that of prolyl-7-angiotensin, which may account for the low biologic activity. Position 8: The C-terminal amino acid seems to be the most important in angiotensins. The heptapeptide formed by removal of phenylalanine with carboxypeptidase is complet ...
... alanyl-7-peptide has a different conformation from that of prolyl-7-angiotensin, which may account for the low biologic activity. Position 8: The C-terminal amino acid seems to be the most important in angiotensins. The heptapeptide formed by removal of phenylalanine with carboxypeptidase is complet ...
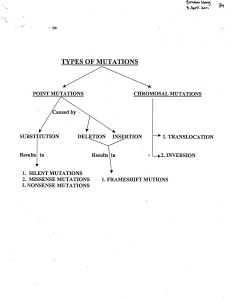
CHROMOSAL MUTATIONS SUBSTITUTION
... • · During translation, only the part of the protein that precedes the stop codon is produced, and the fragment may be digested by the proteases. ' Nonsense mutations are often lethal to the cell. ...
... • · During translation, only the part of the protein that precedes the stop codon is produced, and the fragment may be digested by the proteases. ' Nonsense mutations are often lethal to the cell. ...
Gene Section CLTCL1 (clathrin heavy polypeptide-like 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... CLTCL1/ALK may in fact be cases of CLTC/ALK Disease ? found in a case of ALK+ anaplasic large cell lymphoma. Abnormal protein ? 2197 amino acids, 248-250 kDa; 1634 (nearly all the CLTCL1 protein) N-term amino acids from CLTCL1, fused to the 562 C-term amino acids from ALK (i.e. the entire cytoplasmi ...
... CLTCL1/ALK may in fact be cases of CLTC/ALK Disease ? found in a case of ALK+ anaplasic large cell lymphoma. Abnormal protein ? 2197 amino acids, 248-250 kDa; 1634 (nearly all the CLTCL1 protein) N-term amino acids from CLTCL1, fused to the 562 C-term amino acids from ALK (i.e. the entire cytoplasmi ...
unit 4 practice
... hydroxide solutions of the same concentration. Which statement is correct? A. The initial pH values of both acids are equal. B. At the equivalence points, the solutions of both titrations have pH values ...
... hydroxide solutions of the same concentration. Which statement is correct? A. The initial pH values of both acids are equal. B. At the equivalence points, the solutions of both titrations have pH values ...
Molecules, Genes, and Diseases Session 2 Protein Structure and
... • The polypeptide backbone forms regular arrangements of amino acids that are located near to each other in the linear sequence. • These arrangements are termed the secondary structure of the polypeptide . • The α-helix, β-sheet , and β-bend are examples o f secondary structures. • Collagen helix , ...
... • The polypeptide backbone forms regular arrangements of amino acids that are located near to each other in the linear sequence. • These arrangements are termed the secondary structure of the polypeptide . • The α-helix, β-sheet , and β-bend are examples o f secondary structures. • Collagen helix , ...
Document
... protein that will be produced during translation. It varies in length according to the size of the protein that it encodes. ◦ c. The trailer sequence, or 39 untranslated region (39 UTR), also varies in length and contains information influencing the stability of the mRNA. ◦ a. Bacteria use the RNA t ...
... protein that will be produced during translation. It varies in length according to the size of the protein that it encodes. ◦ c. The trailer sequence, or 39 untranslated region (39 UTR), also varies in length and contains information influencing the stability of the mRNA. ◦ a. Bacteria use the RNA t ...
CELLULAR ADAPTATION TO AMINO ACID AVAILABILITY:
... (Gupta et al. 1995; Livingstone et al. 1995). There are two lines of evidence suggesting that ATF2 phosphorylation belongs to the amino acid response pathway leading to the transcriptional activation of CHOP by amino acids: (i) Leucine starvation induces ATF2 phosphorylation in human cell lines (Ave ...
... (Gupta et al. 1995; Livingstone et al. 1995). There are two lines of evidence suggesting that ATF2 phosphorylation belongs to the amino acid response pathway leading to the transcriptional activation of CHOP by amino acids: (i) Leucine starvation induces ATF2 phosphorylation in human cell lines (Ave ...
DESIGN, SYNTHESIS AND ANTIMICROBIAL SCREENING OF AMINO ACIDS CONJUGATED 2 AMINO4ARYLTHIAZOLE DERIVATIVES
... classes of ‘thiopeptide antibiotics’, a macrocyclic arrays of thiazole bearing amino acid/peptidic residues have been discovered from both microbial and marine origin. 6 They display a very promising antimicrobial activity and were recognized as one of the most ...
... classes of ‘thiopeptide antibiotics’, a macrocyclic arrays of thiazole bearing amino acid/peptidic residues have been discovered from both microbial and marine origin. 6 They display a very promising antimicrobial activity and were recognized as one of the most ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.