WP4 - Hamish Collin
... There is evidence in the literature that some purified cysteine synthase type enzymes are multifunctional and amongst other reactions can take allyl thiol and attach it to an amino acid skeleton to make Allyl cysteine Some other ß-substituted alanines (secondary plant products such as mimosine) are ...
... There is evidence in the literature that some purified cysteine synthase type enzymes are multifunctional and amongst other reactions can take allyl thiol and attach it to an amino acid skeleton to make Allyl cysteine Some other ß-substituted alanines (secondary plant products such as mimosine) are ...
Yeast Nutrients Make Fermentations Better
... Valine is a classic example. Valine is an amino acid that yeast can either produce autonomously, or assimilate from the wort. An intermediate compound in valine production is acetolactate (Fig. 1). Not all of the acetolactate produced will be converted to valine, some will leak out of the cell and i ...
... Valine is a classic example. Valine is an amino acid that yeast can either produce autonomously, or assimilate from the wort. An intermediate compound in valine production is acetolactate (Fig. 1). Not all of the acetolactate produced will be converted to valine, some will leak out of the cell and i ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_5_lecture
... 3. If more amino acids are consumed than are needed, the excess amino acids can be used for energy or converted into carbohydrates or fat. 4. Our bodies can make 12 of the 20 amino acids from other molecules. Eight of them (9 in children) must come from the diet and are called essential amino acids. ...
... 3. If more amino acids are consumed than are needed, the excess amino acids can be used for energy or converted into carbohydrates or fat. 4. Our bodies can make 12 of the 20 amino acids from other molecules. Eight of them (9 in children) must come from the diet and are called essential amino acids. ...
Snímek 1
... Monomers are joined to form long chains with side chains or branches of different lengths. Irregularly packed and therefore, they have low tensile strength, low density, boiling point and melting points than linear polymers. These branches are usually a result of side-reactions during the polymeriza ...
... Monomers are joined to form long chains with side chains or branches of different lengths. Irregularly packed and therefore, they have low tensile strength, low density, boiling point and melting points than linear polymers. These branches are usually a result of side-reactions during the polymeriza ...
bio98a_l10
... • heterotropic allostery (H+, CO2, BPG for Hb) 2. Covalent modification • group addition - often reversible, ie phosphorylation allosteric* = allo (other); steric (shape, object) ...
... • heterotropic allostery (H+, CO2, BPG for Hb) 2. Covalent modification • group addition - often reversible, ie phosphorylation allosteric* = allo (other); steric (shape, object) ...
The biological synthesis of cholesterol
... origin of the acetoacetyl-CoA that enters into the synthesis of hydroxymethylglutarate. Conceivably the initial condensation to the four-carbon level involves an acetyl unit and a malonyl unit41 as in the synthesis of long-chain fatty acids. Energetically this mechanism is certainly more favorable t ...
... origin of the acetoacetyl-CoA that enters into the synthesis of hydroxymethylglutarate. Conceivably the initial condensation to the four-carbon level involves an acetyl unit and a malonyl unit41 as in the synthesis of long-chain fatty acids. Energetically this mechanism is certainly more favorable t ...
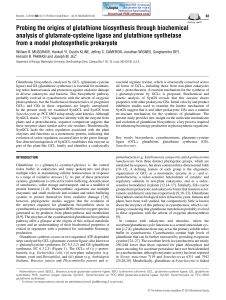
Probing the origins of glutathione biosynthesis through biochemical
... cyanobacteria as protection against ROS (reactive oxygen species) generated as by-products from photosynthesis and metabolism [8,9]. The enzymes of the cyanobacterial glutathione biosynthesis pathway offer a glimpse at the origins of this critical metabolic system and an understanding of their bioch ...
... cyanobacteria as protection against ROS (reactive oxygen species) generated as by-products from photosynthesis and metabolism [8,9]. The enzymes of the cyanobacterial glutathione biosynthesis pathway offer a glimpse at the origins of this critical metabolic system and an understanding of their bioch ...
Method of Analysis for Feed Enzymes: Methodological Problems?
... xylanase on arabinoxylan, an amylase on starch, a proteinase on protein) even in the presence of other reactants. Furthermore, the substrate needs to be of a defined quality. For example, similar results are obtained from xylanase with xylan substrates extracted from birchwood or from wheat (Table 1 ...
... xylanase on arabinoxylan, an amylase on starch, a proteinase on protein) even in the presence of other reactants. Furthermore, the substrate needs to be of a defined quality. For example, similar results are obtained from xylanase with xylan substrates extracted from birchwood or from wheat (Table 1 ...
Allicin, a naturally occurring antibiotic from garlic, specifically inhibits
... acetate into the fatty acid fraction in a dose-dependent manner with an &value lower than 10 ,uM (fig.2). Oat chloroplasts were inhibited to a similar extent with an inhibition rate of 85% at a concentration of 100 PM allicin. To identify the target enzyme of allicin, we applied an enzyme system cap ...
... acetate into the fatty acid fraction in a dose-dependent manner with an &value lower than 10 ,uM (fig.2). Oat chloroplasts were inhibited to a similar extent with an inhibition rate of 85% at a concentration of 100 PM allicin. To identify the target enzyme of allicin, we applied an enzyme system cap ...
18 Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA to Krebs Cycle A/P
... 2.) Lactic acid build up MAY cause a toxic environment for bacteria at some concentration. In other words its waste product becomes toxic due to its ability to reduce proteins and enzymes it comes in contact with (lowers the pH). So some bacteria may produce this as a way to reduce bacterial or fung ...
... 2.) Lactic acid build up MAY cause a toxic environment for bacteria at some concentration. In other words its waste product becomes toxic due to its ability to reduce proteins and enzymes it comes in contact with (lowers the pH). So some bacteria may produce this as a way to reduce bacterial or fung ...
Warm up
... Warm up Introduction to project / Computer rules Work time on Project (due Tuesday) If you get done early…there is an EC assignment due Friday and/or you can work on the next regular assignment due Thursday. ...
... Warm up Introduction to project / Computer rules Work time on Project (due Tuesday) If you get done early…there is an EC assignment due Friday and/or you can work on the next regular assignment due Thursday. ...
Keigo Tanaka Chapter 9 – Cellular Respiration: Harvesting
... 4. Another CO2 molecule is lost, and the resulting compound is oxidized, reducing NAD+ to NADH; the remaining molecule is then attached to coenzyme A by an unstable bond forming succinyl CoA 5. CoA is displaced by a phosphate group, which is transferred to GDP, forming GTP, and then to ADP, forming ...
... 4. Another CO2 molecule is lost, and the resulting compound is oxidized, reducing NAD+ to NADH; the remaining molecule is then attached to coenzyme A by an unstable bond forming succinyl CoA 5. CoA is displaced by a phosphate group, which is transferred to GDP, forming GTP, and then to ADP, forming ...
The Genome Sequence of the SARS
... upstream of the potential initiating methionine residue. We note that Rota et al. (14) did not identify potential proteins of less than 50 amino acids. We attempted to identify putative TRSs upstream of all Orfs, both known and predicted (Tables 2 and 3). However, TRSs are not required for transcrip ...
... upstream of the potential initiating methionine residue. We note that Rota et al. (14) did not identify potential proteins of less than 50 amino acids. We attempted to identify putative TRSs upstream of all Orfs, both known and predicted (Tables 2 and 3). However, TRSs are not required for transcrip ...
Multiple Sequence Alignments
... 2. Varying substitution matrices at different alignment stages according to sequence divergence. 3. Gaps • Positions in early alignments where gaps have been opened receive locally reduced gap penalties • Residue-specific gap penalties and locally reduced gap penalties in hydrophilic regions encoura ...
... 2. Varying substitution matrices at different alignment stages according to sequence divergence. 3. Gaps • Positions in early alignments where gaps have been opened receive locally reduced gap penalties • Residue-specific gap penalties and locally reduced gap penalties in hydrophilic regions encoura ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.