BLUEPRINT OF THE CORE TOPICS IN BIOCHEMISTRY
... A. Energy cannot be transformed from one form to another B. In any spontaneous process the entropy of the universe is maximal C. ∆E = Q + W D. Change in total energy is equal to the amount of heat absorbed by the system less the work done by the system _B__67. This condition shows a decrease in entr ...
... A. Energy cannot be transformed from one form to another B. In any spontaneous process the entropy of the universe is maximal C. ∆E = Q + W D. Change in total energy is equal to the amount of heat absorbed by the system less the work done by the system _B__67. This condition shows a decrease in entr ...
0Gcn2BJ2final
... In addition to being a tightly regulated parameter with a permissive role for many cellular functions, intracellular pH may have a regulatory role as second messenger of external stress conditions [4,14-16]. The concentration of protons in cells is in the range of those of calcium, a well-establishe ...
... In addition to being a tightly regulated parameter with a permissive role for many cellular functions, intracellular pH may have a regulatory role as second messenger of external stress conditions [4,14-16]. The concentration of protons in cells is in the range of those of calcium, a well-establishe ...
Structural Insights into Maize Viviparous14, a Key
... the ligands. This result is not unusual with enzymes that use large hydrophobic substrates. Nonetheless, the structure of the free enzyme provides strong indications of how the substrate might bind in the active site. To identify residues that may contribute to substrate specificity and cleavage in ...
... the ligands. This result is not unusual with enzymes that use large hydrophobic substrates. Nonetheless, the structure of the free enzyme provides strong indications of how the substrate might bind in the active site. To identify residues that may contribute to substrate specificity and cleavage in ...
Lareau et al, eLife, 2014
... of messenger RNA (mRNA), which then passes through a molecular machine called a ribosome. The ribosome reads the genetic code in the mRNA in groups of three letters at a time, and each triplet of letters (or codon) represents an amino acid. The ribosome then joins the relevant amino acids together t ...
... of messenger RNA (mRNA), which then passes through a molecular machine called a ribosome. The ribosome reads the genetic code in the mRNA in groups of three letters at a time, and each triplet of letters (or codon) represents an amino acid. The ribosome then joins the relevant amino acids together t ...
Identical Point Mutations of the R-type Pyruvate
... A silent point mutation, "%CC to CCC, was detected in the R-type PK cDNA of PK Fukushima and PK Maebashi. A point mutation, "'AGG to CGG, was also detected in the R-type PKcDNA ofboth PK-Fukushima and PK Maebashi. This mutation does not change an amino acid residue (Ser). We evaluated the existence ...
... A silent point mutation, "%CC to CCC, was detected in the R-type PK cDNA of PK Fukushima and PK Maebashi. A point mutation, "'AGG to CGG, was also detected in the R-type PKcDNA ofboth PK-Fukushima and PK Maebashi. This mutation does not change an amino acid residue (Ser). We evaluated the existence ...
The Citric Acid Cycle
... The Citric Acid Cycle Can Be a Multistep Catalyst • Oxaloacetate is regenerated • The cycle is a mechanism for oxidizing acetyl CoA to CO2 by NAD+ and Q • The cycle itself is not a pathway for a net degradation of any cycle intermediates • Cycle intermediates can be shared with other pathways, whic ...
... The Citric Acid Cycle Can Be a Multistep Catalyst • Oxaloacetate is regenerated • The cycle is a mechanism for oxidizing acetyl CoA to CO2 by NAD+ and Q • The cycle itself is not a pathway for a net degradation of any cycle intermediates • Cycle intermediates can be shared with other pathways, whic ...
Overview of Metabolism Chapter
... production of ATP to occur in the absence of oxygen. By oxidizing the NADH produced in glycolysis, fermentation regenerates NAD+, which can take part in glycolysis once again to produce more ATP. The muscle regenerates NAD+ from NADH, an oxidation reaction, by reduction of pyruvate. The fermentation ...
... production of ATP to occur in the absence of oxygen. By oxidizing the NADH produced in glycolysis, fermentation regenerates NAD+, which can take part in glycolysis once again to produce more ATP. The muscle regenerates NAD+ from NADH, an oxidation reaction, by reduction of pyruvate. The fermentation ...
ch_02_Chemical Organization
... • Long chains of carbon and hydrogen with a carboxyl group (COOH) at one end • Are relatively nonpolar, except the carboxyl group • Fatty acids may be: • Saturated with hydrogen (no covalent bonds) • Unsaturated (one or more double bonds) • Monounsaturated = one double bond ...
... • Long chains of carbon and hydrogen with a carboxyl group (COOH) at one end • Are relatively nonpolar, except the carboxyl group • Fatty acids may be: • Saturated with hydrogen (no covalent bonds) • Unsaturated (one or more double bonds) • Monounsaturated = one double bond ...
FREE Sample Here
... dissociate. The association rate will be larger than the dissociation rate when complex formation is favorable. The energy that drives this process is referred to as ___________. (a) dissociation energy. ...
... dissociate. The association rate will be larger than the dissociation rate when complex formation is favorable. The energy that drives this process is referred to as ___________. (a) dissociation energy. ...
100 Chapter 21. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl
... The mechanism of nucleophilic acyl substitution involves two critical steps that can influence the rate of the overall reaction: 1) the initial addition to the carbonyl groups, and 2) the elimination of the leaving group. The nature of the acyl group: The rate of addition to the carbonyl carbon is s ...
... The mechanism of nucleophilic acyl substitution involves two critical steps that can influence the rate of the overall reaction: 1) the initial addition to the carbonyl groups, and 2) the elimination of the leaving group. The nature of the acyl group: The rate of addition to the carbonyl carbon is s ...
STEROIDS, BILE ACIDS, STEROID HORMONES
... groups are said to be β substitutents Groups below the plane of the steroid ring system are said to be α substituents ...
... groups are said to be β substitutents Groups below the plane of the steroid ring system are said to be α substituents ...
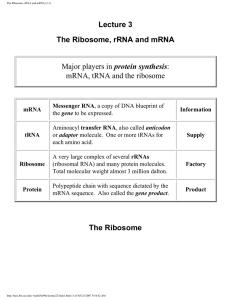
The Ribosome, rRNA and mRNA (3.1)
... contacted exclusively by conserved ribosomal RNA (rRNA) residues from domain V of 23S rRNA; there are no protein side-chain atoms closer than about 18 angstroms to the peptide bond being synthesized. The mechanism of peptide bond synthesis appears to resemble the reverse of the acylation step in ser ...
... contacted exclusively by conserved ribosomal RNA (rRNA) residues from domain V of 23S rRNA; there are no protein side-chain atoms closer than about 18 angstroms to the peptide bond being synthesized. The mechanism of peptide bond synthesis appears to resemble the reverse of the acylation step in ser ...
Recent developments in photorespiration research
... produce CH2 -THF. In the course of these two reactions, the two lipoyl-sulfur atoms of H-protein become fully reduced and must be re-oxidized by L-protein. After completion of this last step, which requires NAD+ and generates NADH, the GDC reaction cycle has been completed and S-oxidized H-protein i ...
... produce CH2 -THF. In the course of these two reactions, the two lipoyl-sulfur atoms of H-protein become fully reduced and must be re-oxidized by L-protein. After completion of this last step, which requires NAD+ and generates NADH, the GDC reaction cycle has been completed and S-oxidized H-protein i ...
Fatty acid transport proteins: a current view of a
... transiently or stably expressed in cells23,24. In addition, FATP members, even from evolutionarily quite different species, can functionally replace each other – the gene encoding a nematode FATP will enhance LCFA uptake when expressed in mammalian cells23 and a gene encoding murine FATP1 can restor ...
... transiently or stably expressed in cells23,24. In addition, FATP members, even from evolutionarily quite different species, can functionally replace each other – the gene encoding a nematode FATP will enhance LCFA uptake when expressed in mammalian cells23 and a gene encoding murine FATP1 can restor ...
Chapter 11
... "elemental composition" is 1:2:3:7 for Complexes I, II, III and IV, respectively. This is clearly inconsistent with a simple, linear formulation and consistent with "floating enzyme complexes" along the lines of the fluid-mosaic model (see next page). So the picture that you should get is of a syste ...
... "elemental composition" is 1:2:3:7 for Complexes I, II, III and IV, respectively. This is clearly inconsistent with a simple, linear formulation and consistent with "floating enzyme complexes" along the lines of the fluid-mosaic model (see next page). So the picture that you should get is of a syste ...
Beijerinckia derxii releases plant growth regulato
... ethylene itself, through different biochemical mechanisms (McKeon et al. 1995), including auto-inhibition. Exogenous ethylene is also effective in stimulating plant development (Taiz and Zeiger 1998). Ethylene and IAA may act together to stimulate the development of the cortical cell layer (Grichko ...
... ethylene itself, through different biochemical mechanisms (McKeon et al. 1995), including auto-inhibition. Exogenous ethylene is also effective in stimulating plant development (Taiz and Zeiger 1998). Ethylene and IAA may act together to stimulate the development of the cortical cell layer (Grichko ...
RNA-Seq Sample Recommendations (Craig Praul, PSU and Caitlyn
... transcript profile. In some cases immediate RNA purification is not possible. If tissues/cells must be stored prior to RNA isolation then the use of products such as RNALater from Qiagen or similar reagents is recommended. The core facility strongly encourages pilot projects to confirm that the chos ...
... transcript profile. In some cases immediate RNA purification is not possible. If tissues/cells must be stored prior to RNA isolation then the use of products such as RNALater from Qiagen or similar reagents is recommended. The core facility strongly encourages pilot projects to confirm that the chos ...
Protein-A Science-Based Approach By Dr. Joe Klemczewski
... source, and whether the source is in liquid or solid state, which influences speed of digestion. I’ll address digestion further when I turn the series toward meal planning, but let’s talk amino acid specificity. ...
... source, and whether the source is in liquid or solid state, which influences speed of digestion. I’ll address digestion further when I turn the series toward meal planning, but let’s talk amino acid specificity. ...
PAM and BLOSUM
... Physical and chemical characteristics • V I – Both small, both hydrophobic, conservative substitution, small penalty • V K – Small large, hydrophobic charged, large penalty • Requires some expert knowledge and judgement ...
... Physical and chemical characteristics • V I – Both small, both hydrophobic, conservative substitution, small penalty • V K – Small large, hydrophobic charged, large penalty • Requires some expert knowledge and judgement ...
IvDimitrov_slides
... 684 non-allergen from food origin 1157 non-allergens from inhalant origin 553 non-allergens from species with toxins, venom or salivary allergens ...
... 684 non-allergen from food origin 1157 non-allergens from inhalant origin 553 non-allergens from species with toxins, venom or salivary allergens ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.