Evolution of codon usage bias in Drosophila
... in the absence of constraints. Not only does the level of bias remain conserved, but often the actual pattern as well. One example is Alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh), which has been sequenced in more than 50 species of Drosophila. Table 1 shows the pattern of codon usage for three amino acids. The subge ...
... in the absence of constraints. Not only does the level of bias remain conserved, but often the actual pattern as well. One example is Alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh), which has been sequenced in more than 50 species of Drosophila. Table 1 shows the pattern of codon usage for three amino acids. The subge ...
as a PDF
... This seems remarkable since alanine, the major hepatic glucogenic amino acid, is not used äs a glucogenic precursor by the kidney (40). These striking differences between renal and liver gluconeogenesis make it attractive to consider a functional coupling between glucose and ammonia metabolism in bo ...
... This seems remarkable since alanine, the major hepatic glucogenic amino acid, is not used äs a glucogenic precursor by the kidney (40). These striking differences between renal and liver gluconeogenesis make it attractive to consider a functional coupling between glucose and ammonia metabolism in bo ...
Lb. curvatus
... by the end of 2 months of aging. Chou, et al., (2003) also observed a high correlation of Lb. curvatus with CLC in cheese. The formation of CLC was more extensive when the cheese was aged at 13°C and then transferred to 4°C. Although NSLAB have been linked to the development of white crystalline def ...
... by the end of 2 months of aging. Chou, et al., (2003) also observed a high correlation of Lb. curvatus with CLC in cheese. The formation of CLC was more extensive when the cheese was aged at 13°C and then transferred to 4°C. Although NSLAB have been linked to the development of white crystalline def ...
Environmental enteric dysfunction is associated with carnitine
... centrifugation. The resulting extract was divided into five fractions: (i) early and (ii) late eluting compounds for analysis by ultra-high performance LC-MS/MS (UPLC-MS/MS) using positive ionization, (iii) for analysis by UPLC-MS/MS using negative ionization, (iv) for analysis using a UPLC-MS/MS pol ...
... centrifugation. The resulting extract was divided into five fractions: (i) early and (ii) late eluting compounds for analysis by ultra-high performance LC-MS/MS (UPLC-MS/MS) using positive ionization, (iii) for analysis by UPLC-MS/MS using negative ionization, (iv) for analysis using a UPLC-MS/MS pol ...
Glutathione and glutamate levels in the diaphragm of patients with
... samples were taken from the apposition zone,y2 cm from the costodiaphragmatic angle at the mid-axillary line. Samples from the middle portion of the vastus lateralis were considered to be representative of the quadriceps muscle. Each biopsy specimen was divided into two pieces and these pieces rando ...
... samples were taken from the apposition zone,y2 cm from the costodiaphragmatic angle at the mid-axillary line. Samples from the middle portion of the vastus lateralis were considered to be representative of the quadriceps muscle. Each biopsy specimen was divided into two pieces and these pieces rando ...
Mitochondrial trans-2-Enoyl-CoA Reductase of Wax Ester
... paramylon (5). The wax ester fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA stemming from pyruvate via an unusual oxygensensitive enzyme, pyruvate:NADP⫹ oxidoreductase (6, 7), the core catalytic component of which is pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase, a typical enzyme of hydrogenosomes (8). Pyruvate:N ...
... paramylon (5). The wax ester fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA stemming from pyruvate via an unusual oxygensensitive enzyme, pyruvate:NADP⫹ oxidoreductase (6, 7), the core catalytic component of which is pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase, a typical enzyme of hydrogenosomes (8). Pyruvate:N ...
Medical faculty 2- d course Module 4 General principles of metabolism
... A. They are intermediates in glycolysis B. They act as enzymes to cause the oxidation of other compounds C. They are involved in a cyclic pathway D. They must be cofactors for enzymes that are oxidoreductases E. All of these ANSWER: C 48. Substrate-level phosphorylation differs from oxidative phosph ...
... A. They are intermediates in glycolysis B. They act as enzymes to cause the oxidation of other compounds C. They are involved in a cyclic pathway D. They must be cofactors for enzymes that are oxidoreductases E. All of these ANSWER: C 48. Substrate-level phosphorylation differs from oxidative phosph ...
Micro Chapter 5 ppt. 11th edition
... 1,3-diphosphoglyceric acid. Because each DHAP molecule can be converted to GP and each GP to 1,3-diphosphoglyceric acid, the result is two molecules of 1,3-diphosphoglyceric acid for each initial molecule of glucose. GP is oxidized by the transfer of two hydrogen atoms to NAD + to form NADH. The enz ...
... 1,3-diphosphoglyceric acid. Because each DHAP molecule can be converted to GP and each GP to 1,3-diphosphoglyceric acid, the result is two molecules of 1,3-diphosphoglyceric acid for each initial molecule of glucose. GP is oxidized by the transfer of two hydrogen atoms to NAD + to form NADH. The enz ...
Science Course Outline Template
... unique to life processes cannot be appreciated. All life processes on this planet have utilized a single specific molecule, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), as a concentrated form of chemical energy to which outside energy sources (as food) are converted and which is then used for biosynthetic purposes ...
... unique to life processes cannot be appreciated. All life processes on this planet have utilized a single specific molecule, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), as a concentrated form of chemical energy to which outside energy sources (as food) are converted and which is then used for biosynthetic purposes ...
Glycogen Metabolism and Gluconeogenesis
... • Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate allosterically activates the glycolysis enzyme Phosphofructokinase-1, promoting the relaxed state, even at relatively high [ATP]. Activity in the presence of fructose2,6-bisphosphate is similar to that observed when [ATP] is low. Thus control by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, ...
... • Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate allosterically activates the glycolysis enzyme Phosphofructokinase-1, promoting the relaxed state, even at relatively high [ATP]. Activity in the presence of fructose2,6-bisphosphate is similar to that observed when [ATP] is low. Thus control by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, ...
VGIchan: Prediction and Classification of Voltage-Gated Ion
... proteins that enable the passage of selected inorganic ions across cell membranes. They open and close in response to changes in transmembrane voltage, and play a key role in electric signaling by excitable cells such as neurons (1 ). They also have a critical role in the function of the nervous sys ...
... proteins that enable the passage of selected inorganic ions across cell membranes. They open and close in response to changes in transmembrane voltage, and play a key role in electric signaling by excitable cells such as neurons (1 ). They also have a critical role in the function of the nervous sys ...
Powerpoint slides
... Convergence is extremely unlikely for highly similar protein families. It then appears implausible to invoke it for less similar families. • The same or very similar functions may be carried out by proteins with very different structures (folds). Therefore, functional constraints cannot force conver ...
... Convergence is extremely unlikely for highly similar protein families. It then appears implausible to invoke it for less similar families. • The same or very similar functions may be carried out by proteins with very different structures (folds). Therefore, functional constraints cannot force conver ...
Caprotein by Mt. Capra Premium Goat
... This provides many advantages over vegetarian sources (such as soy) because they are typically low in one or more of the amino acids even though overall protein content is high. Why are whole proteins superior to isolated proteins? Protein supplements are often offered as whey protein isolates becau ...
... This provides many advantages over vegetarian sources (such as soy) because they are typically low in one or more of the amino acids even though overall protein content is high. Why are whole proteins superior to isolated proteins? Protein supplements are often offered as whey protein isolates becau ...
meat quality differences between purebred and crossbred new
... New Zealand White and Hyplus rabbits are used in commercial crossbreeding with different breeds. After having crossbred several different breeds we can get the effect of heterosis (Masoero 1982, Rochambeau 1988). However, it is proved that not every interbreeding and interlinear crossbreeding can be ...
... New Zealand White and Hyplus rabbits are used in commercial crossbreeding with different breeds. After having crossbred several different breeds we can get the effect of heterosis (Masoero 1982, Rochambeau 1988). However, it is proved that not every interbreeding and interlinear crossbreeding can be ...
Acids, Bases and Salts
... the Brønsted-Lowry theory is an acid-base theory, proposed independently by Danish Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and English Thomas Martin Lowry in 1923. In this system, an acid is defined as any chemical species (molecule or ion) that is able to lose, or "donate" a hydrogen ion (proton), and a base is ...
... the Brønsted-Lowry theory is an acid-base theory, proposed independently by Danish Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and English Thomas Martin Lowry in 1923. In this system, an acid is defined as any chemical species (molecule or ion) that is able to lose, or "donate" a hydrogen ion (proton), and a base is ...
Termination of translation: interplay of mRNA, rRNAs and release
... and UAG remain as stop codons. Puri®ed, recombinant eRF1 from this organism terminates at animal ribosomes programmed with UAA or UAG, but not with UGA (Kervestin et al., 2001). Since protein synthesis carried out in vivo with these ribosomes is terminated at any one of the canonical stop codons, it ...
... and UAG remain as stop codons. Puri®ed, recombinant eRF1 from this organism terminates at animal ribosomes programmed with UAA or UAG, but not with UGA (Kervestin et al., 2001). Since protein synthesis carried out in vivo with these ribosomes is terminated at any one of the canonical stop codons, it ...
Respiration 2 PPT
... ATP synthesis • NADH and FADH2 – Donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via ...
... ATP synthesis • NADH and FADH2 – Donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via ...
Energy „flow” in the organism
... Coenzyme A (CoA). Necessary for carbohydrate and fat metabolism involving acetyl-CoA; amino acid synthesis ...
... Coenzyme A (CoA). Necessary for carbohydrate and fat metabolism involving acetyl-CoA; amino acid synthesis ...
Structure and Properties of Hemoglobin Learning Objectives What
... of ionic & hydrogen bonds b/w dimers and have more freedom of movement ...
... of ionic & hydrogen bonds b/w dimers and have more freedom of movement ...
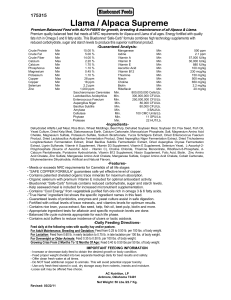
Llama / Alpaca Supreme
... - Contains “Cool Energy” from vegetable& purified fish oils rich in omega 3 & 6 fatty acids. -”True Name” ingredient list shows the specific ingredient names in this feed. - Guaranteed levels of probiotics, enzymes and yeast culture assist in safe digestion. - Fortified with critical levels of trace ...
... - Contains “Cool Energy” from vegetable& purified fish oils rich in omega 3 & 6 fatty acids. -”True Name” ingredient list shows the specific ingredient names in this feed. - Guaranteed levels of probiotics, enzymes and yeast culture assist in safe digestion. - Fortified with critical levels of trace ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.