Kreb`s Cycle
... Why do living things need food? • provides living things • source of energy with the chemical building blocks they need to grow and reproduce. • Source of raw materials for making new molecules ...
... Why do living things need food? • provides living things • source of energy with the chemical building blocks they need to grow and reproduce. • Source of raw materials for making new molecules ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Formation of macromolecules from smaller building block molecules represents another level in the hierarchy of biological organization. There are four classes of macromolecules in living organisms: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids ...
... Formation of macromolecules from smaller building block molecules represents another level in the hierarchy of biological organization. There are four classes of macromolecules in living organisms: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids ...
View as PDF - Helen Money Nutrition
... carbohydrate and fat have specific functions during recovery. Protein is needed to repair muscle, it is recommended that protein intake is increased to compensate for increased demand. The amino acids arginine and glutamine are thought to be particularly important for muscle repair and these can be ...
... carbohydrate and fat have specific functions during recovery. Protein is needed to repair muscle, it is recommended that protein intake is increased to compensate for increased demand. The amino acids arginine and glutamine are thought to be particularly important for muscle repair and these can be ...
Krebs and ETC
... Pyruvate Oxidation or Oxidative Decarboxylation Energy Yield & Products: 2 NADH 2 acetyl-CoA 2 CO2 (released as waste) ...
... Pyruvate Oxidation or Oxidative Decarboxylation Energy Yield & Products: 2 NADH 2 acetyl-CoA 2 CO2 (released as waste) ...
Name: ____________ Pd.: ______ Date: Read Section 2.1 – Atoms
... 21. In each of the diagrams above, the letter “A” represents the ___reactants______ of the chemical reaction and the letter “B” represents the _activation energy_______ of the chemical reaction. 22. In the diagram of a chemical reaction to the left, which reaction pathway requires the least activat ...
... 21. In each of the diagrams above, the letter “A” represents the ___reactants______ of the chemical reaction and the letter “B” represents the _activation energy_______ of the chemical reaction. 22. In the diagram of a chemical reaction to the left, which reaction pathway requires the least activat ...
Cellular Respiration - Seattle Central College
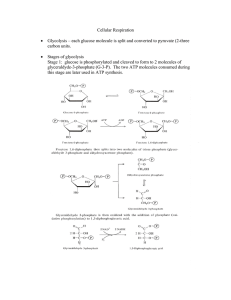
... glucose and the conversion of Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-diphosphate. The net production of ATP per glucose is 2. ...
... glucose and the conversion of Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-diphosphate. The net production of ATP per glucose is 2. ...
Solution Worksheet Respiration
... How many ATP are made in the glycolysis part of cellular respiration? 2 ATP are needed to energize glycolysis but 4 ATP’s are produced. So, the net effect is 2 ATP produced ( via substrate phosphorylation = direct enzymatic transfer of a phosphate from a substrate to ADP to form ATP) How many ATP ar ...
... How many ATP are made in the glycolysis part of cellular respiration? 2 ATP are needed to energize glycolysis but 4 ATP’s are produced. So, the net effect is 2 ATP produced ( via substrate phosphorylation = direct enzymatic transfer of a phosphate from a substrate to ADP to form ATP) How many ATP ar ...
Lecture 39 - Amino Acid Metabolism 2
... Amino Acids as Metabolic Precursors Natural loss of hair color occurs as a result of aging when melanin production shuts down in human melanocytes located near the base of hair follicles and these defective cells are not replaced as they normally are in younger individuals. Gray hair can be colored ...
... Amino Acids as Metabolic Precursors Natural loss of hair color occurs as a result of aging when melanin production shuts down in human melanocytes located near the base of hair follicles and these defective cells are not replaced as they normally are in younger individuals. Gray hair can be colored ...
BIO 101 Blinderman Mercer County Community College Division of
... 10. Examine cellular respiration, C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O as an exergonic reaction 11. Examine photosynthesis , 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ light energy) C6H12O6 + 6O2 as endergonic reaction 12. Describe the cell as a system not in equilibrium as an open system 13. Analyze the ability of cells to couple ...
... 10. Examine cellular respiration, C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O as an exergonic reaction 11. Examine photosynthesis , 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ light energy) C6H12O6 + 6O2 as endergonic reaction 12. Describe the cell as a system not in equilibrium as an open system 13. Analyze the ability of cells to couple ...
info and study guide
... Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex: Overall reaction, purpose of cofactors, mechanism involving TPP Citric acid Cycle: Structures of all intermediates, names of all intermediates, names of regulated enzymes, mechanisms presented in slides only (See worksheet) Electron transport chain: know complexes by ...
... Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex: Overall reaction, purpose of cofactors, mechanism involving TPP Citric acid Cycle: Structures of all intermediates, names of all intermediates, names of regulated enzymes, mechanisms presented in slides only (See worksheet) Electron transport chain: know complexes by ...
Solvil - Vitaflo UK
... Indications Solvil is for use in the dietary management of urea cycle disorders or other inborn errors of metabolism requiring branched chain amino acid (BCAA) supplementation. Dosage and Administration To be determined by the clinician or dietitian and is dependent on the age, bodyweight and medica ...
... Indications Solvil is for use in the dietary management of urea cycle disorders or other inborn errors of metabolism requiring branched chain amino acid (BCAA) supplementation. Dosage and Administration To be determined by the clinician or dietitian and is dependent on the age, bodyweight and medica ...
View/Open
... was carried out by implementing the Benjamini-Hochberg approach in R. Categories with a significant difference in proportional representation among DE and non-DE genes are indicated ...
... was carried out by implementing the Benjamini-Hochberg approach in R. Categories with a significant difference in proportional representation among DE and non-DE genes are indicated ...
Chapter 8: Energy and Metabolism
... 5. Stress particular bonds of a substrate 6. Example: formation of carbonic acid from carbon dioxide and water a. Reaction proceeds in either direction b. Reaction is slow because of a great activation energy c. Carbonic anhydrase: enzyme that speeds the reaction 7. Enzymes given the name of their w ...
... 5. Stress particular bonds of a substrate 6. Example: formation of carbonic acid from carbon dioxide and water a. Reaction proceeds in either direction b. Reaction is slow because of a great activation energy c. Carbonic anhydrase: enzyme that speeds the reaction 7. Enzymes given the name of their w ...
Photosynthesis & Respiration
... Autotrophs: all green plants, use sunlight directly to produce food from inorganic molecules in the environment Heterotrophs: obtain E from food they eat. Eat Heteros, Autotrophs, or both ...
... Autotrophs: all green plants, use sunlight directly to produce food from inorganic molecules in the environment Heterotrophs: obtain E from food they eat. Eat Heteros, Autotrophs, or both ...
Respiration Notes (chapter 8)
... Step 3: Electron Transport Chain (ETC) -occurs on the cristae of the inner mitochondrial membrane. -produces 32-34 ATP using Chemiosmosis - e- of NADH & FADH2 (produced in steps 1&2). -the ETC consists of: 1.NADH dehydrogenase or reductase protein 2.Cytochromes (proteins) 3.at the end of the chain ...
... Step 3: Electron Transport Chain (ETC) -occurs on the cristae of the inner mitochondrial membrane. -produces 32-34 ATP using Chemiosmosis - e- of NADH & FADH2 (produced in steps 1&2). -the ETC consists of: 1.NADH dehydrogenase or reductase protein 2.Cytochromes (proteins) 3.at the end of the chain ...
Carbon-based molecules are life`s building blocks.
... Carbohydrates include sugars and starches found in foods such as bread and pasta. Many lipids are fats or oils. Proteins are necessary for many functions in the body, including the formation of muscle tissue. Nucleic acids are the molecules that carry the genetic code for all living things. As you r ...
... Carbohydrates include sugars and starches found in foods such as bread and pasta. Many lipids are fats or oils. Proteins are necessary for many functions in the body, including the formation of muscle tissue. Nucleic acids are the molecules that carry the genetic code for all living things. As you r ...
Ch. 2 - Basic Chemistry
... Classified according to size (1) Monosaccharides - simple sugars (glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, deoxyribose) ...
... Classified according to size (1) Monosaccharides - simple sugars (glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, deoxyribose) ...
Chemical Basis of Life packet #2
... 9. Proteins are a major part of every living cell and have many different functions within each cell. Carbohydrates also perform numerous roles in living things. Part A: Describe the general composition of a protein molecule. ...
... 9. Proteins are a major part of every living cell and have many different functions within each cell. Carbohydrates also perform numerous roles in living things. Part A: Describe the general composition of a protein molecule. ...
Biology – Unit 3 Review
... A cellular process carried out by most plants and some bacteria which captures light energy and uses it in combination with carbon dioxide and water to create glucose, releases oxygen as a waste product. Cellular Respiration Another cellular process carried out by all cells. A series of chemical rea ...
... A cellular process carried out by most plants and some bacteria which captures light energy and uses it in combination with carbon dioxide and water to create glucose, releases oxygen as a waste product. Cellular Respiration Another cellular process carried out by all cells. A series of chemical rea ...
Muscle Metabolism - Liberty Union High School District
... tissues in the body that are depleted first and need to be replaced • Phosphagen system: ATP must be made, then broken to give Pi back to creatine • Oxidizing lactic acid: most of lactic acid will be converted into glucose in the presence of oxygen • Metabolic rate: if body temp is high the metaboli ...
... tissues in the body that are depleted first and need to be replaced • Phosphagen system: ATP must be made, then broken to give Pi back to creatine • Oxidizing lactic acid: most of lactic acid will be converted into glucose in the presence of oxygen • Metabolic rate: if body temp is high the metaboli ...
Lecture 3 - Winthrop Chemistry, Physics, and Geology
... •The different biologically active molecules and polymers arrange themselvs to form cells •The formation of a lipid bilayer is instrumental in this! •We can distinguish between types of cells based upon the presence of organelles, especially the nucleus •Prokaryotic do not have a nucleus or other or ...
... •The different biologically active molecules and polymers arrange themselvs to form cells •The formation of a lipid bilayer is instrumental in this! •We can distinguish between types of cells based upon the presence of organelles, especially the nucleus •Prokaryotic do not have a nucleus or other or ...
Carbon-Based Molecules
... Nucleic acids are polymers that are made up of monomers called nucleotides. A nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen-containing molecule called a base. Nucleic acids contain the instructions to build proteins. Interactive Reader ...
... Nucleic acids are polymers that are made up of monomers called nucleotides. A nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen-containing molecule called a base. Nucleic acids contain the instructions to build proteins. Interactive Reader ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.