DOGS: THE ULTlMATE ATHLETES
... 6 Reynolds AJ, Fuhrer L, Dunlop HL, Finke MD, Kallfelz FA. Lipid metabolite responses to diet and training in sled dogs. J. Nutr. 1994. 124:2754S-2759S. ...
... 6 Reynolds AJ, Fuhrer L, Dunlop HL, Finke MD, Kallfelz FA. Lipid metabolite responses to diet and training in sled dogs. J. Nutr. 1994. 124:2754S-2759S. ...
Lecture 1 - Doolittle Lab
... In the 1950’s several laboratories were trying to figure out how proteins were made from a biochemical standpoint. The standard biochemical strategy is to purify components and then re-assemble them in the test tube (“in vitro”) to see if they will react to give the expected product. In this case t ...
... In the 1950’s several laboratories were trying to figure out how proteins were made from a biochemical standpoint. The standard biochemical strategy is to purify components and then re-assemble them in the test tube (“in vitro”) to see if they will react to give the expected product. In this case t ...
Biology 1406: Cell and Molecular Biology
... 1. Describe the basic structure of atoms. 2. Interpret chemical and structural formulas. 3. Describe ionic and covalent bonds. 4. Discuss hydrogen bonds and non-polar interactions, and their importance for living organisms. 5. Identify some characteristics of carbon that allow it to play such an imp ...
... 1. Describe the basic structure of atoms. 2. Interpret chemical and structural formulas. 3. Describe ionic and covalent bonds. 4. Discuss hydrogen bonds and non-polar interactions, and their importance for living organisms. 5. Identify some characteristics of carbon that allow it to play such an imp ...
Cellular Respiration 2016
... • To perform their many tasks, cells require energy from outside sources. • In most ecosystems, energy enters as sunlight. ...
... • To perform their many tasks, cells require energy from outside sources. • In most ecosystems, energy enters as sunlight. ...
Cellular Respiration Breathe in… breathe out… or not!
... • To perform their many tasks, cells require energy from outside sources. • In most ecosystems, energy enters as sunlight. ...
... • To perform their many tasks, cells require energy from outside sources. • In most ecosystems, energy enters as sunlight. ...
Gas-Forming reactions Reactions that form a
... (c). Hydrogen, in all its compounds except hydrides, has an oxidation number of +1. (d). Oxygen, in all its compounds except when connected to another oxygen or a fluorine, has an oxidation number of -2. (e). Alkali metals always have an oxidation number of +1 and alkaline earth metals +2. 4. The su ...
... (c). Hydrogen, in all its compounds except hydrides, has an oxidation number of +1. (d). Oxygen, in all its compounds except when connected to another oxygen or a fluorine, has an oxidation number of -2. (e). Alkali metals always have an oxidation number of +1 and alkaline earth metals +2. 4. The su ...
Student notes in ppt
... Lipid Metabolism 1: Overview of lipid transport in animals, fatty acid oxidation, ketogenesis in liver mitochondria ...
... Lipid Metabolism 1: Overview of lipid transport in animals, fatty acid oxidation, ketogenesis in liver mitochondria ...
Introducing Dr. Rodger Murphree
... serotonin, epinephrine, an dopamine. These are the brain chemicals that regulate sleep, pain, energy, stamina, drive, and ambition. Niacin B3 (75% as Niacinamide) – 100mg – is needed to make serotonin. A deficiency can lead to weakness, anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine hydro ...
... serotonin, epinephrine, an dopamine. These are the brain chemicals that regulate sleep, pain, energy, stamina, drive, and ambition. Niacin B3 (75% as Niacinamide) – 100mg – is needed to make serotonin. A deficiency can lead to weakness, anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine hydro ...
AP Review
... ETC accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first 2 stages - the energy released at each step of the chain is used to make ATP (oxidative phosphorylation); through redox rxns. oxidative phosphorylation accounts for 90% of generated ATP ...
... ETC accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first 2 stages - the energy released at each step of the chain is used to make ATP (oxidative phosphorylation); through redox rxns. oxidative phosphorylation accounts for 90% of generated ATP ...
Chapter 13 Lecture Notes: Peptides, Proteins
... Understanding Check: Write the names (using the three letter abbreviation method) of all of the tripeptides that can be made by combining one glycine (gly), one alanine (ala), and one aspartic acid (asp) residue. For example, one of the tripeptides is gly-ala-asp. ...
... Understanding Check: Write the names (using the three letter abbreviation method) of all of the tripeptides that can be made by combining one glycine (gly), one alanine (ala), and one aspartic acid (asp) residue. For example, one of the tripeptides is gly-ala-asp. ...
practice midterm answers
... Quarternary structure of proteins Allosteric interactions Multiple Choice 1) The role of an enzyme in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is to A) bind a transition state intermediate, such that it can be converted back to a substrate B) ensure that all substrate is converted to product C) ensure that prod ...
... Quarternary structure of proteins Allosteric interactions Multiple Choice 1) The role of an enzyme in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is to A) bind a transition state intermediate, such that it can be converted back to a substrate B) ensure that all substrate is converted to product C) ensure that prod ...
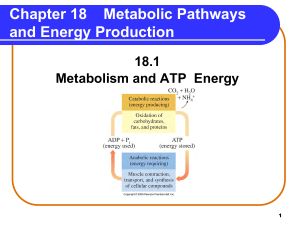
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... • begin digestion in the mouth, where salivary amylase breaks down polysaccharides to smaller polysaccharides (dextrins), maltose, and some glucose. • continue digestion in the small intestine, where pancreatic amylase hydrolyzes dextrins to maltose and glucose. • maltose, lactose, and sucrose are h ...
... • begin digestion in the mouth, where salivary amylase breaks down polysaccharides to smaller polysaccharides (dextrins), maltose, and some glucose. • continue digestion in the small intestine, where pancreatic amylase hydrolyzes dextrins to maltose and glucose. • maltose, lactose, and sucrose are h ...
Unit 5 Lesson 8
... • The micronutrients are boron, chlorine, cooper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, and zinc. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. Especially, they work "behind the scene" as ac ...
... • The micronutrients are boron, chlorine, cooper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, and zinc. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. Especially, they work "behind the scene" as ac ...
Lab Module 8: Phenol-Red Carbohydrate Fermentation Broths
... of types of by-products. Lactobacillus (and human muscle cells) forms lactic acid as a fermentation by-product. Acetobacter forms acetic acid. Many bacteria form mixtures of products including liquids and gases. The particular types of by-products depends on the particular enzyme systems used to per ...
... of types of by-products. Lactobacillus (and human muscle cells) forms lactic acid as a fermentation by-product. Acetobacter forms acetic acid. Many bacteria form mixtures of products including liquids and gases. The particular types of by-products depends on the particular enzyme systems used to per ...
A1985AFW3400002
... was very fortunate to be a member of Randie’s research group at a particularly exciting time. Hal Coore and Randle also devised the simple system that opened up the study of insulin secretion. I should point out, as there seems to be a danger of its being overlooked in these pages, that they showed ...
... was very fortunate to be a member of Randie’s research group at a particularly exciting time. Hal Coore and Randle also devised the simple system that opened up the study of insulin secretion. I should point out, as there seems to be a danger of its being overlooked in these pages, that they showed ...
2–3 Carbon Compounds
... Large carbohydrate molecules such as starch are known as a. lipids. b. monosaccharides. c. proteins. d. polysaccharides. ...
... Large carbohydrate molecules such as starch are known as a. lipids. b. monosaccharides. c. proteins. d. polysaccharides. ...
chapter 8 section 3 notes
... lost to the electron transport chain. Oxygen is released into the air. This reaction is the source of nearly all of the oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere. The H+ ions are released inside the thylakoid. ...
... lost to the electron transport chain. Oxygen is released into the air. This reaction is the source of nearly all of the oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere. The H+ ions are released inside the thylakoid. ...
An overview on effective parameters in production of single cell oil
... Microbial lipoids, known as single cell oil (SCO) [1]. Like all living cells, microorganisms contain lipids. It indicates a triacylglycerol type of oil, similar to that found in plant and animal edible oils and fats [2]. Microorganisms product lipid for essential functioning of cell membranes and ot ...
... Microbial lipoids, known as single cell oil (SCO) [1]. Like all living cells, microorganisms contain lipids. It indicates a triacylglycerol type of oil, similar to that found in plant and animal edible oils and fats [2]. Microorganisms product lipid for essential functioning of cell membranes and ot ...
Flexing Muscle With Just One Amino Acid
... Undergocs thils crLuia,l shape change has But scientists were unable to confirm these acid-but one with a neutral charge. When remained Murky. c) the team studied the structure of the Two weeks ag(), however, a group of mutant protein, they found that it no Canadian researclhers, flexing some _C lon ...
... Undergocs thils crLuia,l shape change has But scientists were unable to confirm these acid-but one with a neutral charge. When remained Murky. c) the team studied the structure of the Two weeks ag(), however, a group of mutant protein, they found that it no Canadian researclhers, flexing some _C lon ...
Slide 1
... Students will understand that 1) the uniformity of the Krebs cycle reactions across all life is due to inheritance from a common ancestor, 2) different lineages have evolved slight variations in the Krebs cycle reactions as they have diverged, and 3) the eukaryotic version of the Krebs cycle actuall ...
... Students will understand that 1) the uniformity of the Krebs cycle reactions across all life is due to inheritance from a common ancestor, 2) different lineages have evolved slight variations in the Krebs cycle reactions as they have diverged, and 3) the eukaryotic version of the Krebs cycle actuall ...
Bacterial identification and antibiotic sensitivity
... Any change from green is considered positive for Dulcitol OR Phenylalanine; NOT both. If the compartment remains green then it is negative for both. Dulcitol (sugar): yellow/golden media color change indicates a positive result Phenylalanine (amino acid): black/smoky grey color change indicate ...
... Any change from green is considered positive for Dulcitol OR Phenylalanine; NOT both. If the compartment remains green then it is negative for both. Dulcitol (sugar): yellow/golden media color change indicates a positive result Phenylalanine (amino acid): black/smoky grey color change indicate ...
Cellular Respiration
... NADH and Electron Transport Chains • The path that electrons take on their way down from glucose to oxygen involves many steps. • The first step is an electron acceptor called NAD+. – NAD is made by cells from niacin, a B vitamin. – The transfer of electrons from organic fuel to NAD+ reduces it to ...
... NADH and Electron Transport Chains • The path that electrons take on their way down from glucose to oxygen involves many steps. • The first step is an electron acceptor called NAD+. – NAD is made by cells from niacin, a B vitamin. – The transfer of electrons from organic fuel to NAD+ reduces it to ...
PASS MOCK EXAM
... A) Chlorophyll a molecules of photosystem II split H20 to replace their electrons while the electrons lost by chlorophyll a in photosystem I get replaced by the electron transport chain. B) Reaction centre ...
... A) Chlorophyll a molecules of photosystem II split H20 to replace their electrons while the electrons lost by chlorophyll a in photosystem I get replaced by the electron transport chain. B) Reaction centre ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.