Enzyme Complete ppt
... • Regulation & coordination of production • product is used by next step in pathway • final product is inhibitor of earlier step • allosteric inhibitor of earlier enzyme ...
... • Regulation & coordination of production • product is used by next step in pathway • final product is inhibitor of earlier step • allosteric inhibitor of earlier enzyme ...
Ch03Pt2
... histones have to have lots of positive charges. The important concept here is that it has to be R groups of amino acids that are not the N- or C-terminal. Which ones would have a positive charge at physiological pH? Check out Table 3.1 for the amino acids R, K and H. ...
... histones have to have lots of positive charges. The important concept here is that it has to be R groups of amino acids that are not the N- or C-terminal. Which ones would have a positive charge at physiological pH? Check out Table 3.1 for the amino acids R, K and H. ...
Practical part
... Principle. Enzymes exhibit selectivity to substrates, which is called substrate specificity. In many instances this property is the essential characteristic that renders enzymes markedly different from inorganic catalysts. The high specificity of enzymes is attributable to the conformational complem ...
... Principle. Enzymes exhibit selectivity to substrates, which is called substrate specificity. In many instances this property is the essential characteristic that renders enzymes markedly different from inorganic catalysts. The high specificity of enzymes is attributable to the conformational complem ...
Cellular Respiration - Kania´s Science Page
... breaking down food to produce ATP in mitochondria using oxygen “aerobic” respiration ...
... breaking down food to produce ATP in mitochondria using oxygen “aerobic” respiration ...
Practice Exam III answers
... What does this imply about the values of Vmax and KM for a “perfect” enzyme? a). The values of both Vmax and KM are very high. b). The values of both Vmax and KM are very low. c). The value of Vmax is very high and the value of KM is very low. d). The value of Vmax is very low and the value of KM is ...
... What does this imply about the values of Vmax and KM for a “perfect” enzyme? a). The values of both Vmax and KM are very high. b). The values of both Vmax and KM are very low. c). The value of Vmax is very high and the value of KM is very low. d). The value of Vmax is very low and the value of KM is ...
PreAP Biology
... • compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.[4A] • investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules.[4B] • compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe th ...
... • compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.[4A] • investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules.[4B] • compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe th ...
A General Method Applicable to the Search for Similarities in the
... A computer adaptable method forfinding similarities in the amino acid sequences of two proteins has been developed.From these findings it is possible to determine whether significant homology exists between the proteins. This information is used to trace their possible evolutionary development. The ...
... A computer adaptable method forfinding similarities in the amino acid sequences of two proteins has been developed.From these findings it is possible to determine whether significant homology exists between the proteins. This information is used to trace their possible evolutionary development. The ...
Genome-Based Metabolic Mapping and C Flux
... et al., 2011). This methodology allowed for mapping fluxes under autotrophic growth conditions (Young et al., 2011), because it overcame the limitation of traditional steady-state 13C metabolic flux analysis (MFA), which fails to resolve the flux from a uniformly steady 13C labeling pattern because of ...
... et al., 2011). This methodology allowed for mapping fluxes under autotrophic growth conditions (Young et al., 2011), because it overcame the limitation of traditional steady-state 13C metabolic flux analysis (MFA), which fails to resolve the flux from a uniformly steady 13C labeling pattern because of ...
FEED NUTRIENTS
... hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and usually sulfur. They consist of one or more chains of amino acids. Proteins are fundamental components of all body cells and include many substances (such as enzymes, hormones, and antibodies) necessary for proper body functions. They are essential in the animal’s rat ...
... hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and usually sulfur. They consist of one or more chains of amino acids. Proteins are fundamental components of all body cells and include many substances (such as enzymes, hormones, and antibodies) necessary for proper body functions. They are essential in the animal’s rat ...
Principle_files/6-Translation n
... The dogma is a framework for understanding the transfer of sequence information between sequential information-carrying biopolymers, in the most common or general case, in living organisms. There are 3 major classes of such biopolymers: DNA and RNA (both nucleic acids), and protein. There are 3×3 = ...
... The dogma is a framework for understanding the transfer of sequence information between sequential information-carrying biopolymers, in the most common or general case, in living organisms. There are 3 major classes of such biopolymers: DNA and RNA (both nucleic acids), and protein. There are 3×3 = ...
Cellular Energy - cloudfront.net
... ATP – adenosine triphosphate ◦ Energy source for cells ◦ Produced by photosynthesis and cellular respiration ◦ Used in many cellular processes ◦ One molecule contains three phosphate groups ...
... ATP – adenosine triphosphate ◦ Energy source for cells ◦ Produced by photosynthesis and cellular respiration ◦ Used in many cellular processes ◦ One molecule contains three phosphate groups ...
Control Mechanisms: Hormones
... when protein kinase A is active, glycogenesis stopped net result of hormone binding is coordinated: activation of glycogenolysis inhibition of glycogenesis ...
... when protein kinase A is active, glycogenesis stopped net result of hormone binding is coordinated: activation of glycogenolysis inhibition of glycogenesis ...
Chemistry in Biology
... A catalyst is a substance that lowers the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction. It does not increase how much product is made and it does not get used up in the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts. ...
... A catalyst is a substance that lowers the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction. It does not increase how much product is made and it does not get used up in the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts. ...
So, you want to know about siderophore synthesis
... substrate by adenylation and the transfer to a thioester linkage with the enzyme, followed by condensation to form a longer chain. This is similar to the process followed in biosynthesis of fatty acids. ...
... substrate by adenylation and the transfer to a thioester linkage with the enzyme, followed by condensation to form a longer chain. This is similar to the process followed in biosynthesis of fatty acids. ...
Chapter 6 How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
... 6.16 Food molecules provide raw materials for biosynthesis Many metabolic pathways are involved in biosynthesis of biological molecules – To survive, cells must be able to biosynthesize molecules that are not present in its foods – Often the cell will convert the intermediate compounds of glycoly ...
... 6.16 Food molecules provide raw materials for biosynthesis Many metabolic pathways are involved in biosynthesis of biological molecules – To survive, cells must be able to biosynthesize molecules that are not present in its foods – Often the cell will convert the intermediate compounds of glycoly ...
Metabolism of BCAAs
... of which is a redox-sensitive CXXC center that plays a major role in catalytic reactions. In this case, the C’s represent the amino acid cysteine, while the X’s can be any amino acid. Both isozymes of BCAT are reversible, and it is this redox center that permits this reversibility. In most cells, BC ...
... of which is a redox-sensitive CXXC center that plays a major role in catalytic reactions. In this case, the C’s represent the amino acid cysteine, while the X’s can be any amino acid. Both isozymes of BCAT are reversible, and it is this redox center that permits this reversibility. In most cells, BC ...
Glycolysis
... • The Glycolytic pathway describes the oxidation of glucose to pyruvate with the generation of ATP and NADH • It is also called as the Embden-Meyerhof Pathway • Glycolysis is a universal pathway; present in all organisms: from yeast to mammals. • In eukaryotes, glycolysis takes place in the cytosol ...
... • The Glycolytic pathway describes the oxidation of glucose to pyruvate with the generation of ATP and NADH • It is also called as the Embden-Meyerhof Pathway • Glycolysis is a universal pathway; present in all organisms: from yeast to mammals. • In eukaryotes, glycolysis takes place in the cytosol ...
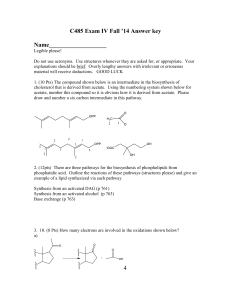
C485 Exam I
... 1. (10 Pts) The compound shown below is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol that is derived from acetate. Using the numbering system shown below for acetate, number this compound so it is obvious how it is derived from acetate. Please draw and number a six carbon intermediate in this ...
... 1. (10 Pts) The compound shown below is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol that is derived from acetate. Using the numbering system shown below for acetate, number this compound so it is obvious how it is derived from acetate. Please draw and number a six carbon intermediate in this ...
Slide 1
... 6.16 Food molecules provide raw materials for biosynthesis Many metabolic pathways are involved in biosynthesis of biological molecules – To survive, cells must be able to biosynthesize molecules that are not present in its foods – Often the cell will convert the intermediate compounds of glycoly ...
... 6.16 Food molecules provide raw materials for biosynthesis Many metabolic pathways are involved in biosynthesis of biological molecules – To survive, cells must be able to biosynthesize molecules that are not present in its foods – Often the cell will convert the intermediate compounds of glycoly ...
proteoma
... an SDS-polyacrylamide gel, and electrophoresis is performed in the second dimension, perpendicular to the original separation. Proteins with the same pI are now separated on the basis of mass. (B) Proteins from E. coli were separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, resolving more than a thou ...
... an SDS-polyacrylamide gel, and electrophoresis is performed in the second dimension, perpendicular to the original separation. Proteins with the same pI are now separated on the basis of mass. (B) Proteins from E. coli were separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, resolving more than a thou ...
The Point is to Make ATP!
... Overview of cellular respiration Aerobic respiration As pyruvate moves into the mitochondria, multiple steps occur Link Reaction (prepares pyruvate to move through ...
... Overview of cellular respiration Aerobic respiration As pyruvate moves into the mitochondria, multiple steps occur Link Reaction (prepares pyruvate to move through ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.