Figure 11-1
... catalyzes the reaction of the H2O2 with a colorless compound to produce a colored product, which is measured spectrophotometrically. ...
... catalyzes the reaction of the H2O2 with a colorless compound to produce a colored product, which is measured spectrophotometrically. ...
Proteins
... • Proteins are instrumental in about everything that an organism does. • These functions include structural support, storage, transport of other substances, intercellular signaling, movement, and defense against foreign substances. • Proteins are the overwhelming enzymes in a cell and regulate metab ...
... • Proteins are instrumental in about everything that an organism does. • These functions include structural support, storage, transport of other substances, intercellular signaling, movement, and defense against foreign substances. • Proteins are the overwhelming enzymes in a cell and regulate metab ...
elisa - WordPress.com
... The reaction can be halted by addition of acid or another stop reagent. Using sulfuric acid turns TMB yellow. The colour may be read at 450 nm. ...
... The reaction can be halted by addition of acid or another stop reagent. Using sulfuric acid turns TMB yellow. The colour may be read at 450 nm. ...
Trends in Sports Drink Formulations
... recommendations to consume 30-60g of carbohydrate per hour were based on saturation of the glucose transport mechanism. Once this metabolic pathway becomes saturated, the body will not absorb any more glucose for the time being. However, this study from U.K. researchers found that combining more tha ...
... recommendations to consume 30-60g of carbohydrate per hour were based on saturation of the glucose transport mechanism. Once this metabolic pathway becomes saturated, the body will not absorb any more glucose for the time being. However, this study from U.K. researchers found that combining more tha ...
Investigation of factors affecting aerobic and respiratory
... phase and increasing towards stationary growth phase. Levels of pox were higher when dO2 was maintained at 30%. On the contrary, cydAB was expressed in all conditions, suggesting that synthesis of cytochrome bd quinol oxidase is not strictly related to the presence of oxygen. However, its functional ...
... phase and increasing towards stationary growth phase. Levels of pox were higher when dO2 was maintained at 30%. On the contrary, cydAB was expressed in all conditions, suggesting that synthesis of cytochrome bd quinol oxidase is not strictly related to the presence of oxygen. However, its functional ...
UNIT 2. Structure and function of proteins.
... gel are separated thanks to the solvent migration (buthanol: water: acetic acid 4:1:1) by capillarity. Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): amino acids are separated on the base of their polarity by the used of a column having a ...
... gel are separated thanks to the solvent migration (buthanol: water: acetic acid 4:1:1) by capillarity. Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): amino acids are separated on the base of their polarity by the used of a column having a ...
Enzymes are Most Effective at Optimal Conditions
... role in various enzyme activities. This is because a higher concentration of substrate means it takes less time for substrate molecules to collide with the active site of the enzyme and the reaction rate increases (fig. 2b). Whereas, a low concentration of substrate means it takes longer for substra ...
... role in various enzyme activities. This is because a higher concentration of substrate means it takes less time for substrate molecules to collide with the active site of the enzyme and the reaction rate increases (fig. 2b). Whereas, a low concentration of substrate means it takes longer for substra ...
A new approach to increase yields and improve
... Most frequently, bacteria are grown in shake flasks or plates using commercially-available or ‘in-house’ adaptations of LB, TB or M9. As illustrated in Figure 1, when supplied with a carbon source such as glucose, bacteria grow and divide rapidly at their maximum growth rate. However, as uncontrolle ...
... Most frequently, bacteria are grown in shake flasks or plates using commercially-available or ‘in-house’ adaptations of LB, TB or M9. As illustrated in Figure 1, when supplied with a carbon source such as glucose, bacteria grow and divide rapidly at their maximum growth rate. However, as uncontrolle ...
Microbial Degradation of Cycloparaffinic
... unable to grow on propane, can utilize the cyclohexanone produced as a co-metabolic product from cyclohexane by JOB^. Since the only labelled substrate present was cyclohexane, these data show a definite enhancement of cycloparaffin degradation by microbial co-metabolism and commensalism. A similar ...
... unable to grow on propane, can utilize the cyclohexanone produced as a co-metabolic product from cyclohexane by JOB^. Since the only labelled substrate present was cyclohexane, these data show a definite enhancement of cycloparaffin degradation by microbial co-metabolism and commensalism. A similar ...
Mader 11 ch 3 Chemistry of Organic Molecules Part 2
... Have primary, secondary and tertiary shape (structure) Denaturing can change structure back to primary ...
... Have primary, secondary and tertiary shape (structure) Denaturing can change structure back to primary ...
active site
... • Too Cold - H bonds and van der Waals forces aren’t flexible enough to allow the induced fit for catalysis. • Too Hot - they are too weak to maintain the enzymes shape and break apart. ...
... • Too Cold - H bonds and van der Waals forces aren’t flexible enough to allow the induced fit for catalysis. • Too Hot - they are too weak to maintain the enzymes shape and break apart. ...
Microbial Degradation of Cycloparaffinic
... unable to grow on propane, can utilize the cyclohexanone produced as a co-metabolic product from cyclohexane by JOB^. Since the only labelled substrate present was cyclohexane, these data show a definite enhancement of cycloparaffin degradation by microbial co-metabolism and commensalism. A similar ...
... unable to grow on propane, can utilize the cyclohexanone produced as a co-metabolic product from cyclohexane by JOB^. Since the only labelled substrate present was cyclohexane, these data show a definite enhancement of cycloparaffin degradation by microbial co-metabolism and commensalism. A similar ...
Triple Science Revision or Home work Booklet
... living things, such as reactions involved in respiration, photosynthesis, growth, protein synthesis. Describe the structure of enzymes in as much detail as you can, refer to genes in your explanation. Enzymes are proteins. Proteins made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. Proteins, large mo ...
... living things, such as reactions involved in respiration, photosynthesis, growth, protein synthesis. Describe the structure of enzymes in as much detail as you can, refer to genes in your explanation. Enzymes are proteins. Proteins made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. Proteins, large mo ...
2.3. Three-Dimensional structure and function of proteins.
... These numbers are approximate, but entirely suitable for our purposes. ...
... These numbers are approximate, but entirely suitable for our purposes. ...
Lipids
... sphingoid base linked to a fatty acid via an amide bond. They are rarely found at greater than trace levels in tissues, although they can exert important biological effects. Ceramides are formed as the key intermediates in the biosynthesis of all the complex sphingolipids, in which the terminal prim ...
... sphingoid base linked to a fatty acid via an amide bond. They are rarely found at greater than trace levels in tissues, although they can exert important biological effects. Ceramides are formed as the key intermediates in the biosynthesis of all the complex sphingolipids, in which the terminal prim ...
Industrial Microbiology
... of a single mating type; involves removal of cell walls, mixing two different solutions of protoplasts, and growth in selective media Can be done using species that are not closely related ...
... of a single mating type; involves removal of cell walls, mixing two different solutions of protoplasts, and growth in selective media Can be done using species that are not closely related ...
Protein and Amino Acids
... This suggests what? Quality of protein is important in the horse’s diet Amino acid profiles are important While microbial amino acid synthesis occurs, it is not ...
... This suggests what? Quality of protein is important in the horse’s diet Amino acid profiles are important While microbial amino acid synthesis occurs, it is not ...
BSU Honors Biology Chapter 5 Reading Guide Cell
... Because an enzyme must have a precise shape to work correctly, it is possible for the cell to control when an enzyme is active by altering its shape. Many enzymes have shapes that can be altered by the binding of “signal” molecules to their surfaces. Such enzymes are called allosteric (Latin, other ...
... Because an enzyme must have a precise shape to work correctly, it is possible for the cell to control when an enzyme is active by altering its shape. Many enzymes have shapes that can be altered by the binding of “signal” molecules to their surfaces. Such enzymes are called allosteric (Latin, other ...
5-1 Necleotide Metabolism (purine)
... Amidophosphoribosyl transferase is an important regulatory enzyme in purine biosynthesis. It is strongly inhibited by the end products IMP, AMP, and GMP. This type of inhibition is called FEEDBACK INHIBITION. ...
... Amidophosphoribosyl transferase is an important regulatory enzyme in purine biosynthesis. It is strongly inhibited by the end products IMP, AMP, and GMP. This type of inhibition is called FEEDBACK INHIBITION. ...
Chapter 5 - Hale AP Biology
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
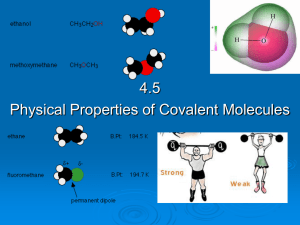
4.5 Physical properties of molecular covalent
... Covalent molecules are not charged because they are overall neutral and therefore do not conduct electricity. • Some covalent molecules can react with water and produce free ions which can carry an electrical current. • E.g. ammonia, NH3 NH3 (l) + H2O (l) ↔ NH4+ (aq) + OH- (aq) ...
... Covalent molecules are not charged because they are overall neutral and therefore do not conduct electricity. • Some covalent molecules can react with water and produce free ions which can carry an electrical current. • E.g. ammonia, NH3 NH3 (l) + H2O (l) ↔ NH4+ (aq) + OH- (aq) ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.