Industrial Microbiology
... of a single mating type; involves removal of cell walls, mixing two different solutions of protoplasts, and growth in selective media Can be done using species that are not closely related ...
... of a single mating type; involves removal of cell walls, mixing two different solutions of protoplasts, and growth in selective media Can be done using species that are not closely related ...
chemical reactions and energy changes
... another. The resulting cups of tea will taste different because they contain different concentrations of sugar. Concentration can be specified in a number of ways, one of which would be the mass of dissolved sugar in a particular volume of solution, i.e. grams per litre. However, chemical reactions ...
... another. The resulting cups of tea will taste different because they contain different concentrations of sugar. Concentration can be specified in a number of ways, one of which would be the mass of dissolved sugar in a particular volume of solution, i.e. grams per litre. However, chemical reactions ...
Amino Acid and Fatty Acid Profile of Twenty Wild Plants
... nitrogen in the body; as well as glucose that the body uses as energy and strengthens the immune system producing antibodies. It also regulates toxic substances discharged in their inherent energy need muscles. The percentage of proline fluctuates between 0.24% (T. tetraptera) to 8.78% (S. melongena ...
... nitrogen in the body; as well as glucose that the body uses as energy and strengthens the immune system producing antibodies. It also regulates toxic substances discharged in their inherent energy need muscles. The percentage of proline fluctuates between 0.24% (T. tetraptera) to 8.78% (S. melongena ...
Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell)
... A) It contains two phosphate groups. B) Extremely stable bonds link the second and third phosphate groups. C) It contains the six-carbon sugar hexose. D) It contains a nitrogenous base molecule called adenine. E) It can be coupled with an exergonic reaction. Answer: D Topic: 5.13 Skill: Factual Reca ...
... A) It contains two phosphate groups. B) Extremely stable bonds link the second and third phosphate groups. C) It contains the six-carbon sugar hexose. D) It contains a nitrogenous base molecule called adenine. E) It can be coupled with an exergonic reaction. Answer: D Topic: 5.13 Skill: Factual Reca ...
Biochemistry - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... So now we have to go on in our further steps. This is the part (Refer Slide Time: 15:00) where we have the dithiol that undergoes oxidation and reduction. One important thing of this is this dithiol reacts with the lipoic acid with the lysine of the…Where is this lysine? It is present in E2 and thi ...
... So now we have to go on in our further steps. This is the part (Refer Slide Time: 15:00) where we have the dithiol that undergoes oxidation and reduction. One important thing of this is this dithiol reacts with the lipoic acid with the lysine of the…Where is this lysine? It is present in E2 and thi ...
Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell)
... A) It contains two phosphate groups. B) Extremely stable bonds link the second and third phosphate groups. C) It contains the six-carbon sugar hexose. D) It contains a nitrogenous base molecule called adenine. E) It can be coupled with an exergonic reaction. Answer: D Topic: 5.13 Skill: Factual Reca ...
... A) It contains two phosphate groups. B) Extremely stable bonds link the second and third phosphate groups. C) It contains the six-carbon sugar hexose. D) It contains a nitrogenous base molecule called adenine. E) It can be coupled with an exergonic reaction. Answer: D Topic: 5.13 Skill: Factual Reca ...
Nuclear and mitochondrial forms of human uracil
... synthesised in the cytoplasm, and imported into their respective • To whom correspondence should be addressed ...
... synthesised in the cytoplasm, and imported into their respective • To whom correspondence should be addressed ...
INFLUENCE OF WATER - ETHANOL SOLVENT ON
... pK value on 0. 86 and increase pKH2 on 0. 94 logarithmic unit. In the first case process corresponds to the mechanism of dissociation of cationic acids, and in the second - the uncharged. The increase of ethanol concentration results to the considerable increase of stability constants of L-tyrosine ...
... pK value on 0. 86 and increase pKH2 on 0. 94 logarithmic unit. In the first case process corresponds to the mechanism of dissociation of cationic acids, and in the second - the uncharged. The increase of ethanol concentration results to the considerable increase of stability constants of L-tyrosine ...
Lipids 44:
... The very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (VLCPUFA), arachidonic acid (ARA, 20:4x-6), is a component of neuron tissues such as brain and retina cells and an important component of the human diet. ARA is a primary substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoids, including the 2-group prostaglandin ...
... The very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (VLCPUFA), arachidonic acid (ARA, 20:4x-6), is a component of neuron tissues such as brain and retina cells and an important component of the human diet. ARA is a primary substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoids, including the 2-group prostaglandin ...
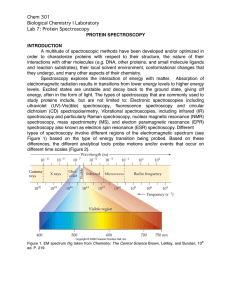
Chem 301 Biological Chemistry I Laboratory Lab 7: Protein
... organic molecule identification and chemical structure determination. But NMR is a powerful tool for studying biological molecules including proteins, nucleic acids, lipids and carbohydrates. The same principles apply but additional information can also be garnered from NMR spectra of these more com ...
... organic molecule identification and chemical structure determination. But NMR is a powerful tool for studying biological molecules including proteins, nucleic acids, lipids and carbohydrates. The same principles apply but additional information can also be garnered from NMR spectra of these more com ...
2.5 | Four Types of Biological Molecules
... As the backbone of sugar molecules increases in length, so too does the number of asymmetric carbon atoms and, consequently, the number of stereoisomers. Aldotetroses have two asymmetric carbons and thus can exist in four different configurations (Figure 2.14). Similarly, there are 8 different aldop ...
... As the backbone of sugar molecules increases in length, so too does the number of asymmetric carbon atoms and, consequently, the number of stereoisomers. Aldotetroses have two asymmetric carbons and thus can exist in four different configurations (Figure 2.14). Similarly, there are 8 different aldop ...
Two-Metal-Ion Catalysis in Adenylyl Cyclase
... structure, -L-2⬘,3⬘-dd-5⬘-ATP appears to bind as a complex with two metal ions. The first metal (metal A) is coordinated by the pro-R oxygen of the ␣ phosphate, a carboxylate oxygen from each of the invariant aspartic acid residues [Asp396 (D396) and D440], and a water molecule. The four ligands fo ...
... structure, -L-2⬘,3⬘-dd-5⬘-ATP appears to bind as a complex with two metal ions. The first metal (metal A) is coordinated by the pro-R oxygen of the ␣ phosphate, a carboxylate oxygen from each of the invariant aspartic acid residues [Asp396 (D396) and D440], and a water molecule. The four ligands fo ...
IDENTIFICATION OF LEAD COMPOUNDS WITH COBRA VENOM NEUTRALISING ACTIVITY IN
... effects, cost effective and need not require sophisticated storage system when compared to the antivenom therapy. There is also a growing realization that diseases have multifactorial causation, a combination of drugs acting at a number of targets simultaneously is likely to be more effective than d ...
... effects, cost effective and need not require sophisticated storage system when compared to the antivenom therapy. There is also a growing realization that diseases have multifactorial causation, a combination of drugs acting at a number of targets simultaneously is likely to be more effective than d ...
Score A_c5_17022012
... (i) What is the reduced co-enzyme? _______ [1m] (ii) What is the reaction involved in the production of ATP when the reduced co-enzyme in e(i) enters the electron transport system? _________________ [1m] ...
... (i) What is the reduced co-enzyme? _______ [1m] (ii) What is the reaction involved in the production of ATP when the reduced co-enzyme in e(i) enters the electron transport system? _________________ [1m] ...
This Exam contains 12 pages and consists of 168 Points.
... C7 (10 pts): Do either part a or part b, but not both! Choice a: In question 6, the concentration of glucose will initially be different across the cell membrane, with a concentration of 1 mM on the outside and 0.5 mM on the inside. The membrane potential across the cell membrane is -0.01 volts, wit ...
... C7 (10 pts): Do either part a or part b, but not both! Choice a: In question 6, the concentration of glucose will initially be different across the cell membrane, with a concentration of 1 mM on the outside and 0.5 mM on the inside. The membrane potential across the cell membrane is -0.01 volts, wit ...
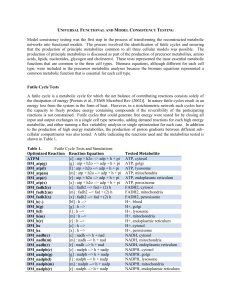
Universal Functional and Model Consistency Testing
... production of principle metabolites is discussed as part of the production of precursor metabolites, amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, glycogen and cholesterol. These tests represented the most essential metabolic functions that are common to the three cell types. Biomass equations, although differe ...
... production of principle metabolites is discussed as part of the production of precursor metabolites, amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, glycogen and cholesterol. These tests represented the most essential metabolic functions that are common to the three cell types. Biomass equations, although differe ...
PPT File
... •Two other enzymes, glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase and fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase transfer high potential electrons from FADH2 to Q to form ubiquinol –Also do not pump protons ...
... •Two other enzymes, glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase and fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase transfer high potential electrons from FADH2 to Q to form ubiquinol –Also do not pump protons ...
Biology-N5-Past-Paper-Questions-Cell-Biology
... waste product from photosynthesis / needed for chemical reactions Specific organs named other than lungs or placenta ...
... waste product from photosynthesis / needed for chemical reactions Specific organs named other than lungs or placenta ...
Herbicide Modes of Action (effect on plant growth)
... Contained here are pages 8-10 of the 2016 Guide for Weed, Disease, and Insect Management in Nebraska. The 300+ page guide is available at Marketplace.unl.edu ...
... Contained here are pages 8-10 of the 2016 Guide for Weed, Disease, and Insect Management in Nebraska. The 300+ page guide is available at Marketplace.unl.edu ...
- WordPress.com
... Fructose is metabolized by A. fructose 1-phosphate pathway B. fructose 6-phosphate pathway C. glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate pathway D.both (a) and (b) Answer: Option D ...
... Fructose is metabolized by A. fructose 1-phosphate pathway B. fructose 6-phosphate pathway C. glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate pathway D.both (a) and (b) Answer: Option D ...
an introduction to alpha-fetoprotein and the growth inhibitory peptide
... the flow of materials across the body and cellular membranes e.g. albumin and AFP. • Regulatory proteins- they act as sensors and switches to control protein activity and gene function. • Signaling proteins- including cell-surface receptors and other proteins that transmit external signals to the ce ...
... the flow of materials across the body and cellular membranes e.g. albumin and AFP. • Regulatory proteins- they act as sensors and switches to control protein activity and gene function. • Signaling proteins- including cell-surface receptors and other proteins that transmit external signals to the ce ...
Chapter 5 Gases - Saint Demetrios Astoria School
... From Structure to Function (cont’d.) • Metabolism: all enzyme-mediated chemical reactions by which cells acquire and use energy – Enzyme: organic molecule that speeds up a reaction without being changed by it ...
... From Structure to Function (cont’d.) • Metabolism: all enzyme-mediated chemical reactions by which cells acquire and use energy – Enzyme: organic molecule that speeds up a reaction without being changed by it ...
Lipid metabolism in cancer
... Dysregulated lipid metabolism is an established hallmark of cancer. Lipids play diverse roles in maintaining cellular structure, forming membrane microdomains for functional scaffolding of protein complexes, serving as fat storage depots, and acting as signaling molecules. All of these processes are ...
... Dysregulated lipid metabolism is an established hallmark of cancer. Lipids play diverse roles in maintaining cellular structure, forming membrane microdomains for functional scaffolding of protein complexes, serving as fat storage depots, and acting as signaling molecules. All of these processes are ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.