Transforming growth factor β1
... from one condition to another. In the context of hepatic regeneration, TGF-β1 is antiproliferative rather than pro-fibrogenic (Bissell, 2001). Different reports have linked TGF-B1 to different pathological hepatic states like cirrhosis and tumors (Hayashi and Sakai, 2012). Mechanism of action of TGF ...
... from one condition to another. In the context of hepatic regeneration, TGF-β1 is antiproliferative rather than pro-fibrogenic (Bissell, 2001). Different reports have linked TGF-B1 to different pathological hepatic states like cirrhosis and tumors (Hayashi and Sakai, 2012). Mechanism of action of TGF ...
protpars
... This has the problem that it allows replacements which are not consistent with the genetic code, counting them equally with replacements that are consistent. Fitch, on the other hand, counted the minimum number of nucleotide substitutions that would be needed to achieve the given protein sequences. ...
... This has the problem that it allows replacements which are not consistent with the genetic code, counting them equally with replacements that are consistent. Fitch, on the other hand, counted the minimum number of nucleotide substitutions that would be needed to achieve the given protein sequences. ...
NF96-251 A Comparative Study of Fiber Digestion and Subsequent
... small intestine where the majority of the essential nutrients such as amino acids, lipids, minerals and vitamins are absorbed. The microbial population of the rumen has a protein requirement which it obtains from the diet. Microbes leaving the rumen provide a protein source to the animal (host). "By ...
... small intestine where the majority of the essential nutrients such as amino acids, lipids, minerals and vitamins are absorbed. The microbial population of the rumen has a protein requirement which it obtains from the diet. Microbes leaving the rumen provide a protein source to the animal (host). "By ...
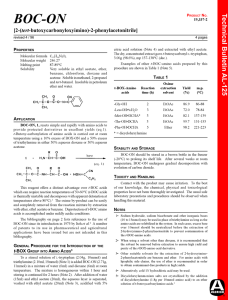
BOC-ON - Sigma
... Active Analog of the C-Terminal Heptapeptide with ,-Hydroxynorleucine Sulfate Replacing Tyrosine Sulfate. J. Med. Chem. 1978, 21, 1030. 13 Cachia, P.J.; Sykes, B.D.; Hodges, R.S. Calcium-dependant Inhibitory Region of Troponin: A protein Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study of the Interaction between T ...
... Active Analog of the C-Terminal Heptapeptide with ,-Hydroxynorleucine Sulfate Replacing Tyrosine Sulfate. J. Med. Chem. 1978, 21, 1030. 13 Cachia, P.J.; Sykes, B.D.; Hodges, R.S. Calcium-dependant Inhibitory Region of Troponin: A protein Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study of the Interaction between T ...
Nucleic Acids Research
... in CHO group 1 mutants. Based on similarity of the predicted ERCC-1 amino acid sequence with functional domains of other proteins, a putative nuclear location DNA signal (NLS), binding domain and ADPmonoribosylation site have been assigned to the ERCC-1 protein (12). Furthermore, a significant homol ...
... in CHO group 1 mutants. Based on similarity of the predicted ERCC-1 amino acid sequence with functional domains of other proteins, a putative nuclear location DNA signal (NLS), binding domain and ADPmonoribosylation site have been assigned to the ERCC-1 protein (12). Furthermore, a significant homol ...
Test 2
... Competitive and Uncompetititve inhibitors can differentiated using a Lineweaver-Burke analysis of Vo data obtained under different inhibitor concentrations. Since a competitive inhibitor can be competed off by high substrate concentrations, all lines obtained at different [S] concentrations will con ...
... Competitive and Uncompetititve inhibitors can differentiated using a Lineweaver-Burke analysis of Vo data obtained under different inhibitor concentrations. Since a competitive inhibitor can be competed off by high substrate concentrations, all lines obtained at different [S] concentrations will con ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: REACTIONS WITH GRIGNARD REAGENTS
... 1. Grignard reagents are made by adding a halogenoalkane to small bits of magnesium in a flask containing ethoxyethane (commonly called diethyl ether or just "ether"). The flask is fitted with a reflux condenser, and the mixture is warmed over a water bath for 20 - 30 minutes. a) Write the structure ...
... 1. Grignard reagents are made by adding a halogenoalkane to small bits of magnesium in a flask containing ethoxyethane (commonly called diethyl ether or just "ether"). The flask is fitted with a reflux condenser, and the mixture is warmed over a water bath for 20 - 30 minutes. a) Write the structure ...
CHEMISTRY OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS AND THEIR UTILIZATION
... changes in function and structure of proteins in our daily life. In this paragraph, several instances of changes related with proteins that are recognizable by our senses (such as color, taste, and texture) will be briefly introduced. The color of skeletal muscles varies with fish species. For examp ...
... changes in function and structure of proteins in our daily life. In this paragraph, several instances of changes related with proteins that are recognizable by our senses (such as color, taste, and texture) will be briefly introduced. The color of skeletal muscles varies with fish species. For examp ...
CHEMISTRY OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS AND THEIR UTILIZATION
... changes in function and structure of proteins in our daily life. In this paragraph, several instances of changes related with proteins that are recognizable by our senses (such as color, taste, and texture) will be briefly introduced. The color of skeletal muscles varies with fish species. For examp ...
... changes in function and structure of proteins in our daily life. In this paragraph, several instances of changes related with proteins that are recognizable by our senses (such as color, taste, and texture) will be briefly introduced. The color of skeletal muscles varies with fish species. For examp ...
Carbon conversion efficiency and central - Shachar
... convert carbon and nitrogen precursors provided by the mother plant into stable reserves required for germination and seedling establishment. The efficiency of the overall metabolic processes involved in accumulating seed storage products will determine the amount of reserve material available for t ...
... convert carbon and nitrogen precursors provided by the mother plant into stable reserves required for germination and seedling establishment. The efficiency of the overall metabolic processes involved in accumulating seed storage products will determine the amount of reserve material available for t ...
A strategically designed small molecule attacks alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in tumor cells
... a correspondingly rapid, powerful redox signal in tumor cell mitochondria. This signal was associated with redox modification of KGDH (including extensive enzyme glutathionylation and redox blockage of enzyme lipoate sulfhydryls), correlating with KGDH inactivation. The source of this tumor-specific ...
... a correspondingly rapid, powerful redox signal in tumor cell mitochondria. This signal was associated with redox modification of KGDH (including extensive enzyme glutathionylation and redox blockage of enzyme lipoate sulfhydryls), correlating with KGDH inactivation. The source of this tumor-specific ...
Background information map of Eragrain®-Teff
... Starch can be classified in rapidly digestible (RDS), slowly digestible (SDS) and resistant starch (RS), dependent on the rate of starch breakdown into glucose by digestion enzymes in vitro3. The role of RS on health and weight loss is discussed, however there is a growing set of scientific data on ...
... Starch can be classified in rapidly digestible (RDS), slowly digestible (SDS) and resistant starch (RS), dependent on the rate of starch breakdown into glucose by digestion enzymes in vitro3. The role of RS on health and weight loss is discussed, however there is a growing set of scientific data on ...
A strategically designed small molecule attacks alpha
... a correspondingly rapid, powerful redox signal in tumor cell mitochondria. This signal was associated with redox modification of KGDH (including extensive enzyme glutathionylation and redox blockage of enzyme lipoate sulfhydryls), correlating with KGDH inactivation. The source of this tumor-specific ...
... a correspondingly rapid, powerful redox signal in tumor cell mitochondria. This signal was associated with redox modification of KGDH (including extensive enzyme glutathionylation and redox blockage of enzyme lipoate sulfhydryls), correlating with KGDH inactivation. The source of this tumor-specific ...
Kinetics of gas-phase hydrogen/deuterium exchange and gas
... Pro, Trp and Tyr was found to occur with CD3OD, D2O but not with D2S, although, due to large differences in proton affinities of the neutral amino acids and the deuterium donors, no exchange is predicted for all of them. The suggestion5,14 that formation of hydrogen bonds within the exchange complex ...
... Pro, Trp and Tyr was found to occur with CD3OD, D2O but not with D2S, although, due to large differences in proton affinities of the neutral amino acids and the deuterium donors, no exchange is predicted for all of them. The suggestion5,14 that formation of hydrogen bonds within the exchange complex ...
AULAS DE BIOQUÍMICA
... The inner membrane is impermeable to most small molecules and ions, including protons (H); the only species that cross this membrane do so through specific transporters. The inner membrane bears the components of the respiratory chain and the ATP synthase. Outer membrane contains porins (< 5000). Ma ...
... The inner membrane is impermeable to most small molecules and ions, including protons (H); the only species that cross this membrane do so through specific transporters. The inner membrane bears the components of the respiratory chain and the ATP synthase. Outer membrane contains porins (< 5000). Ma ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... Chapter 7 - Coenzymes and Vitamins • Some enzymes require cofactors for activity (1) Essential ions (mostly metal ions) (2) Coenzymes (organic compounds) ...
... Chapter 7 - Coenzymes and Vitamins • Some enzymes require cofactors for activity (1) Essential ions (mostly metal ions) (2) Coenzymes (organic compounds) ...
PRODUCT PROFILE: AVPY (ADVANCED VOLUMIZING
... Cinnulin-PF: An aqueous extract of cinnamon that is loaded with uniquely linked proanthocyanidin antioxidants. These compounds "turn on" cellular signaling mechanisms normally carried out by insulin. Cinnulin-PF may help to maintain blood glucose, cholesterol and triglyceride levels that are already ...
... Cinnulin-PF: An aqueous extract of cinnamon that is loaded with uniquely linked proanthocyanidin antioxidants. These compounds "turn on" cellular signaling mechanisms normally carried out by insulin. Cinnulin-PF may help to maintain blood glucose, cholesterol and triglyceride levels that are already ...
Vitamin B12 deficiency, methylmalonic acidemia
... It should be recalled that although methionine is an essential amino acid, only its homocysteine portion cannot be synthesized by humans. The enzyme 5-methyl THF methyltransferase has a requirement for methyl B12 coenzyme. This enzyme catalyzes the methylation of homocysteine shown in the above reac ...
... It should be recalled that although methionine is an essential amino acid, only its homocysteine portion cannot be synthesized by humans. The enzyme 5-methyl THF methyltransferase has a requirement for methyl B12 coenzyme. This enzyme catalyzes the methylation of homocysteine shown in the above reac ...
Insights From The Molecular Docking Of
... databases and can view the three-dimensional structures (in case it is available in the known three-dimensional protein structures deposited to the Protein Data Bank) using the graphics plug-in Jmol. The proposed server is the first of its kind and can be freely accessed through the World Wide Web. ...
... databases and can view the three-dimensional structures (in case it is available in the known three-dimensional protein structures deposited to the Protein Data Bank) using the graphics plug-in Jmol. The proposed server is the first of its kind and can be freely accessed through the World Wide Web. ...
Chapter 7: Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
... Electrons from Glucose • As a material is oxidized, the electrons it loses transfer to another material, which is thereby reduced. • Such redox reactions transfer a lot of energy. • Much of the energy liberated by the oxidation of the reducing agent is captured in the reduction of the ...
... Electrons from Glucose • As a material is oxidized, the electrons it loses transfer to another material, which is thereby reduced. • Such redox reactions transfer a lot of energy. • Much of the energy liberated by the oxidation of the reducing agent is captured in the reduction of the ...
Optimization of Programmed Suppression in a Cell
... in a reaction mixture may influence not only the suppression yield but also the extent of background suppression (misreading by the malfunction of ribosome, which is the adaptation of noncognate tRNA as a decoder). Figure 2 exhibits the effects of different Mg2+ concentrations on EPO mutein synthesi ...
... in a reaction mixture may influence not only the suppression yield but also the extent of background suppression (misreading by the malfunction of ribosome, which is the adaptation of noncognate tRNA as a decoder). Figure 2 exhibits the effects of different Mg2+ concentrations on EPO mutein synthesi ...
Chapter 4. Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... We often think that a compound consisting of nonmetals only must be molecular [counterexample: (NH4)2SO4, which is ionic!] We do not realize that insoluble really means poorly soluble. We do not appreciate the difference between equivalence point and end point. We usually think that an oxidation nec ...
... We often think that a compound consisting of nonmetals only must be molecular [counterexample: (NH4)2SO4, which is ionic!] We do not realize that insoluble really means poorly soluble. We do not appreciate the difference between equivalence point and end point. We usually think that an oxidation nec ...
Energy - Moodle NTOU
... terms: catabolic and anabolic pathways; kinetic and potential energy; open and closed systems; exergonic and endergonic reactions 2. In your own words, explain the second law of thermodynamics and explain why it is not violated by living organisms 3. Explain in general terms how cells obtain the ene ...
... terms: catabolic and anabolic pathways; kinetic and potential energy; open and closed systems; exergonic and endergonic reactions 2. In your own words, explain the second law of thermodynamics and explain why it is not violated by living organisms 3. Explain in general terms how cells obtain the ene ...
Name: Date: ______ NUID
... 1. How can just a few elements give rise to all biological diversity? At what level, if any, are all biological organisms similar? Given this biochemical similarity, how is the structural and functional diversity of living things possible? Ans: Living things are composed primarily of macromolecules, ...
... 1. How can just a few elements give rise to all biological diversity? At what level, if any, are all biological organisms similar? Given this biochemical similarity, how is the structural and functional diversity of living things possible? Ans: Living things are composed primarily of macromolecules, ...
Pharmaceutical Faculty 3- d course Module 1 General principles of
... Inorganic phosphate D. Oxygen E. High-energy ATP bonds ANSWER: E ...
... Inorganic phosphate D. Oxygen E. High-energy ATP bonds ANSWER: E ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.