Curriculum Vitae
... Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC) • Provide bioanalytical and pharmacokinetics support to the preclinical-development of novel nano-delivery systems of antiviral drugs (toxicokinetics, bioavailability, dose proportionality, quantitative tissue distri ...
... Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC) • Provide bioanalytical and pharmacokinetics support to the preclinical-development of novel nano-delivery systems of antiviral drugs (toxicokinetics, bioavailability, dose proportionality, quantitative tissue distri ...
Chapter 5 - Red Hook Central Schools
... • Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells. • Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, defense against foreign substances, and organic catalysts (enzymes). • Proteins are polymers called polypeptides. • Amino acids a ...
... • Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells. • Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, defense against foreign substances, and organic catalysts (enzymes). • Proteins are polymers called polypeptides. • Amino acids a ...
Summary - Clydebank High School
... cancels out the polarity of the bonds. For example, +O=C+=O- is a non-polar molecule as it has a ........................................ shape. 10. Bonds in which a hydrogen atom are bonded to a much more electronegative element are very strongly polar. The elements which are much more electrone ...
... cancels out the polarity of the bonds. For example, +O=C+=O- is a non-polar molecule as it has a ........................................ shape. 10. Bonds in which a hydrogen atom are bonded to a much more electronegative element are very strongly polar. The elements which are much more electrone ...
Phosphorus_Cycle
... mineral deposits, it is absorbed by plants and recycled within ecosystems. •The phosphates (inorganic phosphates, mainly orthophosphate ions; PO43-, HPO42-, H2PO4-, H3PO4) are utilized by plants in metabolism and then passed on to heterotrophic organism through food chain. The decomposition of organ ...
... mineral deposits, it is absorbed by plants and recycled within ecosystems. •The phosphates (inorganic phosphates, mainly orthophosphate ions; PO43-, HPO42-, H2PO4-, H3PO4) are utilized by plants in metabolism and then passed on to heterotrophic organism through food chain. The decomposition of organ ...
Divergence and Convergence in Enzyme Evolution
... motifs that are represented in such databases as InterPro (15). Therefore, proteins within the same superfamily can be confidently inferred to have evolved from a common ancestor, even though they might have dramatically different enzymatic activities or no (known) activity at all (16 –18). Most stu ...
... motifs that are represented in such databases as InterPro (15). Therefore, proteins within the same superfamily can be confidently inferred to have evolved from a common ancestor, even though they might have dramatically different enzymatic activities or no (known) activity at all (16 –18). Most stu ...
Source
... • During the production of cheese, rennet is commonly used as the coagulating agent. • In rennet, there is an enzyme called rennin that curdles the milk. • The sources of rennet are from young mammals stomach. • Mammals consist of cows, goats and also pigs. • Rennet is extracted from the stomach by ...
... • During the production of cheese, rennet is commonly used as the coagulating agent. • In rennet, there is an enzyme called rennin that curdles the milk. • The sources of rennet are from young mammals stomach. • Mammals consist of cows, goats and also pigs. • Rennet is extracted from the stomach by ...
1 course syllabus bio 1023 - introductory nutrition
... 4. Discuss acids, bases, and the pH scale. 5. Added vocabulary and concepts: oxidized reduced organic molecules inorganic molecules (Chapter 4 – Carbohydrates) 1. Relate the major carbohydrates: monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharide in terms of their basic chemical structures and food sou ...
... 4. Discuss acids, bases, and the pH scale. 5. Added vocabulary and concepts: oxidized reduced organic molecules inorganic molecules (Chapter 4 – Carbohydrates) 1. Relate the major carbohydrates: monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharide in terms of their basic chemical structures and food sou ...
Question Booklet Unit 1
... (iii) What would happen to the mass of the model cell during the two hour period? ...
... (iii) What would happen to the mass of the model cell during the two hour period? ...
Biology-N5-Past-Paper-Questions-Cell-Biology1
... waste product from photosynthesis / needed for chemical reactions Specific organs named other than lungs or placenta ...
... waste product from photosynthesis / needed for chemical reactions Specific organs named other than lungs or placenta ...
Supplementary Methods (a) Chemically
... for each LC-MS/MS run. This offset was then applied to adjust precursor masses in the peak lists ...
... for each LC-MS/MS run. This offset was then applied to adjust precursor masses in the peak lists ...
and Medium-Chain-Length Fatty Acids
... The initial substrate for the Leu pathway is 2-oxo-3methylbutyric acid (Fig. 1). The ␣-ketoacid (2-oxoacid) elongation (␣KAE) model requires that IPMS, IPMDH, and IPMDCase accept, in addition to the terminal isopropyl group of 2-oxo-3-methylbutyric acid, both n- and branched alkyl substituents rangi ...
... The initial substrate for the Leu pathway is 2-oxo-3methylbutyric acid (Fig. 1). The ␣-ketoacid (2-oxoacid) elongation (␣KAE) model requires that IPMS, IPMDH, and IPMDCase accept, in addition to the terminal isopropyl group of 2-oxo-3-methylbutyric acid, both n- and branched alkyl substituents rangi ...
Bio426Lecture28Apr10
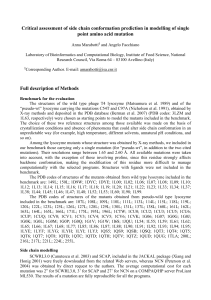
... After life effects of phenolic compounds. Plant litter decomposition, and release of nutrients from decomposing litter, are strongly influenced by the chemical composition of the litter. Litter higher in tannins and lignin decomposes more ...
... After life effects of phenolic compounds. Plant litter decomposition, and release of nutrients from decomposing litter, are strongly influenced by the chemical composition of the litter. Litter higher in tannins and lignin decomposes more ...
Your views are welcomed upon the theme of
... teachers do teach that reactions occur to allow atoms to get full shells (although I can think of few common reactions they could use to illustrate such a principle), but I would doubt many do. Certainly some school texts books can be read to imply this. However, I suspect that to some extent the ‘o ...
... teachers do teach that reactions occur to allow atoms to get full shells (although I can think of few common reactions they could use to illustrate such a principle), but I would doubt many do. Certainly some school texts books can be read to imply this. However, I suspect that to some extent the ‘o ...
Unit 3 Physical Science: Chemical Reactions
... unit because it is particularly affected by acid precipitation and other forms of air pollution owing to prevailing winds in North America. These winds carry large amounts of air pollutants from the more populated and industrialized regions of the United States and Canada. The problem is further com ...
... unit because it is particularly affected by acid precipitation and other forms of air pollution owing to prevailing winds in North America. These winds carry large amounts of air pollutants from the more populated and industrialized regions of the United States and Canada. The problem is further com ...
circular paper chromatography 95 - Journal of the Indian Institute of
... centre of a circuIrrr filter-paper. The soh!tion (about 1-·8{"1.) containing mixture of amino ,\cids to be r.nalyscd, was applied along the circumference of the circle from the tip of a capillary lllbe. Usually maximum number of eight spots could be placed" leaving some space between the adjoining s ...
... centre of a circuIrrr filter-paper. The soh!tion (about 1-·8{"1.) containing mixture of amino ,\cids to be r.nalyscd, was applied along the circumference of the circle from the tip of a capillary lllbe. Usually maximum number of eight spots could be placed" leaving some space between the adjoining s ...
Lecture Notes of Seminario Interdisciplinare di Matematica Vol. 9
... A basic approach to fold recognition is comparative modelling. Let A be the amino acid sequence of a protein with unknown tertiary structure, align the sequence A to the primary structures of all proteins in the database of tertiary protein structures. Suppose the sequence A best aligns to the prima ...
... A basic approach to fold recognition is comparative modelling. Let A be the amino acid sequence of a protein with unknown tertiary structure, align the sequence A to the primary structures of all proteins in the database of tertiary protein structures. Suppose the sequence A best aligns to the prima ...
Enzymes - دانشکده پزشکی
... Phosphorylation is the most common type of modification Two important classes of enzymes are: – Kinases Add a phosphate group to another protein/enzyme (phosphorylation) ...
... Phosphorylation is the most common type of modification Two important classes of enzymes are: – Kinases Add a phosphate group to another protein/enzyme (phosphorylation) ...
Principles of Biochemistry 4/e
... A total of 10 H+ are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane for every two electrons donated to Complex I and the electrons transferred to oxygen to make H2O. ...
... A total of 10 H+ are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane for every two electrons donated to Complex I and the electrons transferred to oxygen to make H2O. ...
Chapter 1: An Introduction to Chemistry
... Fats (solid triglycerides) and an oil (a liquid triglyceride). ...
... Fats (solid triglycerides) and an oil (a liquid triglyceride). ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.