슬라이드 1
... • The General Characteristics of Enzymes. Enzymes are highly efficient protein catalysts which are involved iii almost every biological reaction. They are often quite specific in terms of the substance acted upon and the type of reaction catalyzed. • Enzyme Nomenclature and Classification. Enzymes ...
... • The General Characteristics of Enzymes. Enzymes are highly efficient protein catalysts which are involved iii almost every biological reaction. They are often quite specific in terms of the substance acted upon and the type of reaction catalyzed. • Enzyme Nomenclature and Classification. Enzymes ...
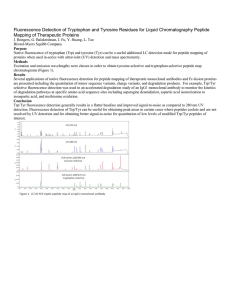
Fluorescence Detection of Tryptophan and Tyrosine Residues for
... Native fluorescence of tryptophan (Trp) and tyrosine (Tyr) can be a useful additional LC detection mode for peptide mapping of proteins when used in-series with ultraviolet (UV) detection and mass spectrometry. Methods Excitation and emission wavelengths were chosen in order to obtain tyrosine-selec ...
... Native fluorescence of tryptophan (Trp) and tyrosine (Tyr) can be a useful additional LC detection mode for peptide mapping of proteins when used in-series with ultraviolet (UV) detection and mass spectrometry. Methods Excitation and emission wavelengths were chosen in order to obtain tyrosine-selec ...
Micro Chapter 5 ppt. 11th edition
... (c) Substrate concentration. With increasing concentration of substrate molecules, the rate of reaction increases until the active sites on all the enzyme molecules are filled, at which point the maximum rate of reaction is reached. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... (c) Substrate concentration. With increasing concentration of substrate molecules, the rate of reaction increases until the active sites on all the enzyme molecules are filled, at which point the maximum rate of reaction is reached. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... that mRNA. mRNA has been observed in tRNA, rRNA, and mRNA molecules of eukaryotes but not prokaryotes. RNA editing mechanisms include nucleoside modifications such as C to U and A to I deaminations, as well as non-templated nucleotide additions and insertions. RNA editing alters the amino acid seque ...
... that mRNA. mRNA has been observed in tRNA, rRNA, and mRNA molecules of eukaryotes but not prokaryotes. RNA editing mechanisms include nucleoside modifications such as C to U and A to I deaminations, as well as non-templated nucleotide additions and insertions. RNA editing alters the amino acid seque ...
9701/04 - StudyGuide.PK
... Use this information to suggest a likely structure for the organic product of each of the following reactions. (i) NO2 bromination ...
... Use this information to suggest a likely structure for the organic product of each of the following reactions. (i) NO2 bromination ...
Document
... vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. Other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. ...
... vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. Other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. ...
Chapter 4
... Three types of RNA molecules perform different but complementary roles in protein synthesis (translation) Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries information copied from DNA in the form of a series of three base “words” termed codons Transfer RNA (tRNA) deciphers the code and delivers the specified amino ...
... Three types of RNA molecules perform different but complementary roles in protein synthesis (translation) Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries information copied from DNA in the form of a series of three base “words” termed codons Transfer RNA (tRNA) deciphers the code and delivers the specified amino ...
Intracellular metal transport proteins
... Department of Analytical and Bioinorganic Chemistry, Kyoto Pharmaceutical University ...
... Department of Analytical and Bioinorganic Chemistry, Kyoto Pharmaceutical University ...
Slide 1 - KSUMSC
... glutamate by transamination reactions with αketoglutarate Oxidative deamination of glutamate will ...
... glutamate by transamination reactions with αketoglutarate Oxidative deamination of glutamate will ...
Function of prostaglandins
... Synthesis of prostaglandins and thromboxanes from arachidonic acid. Many stimuli (e.g. epinephrine, thrombin and bradykinin) activate phospholipase A2 which hydrolyzes arachidonic acid from membrane ...
... Synthesis of prostaglandins and thromboxanes from arachidonic acid. Many stimuli (e.g. epinephrine, thrombin and bradykinin) activate phospholipase A2 which hydrolyzes arachidonic acid from membrane ...
FREE Sample Here
... use energy from their environment; (3) have the capacity to precisely self-replicate and self-assemble; (4) exploit a chemical interplay with their environment; (5) possess programmatically defined functions; and (6) evolve to new forms over many generations. 30. Cellular foundations Page: 3 Difficu ...
... use energy from their environment; (3) have the capacity to precisely self-replicate and self-assemble; (4) exploit a chemical interplay with their environment; (5) possess programmatically defined functions; and (6) evolve to new forms over many generations. 30. Cellular foundations Page: 3 Difficu ...
anabolic and catabolic reactions. Energetics of bacterial growth
... Some textbooks of microbiology still indicate that glucose oxidation involves three coupling sites, with the complete oxidation of glucose producing 38 ATP mol per mol (8), but bacteria do not usually have three phosphorylation sites (37, 39). In E. coli there are several pathways of respiration, an ...
... Some textbooks of microbiology still indicate that glucose oxidation involves three coupling sites, with the complete oxidation of glucose producing 38 ATP mol per mol (8), but bacteria do not usually have three phosphorylation sites (37, 39). In E. coli there are several pathways of respiration, an ...
Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism
... Carbohydrates are the most abundant organic molecules in nature Photosynthesis energy stored in carbohydrates; Carbohydrates are the metabolic precursors of all other biomolecules; Important component of cell structures; Important function in cell-cell recognition; Carbohydrate chemistry: ...
... Carbohydrates are the most abundant organic molecules in nature Photosynthesis energy stored in carbohydrates; Carbohydrates are the metabolic precursors of all other biomolecules; Important component of cell structures; Important function in cell-cell recognition; Carbohydrate chemistry: ...
FREE Sample Here
... use energy from their environment; (3) have the capacity to precisely self-replicate and self-assemble; (4) exploit a chemical interplay with their environment; (5) possess programmatically defined functions; and (6) evolve to new forms over many generations. 30. Cellular foundations Page: 3 Difficu ...
... use energy from their environment; (3) have the capacity to precisely self-replicate and self-assemble; (4) exploit a chemical interplay with their environment; (5) possess programmatically defined functions; and (6) evolve to new forms over many generations. 30. Cellular foundations Page: 3 Difficu ...
DIETARY FAT
... • There are no UL’s set for Total Fat, Fatty Acids and Cholesterol because there are insufficient data to use the model of risk assessment to set a UL for total fat, monounsaturated fatty acids, and n-6 and n3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ...
... • There are no UL’s set for Total Fat, Fatty Acids and Cholesterol because there are insufficient data to use the model of risk assessment to set a UL for total fat, monounsaturated fatty acids, and n-6 and n3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ...
Balancing Reaction Equations Oxidation State Reduction
... Balance each of these two reactions using the eight steps we discussed. Assume that the reactions take place in alkaline solution. ...
... Balance each of these two reactions using the eight steps we discussed. Assume that the reactions take place in alkaline solution. ...
ENERGY
... (FFA) and glycerol and used as an energy fuel within the aerobic system. FFA are broken down into Acetyl CoA, which enters and is broken down by the Krebs Cycle and the ETC in the process termed beta-oxidation. FFA produce more Acetyl CoA and consequently produce far greater energy than the breakdow ...
... (FFA) and glycerol and used as an energy fuel within the aerobic system. FFA are broken down into Acetyl CoA, which enters and is broken down by the Krebs Cycle and the ETC in the process termed beta-oxidation. FFA produce more Acetyl CoA and consequently produce far greater energy than the breakdow ...
METABOLISM - UMK C.A.R.N.I.V.O.R.E.S. 3 | C-alm, A
... Reaction that take places as many part of biochemical processes – hydrolysis of the compound adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ...
... Reaction that take places as many part of biochemical processes – hydrolysis of the compound adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ...
REVISION FOR ENERGY
... (FFA) and glycerol and used as an energy fuel within the aerobic system. FFA are broken down into Acetyl CoA, which enters and is broken down by the Krebs Cycle and the ETC in the process termed beta-oxidation. FFA produce more Acetyl CoA and consequently produce far greater energy than the breakdow ...
... (FFA) and glycerol and used as an energy fuel within the aerobic system. FFA are broken down into Acetyl CoA, which enters and is broken down by the Krebs Cycle and the ETC in the process termed beta-oxidation. FFA produce more Acetyl CoA and consequently produce far greater energy than the breakdow ...
Interaction
... methyl group and hydrogen bonding with the OH group but the residues are facing away from the heterocompound Hydrophobic interaction with the aromatic ring in the heterocompound Hydrophobic interaction with the aromatic ring in the heterocompound Hydrophobic interaction with the aromatic ring in the ...
... methyl group and hydrogen bonding with the OH group but the residues are facing away from the heterocompound Hydrophobic interaction with the aromatic ring in the heterocompound Hydrophobic interaction with the aromatic ring in the heterocompound Hydrophobic interaction with the aromatic ring in the ...
origins debate intro
... an information handout on the Replication-First Hypothesis. Team 2 will be given an information handout on the Metabolism-First Hypothesis. The teams will have 30 minutes to understand their hypothesis. Students should take notes, as they will not be allowed to keep the original handout. (2) Next, j ...
... an information handout on the Replication-First Hypothesis. Team 2 will be given an information handout on the Metabolism-First Hypothesis. The teams will have 30 minutes to understand their hypothesis. Students should take notes, as they will not be allowed to keep the original handout. (2) Next, j ...
The regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis in some
... discussed in the context of the suggestion made by Intriago and Floodgate (Journal of General Microbiology 137, 1503-1509,1991) that Ffexibucterstrains possess both the anaerobic and aerobic pathways for unsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis, the activity of the latter being modulated by the intracell ...
... discussed in the context of the suggestion made by Intriago and Floodgate (Journal of General Microbiology 137, 1503-1509,1991) that Ffexibucterstrains possess both the anaerobic and aerobic pathways for unsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis, the activity of the latter being modulated by the intracell ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.