Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
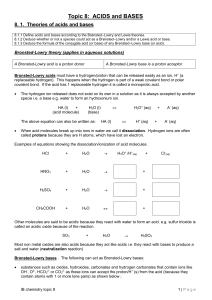
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
falciparum - Griffith Research Online
... Background: Plasmodium falciparum, the causative agent of human malaria, expresses two aminopeptidases, PfM1AAP and PfM17LAP, critical to generating a free amino acid pool used by the intraerythrocytic stage of the parasite for proteins synthesis, growth and development. These exopeptidases are pote ...
... Background: Plasmodium falciparum, the causative agent of human malaria, expresses two aminopeptidases, PfM1AAP and PfM17LAP, critical to generating a free amino acid pool used by the intraerythrocytic stage of the parasite for proteins synthesis, growth and development. These exopeptidases are pote ...
Role of Krebs Cycle in the Mechanism of Stability Internal Medium
... practical application of this method treatment on the cancer disease patient. ...
... practical application of this method treatment on the cancer disease patient. ...
Functions
... Minerals serve as structural constituents of soft tissues. Minerals are essential for the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle contraction. Minerals play a vital role in the acid-base equilibrium of the body, and thus regulate the pH of the blood and other body fluids. Minerals serve as essenti ...
... Minerals serve as structural constituents of soft tissues. Minerals are essential for the transmission of nerve impulses and muscle contraction. Minerals play a vital role in the acid-base equilibrium of the body, and thus regulate the pH of the blood and other body fluids. Minerals serve as essenti ...
Antiprotozoal drugs
... • Hepatic abscess • Symptoms often occur days or even years after infection • Patients are frequently asymptomatic, but infectious ...
... • Hepatic abscess • Symptoms often occur days or even years after infection • Patients are frequently asymptomatic, but infectious ...
Stable isotope labeled Media products
... CIL’S most flexible media, Celtone Base Powder is a mixture of amino acids, peptides, vitamins and other essential nutrients, which provide a “rich” environment for excellent bacterial cell growth and high protein expression. The advantage of Celtone powder is that researchers can formulate a custom ...
... CIL’S most flexible media, Celtone Base Powder is a mixture of amino acids, peptides, vitamins and other essential nutrients, which provide a “rich” environment for excellent bacterial cell growth and high protein expression. The advantage of Celtone powder is that researchers can formulate a custom ...
Cell Respiration
... • only about 2% of the energy available from the oxidation of glucose is captured as ATP • energy originally contained in glucose is still held in pyruvic acid ...
... • only about 2% of the energy available from the oxidation of glucose is captured as ATP • energy originally contained in glucose is still held in pyruvic acid ...
University of Groningen Metabolic adaptations in models of
... In summary, many signals have been implicated in zonation of protein expression alongside the portocentral axis. In this respect, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling and its antagonist, the Ha-RAS signaling pathway appear to have a major contribution. It is however not clear which factors induce the heterog ...
... In summary, many signals have been implicated in zonation of protein expression alongside the portocentral axis. In this respect, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling and its antagonist, the Ha-RAS signaling pathway appear to have a major contribution. It is however not clear which factors induce the heterog ...
Heme- Fe 2+ (ferrous) - LSU School of Medicine
... Majority of amino acids used for de novo protein synthesis (80%) derives from the degradation of existing proteins ...
... Majority of amino acids used for de novo protein synthesis (80%) derives from the degradation of existing proteins ...
Nutritional Aspects of Inborn Errors of Metabolism
... Inherited metabolic disorders in volve différent nutritional aspects. On the one hand, the disease itself can impair normal nutrition. During the end of the fetal growth period and the first two years of life, the human brain grows at an impressive rate. This brain growth spurt period (1) is associa ...
... Inherited metabolic disorders in volve différent nutritional aspects. On the one hand, the disease itself can impair normal nutrition. During the end of the fetal growth period and the first two years of life, the human brain grows at an impressive rate. This brain growth spurt period (1) is associa ...
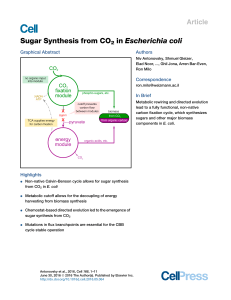
Sugar Synthesis from CO2 in Escherichia coli
... cycle, while reducing power and energy are obtained by oxidizing a supplied organic compound (e.g., pyruvate). Genome sequencing reveals that mutations in flux branchpoints, connecting the non-native CBB cycle to biosynthetic pathways, are essential for this phenotype. The successful evolution of a ...
... cycle, while reducing power and energy are obtained by oxidizing a supplied organic compound (e.g., pyruvate). Genome sequencing reveals that mutations in flux branchpoints, connecting the non-native CBB cycle to biosynthetic pathways, are essential for this phenotype. The successful evolution of a ...
bio98a_l10
... • homotropic allostery (O2 for hemoglobin) • heterotropic allostery (H+, CO2, BPG for Hb) 2. Covalent modification • group addition - often reversible, ie phosphorylation allosteric* = allo (other); steric (shape, object) ...
... • homotropic allostery (O2 for hemoglobin) • heterotropic allostery (H+, CO2, BPG for Hb) 2. Covalent modification • group addition - often reversible, ie phosphorylation allosteric* = allo (other); steric (shape, object) ...
Fluorescent Amino Acids: Modular Building Blocks for the Assembly
... With the merging of chemical synthesis and biology, the ability to exploit nature’s machinery to modify the protein biopolymer with non-natural amino acid surrogates has become viable. Several groups have incorporated FlAAs into full-length proteins to enable their detection and to interrogate biolo ...
... With the merging of chemical synthesis and biology, the ability to exploit nature’s machinery to modify the protein biopolymer with non-natural amino acid surrogates has become viable. Several groups have incorporated FlAAs into full-length proteins to enable their detection and to interrogate biolo ...
Three multidomain esterases from the cellulolytic
... characterized XynB enzyme (781 amino acids) includes an internal acetylesterase domain in addition to its N-terminal xylanase catalytic domain. A third gene, xynE, is predicted to encode a multidomain enzyme of 792 amino acids including a family 11 xylanase domain and a C-terminal esterase domain. T ...
... characterized XynB enzyme (781 amino acids) includes an internal acetylesterase domain in addition to its N-terminal xylanase catalytic domain. A third gene, xynE, is predicted to encode a multidomain enzyme of 792 amino acids including a family 11 xylanase domain and a C-terminal esterase domain. T ...
A New Type of a Multifunctional ß-Oxidation
... acetyl-CoA yielding thiolytic cleavage of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA esters formed in the dehydrogenation process. Because the fatty acid chains are reduced by only two carbon atoms in the course of these successive reactions, the reaction sequence has to be repeated until the fatty acids have been complete ...
... acetyl-CoA yielding thiolytic cleavage of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA esters formed in the dehydrogenation process. Because the fatty acid chains are reduced by only two carbon atoms in the course of these successive reactions, the reaction sequence has to be repeated until the fatty acids have been complete ...
Transcript
... together or more than two. (More rule than exception.) b. Proteins that carry out enzymatic activity or structural feature will stick together inside the cell in their normal state. (More the rule than exception.) c. Cell is not a bag of water with globular proteins floating, but little centers, pla ...
... together or more than two. (More rule than exception.) b. Proteins that carry out enzymatic activity or structural feature will stick together inside the cell in their normal state. (More the rule than exception.) c. Cell is not a bag of water with globular proteins floating, but little centers, pla ...
Translation - Advanced
... protein made of amino acids. Translation uses the products of transcription, mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA, to convert the mRNA sequence into a polypeptide according to the genetic code. The mRNA moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to interact with a ribosome, which serves as the site of translation. Tra ...
... protein made of amino acids. Translation uses the products of transcription, mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA, to convert the mRNA sequence into a polypeptide according to the genetic code. The mRNA moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to interact with a ribosome, which serves as the site of translation. Tra ...
Acids and Bases
... bulb will not glow. If an electrolyte, such as sodium chloride, is dissolved in the water, the light bulb will glow because the solution can now conduct electricity. The amount of electric current that can be carried by an electrolyte solution is proportional to the number of ions dissolved. Thus, t ...
... bulb will not glow. If an electrolyte, such as sodium chloride, is dissolved in the water, the light bulb will glow because the solution can now conduct electricity. The amount of electric current that can be carried by an electrolyte solution is proportional to the number of ions dissolved. Thus, t ...
Physics - BC Open Textbooks
... • Inputs — NADH, FADH2 • Outputs — H2O, ~ 36 ATP/ glucose total • 34% efficient at capturing energy — 66% leaving as heat • Location — inner membrane of the mitochondria ...
... • Inputs — NADH, FADH2 • Outputs — H2O, ~ 36 ATP/ glucose total • 34% efficient at capturing energy — 66% leaving as heat • Location — inner membrane of the mitochondria ...
Chapter 4 PowerPoint
... • Inputs — NADH, FADH2. • Outputs — H2O, ~ 36 ATP/ glucose total. • 34% efficient at capturing energy — 66% leaving as heat. • Location — inner membrane of the mitochondria. ...
... • Inputs — NADH, FADH2. • Outputs — H2O, ~ 36 ATP/ glucose total. • 34% efficient at capturing energy — 66% leaving as heat. • Location — inner membrane of the mitochondria. ...
Chapter 4 PowerPoint
... • Inputs — NADH, FADH2. • Outputs — H2O, ~ 36 ATP/ glucose total. • 34% efficient at capturing energy — 66% leaving as heat. • Location — inner membrane of the mitochondria. ...
... • Inputs — NADH, FADH2. • Outputs — H2O, ~ 36 ATP/ glucose total. • 34% efficient at capturing energy — 66% leaving as heat. • Location — inner membrane of the mitochondria. ...
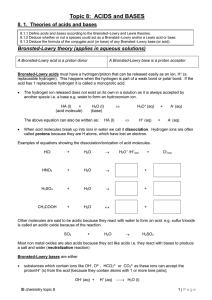
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
... positive ions like the H+ which never exists on its own and either reacts with water to form H3O+ or with a another base to form water. Other examples include CH3+ and Br+ (Hal+) which you will study in organic chemistry. molecules containing positive centres (mostly organic molecules) as a res ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.