Rapid increase of cytosolic content of acetyl-CoA
... 1993; Trumble et al., 1995). Since malonyl-CoA, produced only by ACC, inhibits the activity of CPT-I and since fatty acid oxidation is a major source of energy production in heart and muscle tissues, ACC-β w a s postulated to control fatty acid oxidation rather than biosynthesis. ACC-α and β are gen ...
... 1993; Trumble et al., 1995). Since malonyl-CoA, produced only by ACC, inhibits the activity of CPT-I and since fatty acid oxidation is a major source of energy production in heart and muscle tissues, ACC-β w a s postulated to control fatty acid oxidation rather than biosynthesis. ACC-α and β are gen ...
Chapter 6 Current Views of the Fat Cell as an Endocrine Cell
... kinase B45 or induction or inhibition of certain protein kinase C isoforms by FAs [46–48], and ceramide accumulation (in palmitate- but not oleate-induced lipotoxicity [1, 27, 41, 49, 50] can be involved in cytotoxic effects of FAs. Exogenous FAs can cause apoptosis within hours in cultured cells [5 ...
... kinase B45 or induction or inhibition of certain protein kinase C isoforms by FAs [46–48], and ceramide accumulation (in palmitate- but not oleate-induced lipotoxicity [1, 27, 41, 49, 50] can be involved in cytotoxic effects of FAs. Exogenous FAs can cause apoptosis within hours in cultured cells [5 ...
Additional File 1
... Supplemental Figure S1. Each KEGG pathway set has an intrinsic predictability, as measured by AUC. (A) For each KEGG set, the average and standard deviation of AUCs obtained using 100 random seed sets of fixed size centrality. (B) AUC distributions obtained for example pathways. ...
... Supplemental Figure S1. Each KEGG pathway set has an intrinsic predictability, as measured by AUC. (A) For each KEGG set, the average and standard deviation of AUCs obtained using 100 random seed sets of fixed size centrality. (B) AUC distributions obtained for example pathways. ...
Diabetes mellitus
... 3) repeated measurement of glycemia on glucometr in 30 a 90 min time intervals 4) determination of glukosuria in urine sample ...
... 3) repeated measurement of glycemia on glucometr in 30 a 90 min time intervals 4) determination of glukosuria in urine sample ...
The Role of the Carnitine System in Human Metabolism
... In the fasting state, the body becomes catabolic and reverses the metabolism. Glycogen is converted to glucose, free fatty acids are oxidized in all tissues except the brain and the liver produces ketones(5), not CO2 and water. Protein releases alanine and glutamine for gluconeogenesis in the liver ...
... In the fasting state, the body becomes catabolic and reverses the metabolism. Glycogen is converted to glucose, free fatty acids are oxidized in all tissues except the brain and the liver produces ketones(5), not CO2 and water. Protein releases alanine and glutamine for gluconeogenesis in the liver ...
Designer small molecules to target calcium signalling Joanna M
... Stephen J. Mills and Barry V.L. Potter University of Bath, Bath, UK ...
... Stephen J. Mills and Barry V.L. Potter University of Bath, Bath, UK ...
Lipids- Structure and Metabolism
... A.S.Warsyin intestinal mucosa and absorbed they can be absorbed intact and hydrolysed ...
... A.S.Warsyin intestinal mucosa and absorbed they can be absorbed intact and hydrolysed ...
投影片 1
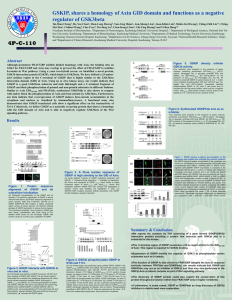
... interaction domain (GID) of Axin. Using an in vitro kinase assay, our results indicate that GSKIP is a good GSK3beta substrate and both full-length and a C-terminal fragment of GSKIP can block phosphorylation of primed and non-primed substrates in different fashions. Similar to Axin GID381-405 and F ...
... interaction domain (GID) of Axin. Using an in vitro kinase assay, our results indicate that GSKIP is a good GSK3beta substrate and both full-length and a C-terminal fragment of GSKIP can block phosphorylation of primed and non-primed substrates in different fashions. Similar to Axin GID381-405 and F ...
Presentation @ 1:30 - Bioinformatics at School of Informatics
... Proteins are molecules of life, made up of chain of amino acids. There are 20 known amino acids and each are represented by a letter Proteome is sum of all proteins in an organism, tissue or sample under study ...
... Proteins are molecules of life, made up of chain of amino acids. There are 20 known amino acids and each are represented by a letter Proteome is sum of all proteins in an organism, tissue or sample under study ...
Zygorrhynchus moelleri
... in an earlier investigation (Moses, 1957). The latter were grown for 13 hr. only instead of the customary 18 hr., and were subsequently resuspended in a modified growth medium containing glucose and acetate as carbon source, and shaken in an atmosphere of pure 0 , (Moses, 1957). Cells of sample I we ...
... in an earlier investigation (Moses, 1957). The latter were grown for 13 hr. only instead of the customary 18 hr., and were subsequently resuspended in a modified growth medium containing glucose and acetate as carbon source, and shaken in an atmosphere of pure 0 , (Moses, 1957). Cells of sample I we ...
ppt - 3.LF UK 2015
... Isoenzymes (isozymes) are enzymes which catalyze the same reaction but differ in their primary structure and phyzico chemical properties Isoenzymes are • produced by different genes (= true isozymes) ...
... Isoenzymes (isozymes) are enzymes which catalyze the same reaction but differ in their primary structure and phyzico chemical properties Isoenzymes are • produced by different genes (= true isozymes) ...
1 Determinants of protein-protein interfaces
... Note that the polar residues (Asn, Asp, Ser, Cys and Thr) with a minimal distance from their polar groups to the backbone are likely to be engaged in dehydrons, according to Table 1. It is presumed [10] that this arises not only because they have minimal nonpolar carbonaceous groups, but also becau ...
... Note that the polar residues (Asn, Asp, Ser, Cys and Thr) with a minimal distance from their polar groups to the backbone are likely to be engaged in dehydrons, according to Table 1. It is presumed [10] that this arises not only because they have minimal nonpolar carbonaceous groups, but also becau ...
basic principles of isoelectric focusing in biomedical engineering
... point, it has no net charge and cannot be moved in a gel matrix by the electric field. It may, however, move from that position by diffusion. The pH gradient forces a protein to remain in its isoelectric point position, thus concentrating it; this concentrating effect is called "focusing". Increasin ...
... point, it has no net charge and cannot be moved in a gel matrix by the electric field. It may, however, move from that position by diffusion. The pH gradient forces a protein to remain in its isoelectric point position, thus concentrating it; this concentrating effect is called "focusing". Increasin ...
Close relationship between non-viral retroposons in Drosophila
... Recently, it has been suggested that long oligo-A terminated sequences, such as mammalian LI and Drosophila F elements, might originate from the self-mediated cDNA conversion of transcripts that encode reverse transcriptase-like polypeptides (10,11,12,13,16). The 210 amino acid long G3A orf E (fig. ...
... Recently, it has been suggested that long oligo-A terminated sequences, such as mammalian LI and Drosophila F elements, might originate from the self-mediated cDNA conversion of transcripts that encode reverse transcriptase-like polypeptides (10,11,12,13,16). The 210 amino acid long G3A orf E (fig. ...
Genomic organization of infectious salmon anaemia virus
... open reading frame encoding the P1, PB1, NP, P2, P3 and HA proteins, respectively. Segment 7 encoded the P4/P5 proteins and segment 8 encoded the P6/P7 proteins. Seven virion proteins with molecular masses between 25 and 72 kDa were found by SDS–PAGE analysis. The 72 and 42 kDa proteins were immunor ...
... open reading frame encoding the P1, PB1, NP, P2, P3 and HA proteins, respectively. Segment 7 encoded the P4/P5 proteins and segment 8 encoded the P6/P7 proteins. Seven virion proteins with molecular masses between 25 and 72 kDa were found by SDS–PAGE analysis. The 72 and 42 kDa proteins were immunor ...
Quinolizidine Alkaloids
... *It’s not water soluble, it’s a tetracyclic molecule, it’s a dymeric Quinolizidine alkaloids because it has two Quinolizidine nucleus formed by the incorporation of a third Lysine molecule with definitely two N, and this compound can be modified by oxidation and eliminating of terminal link and con ...
... *It’s not water soluble, it’s a tetracyclic molecule, it’s a dymeric Quinolizidine alkaloids because it has two Quinolizidine nucleus formed by the incorporation of a third Lysine molecule with definitely two N, and this compound can be modified by oxidation and eliminating of terminal link and con ...
Chapter
... • Group specificity - the enzyme will act only on molecules that have specific functional groups, such as amino, phosphate and methyl groups. • Linkage specificity - the enzyme will act on a particular type of chemical bond regardless of the rest of the molecular structure. • Stereochemical specific ...
... • Group specificity - the enzyme will act only on molecules that have specific functional groups, such as amino, phosphate and methyl groups. • Linkage specificity - the enzyme will act on a particular type of chemical bond regardless of the rest of the molecular structure. • Stereochemical specific ...
Protein contact prediction from amino acid co
... performance of the method originates from the method’s strengths and is not a result of overfitting. The training has been conducted on a subset of 231 proteins from CASP9 and CASP10, while the test set consisted of 89 proteins from CASP11 (all non-cancelled targets). Several proteins have been excl ...
... performance of the method originates from the method’s strengths and is not a result of overfitting. The training has been conducted on a subset of 231 proteins from CASP9 and CASP10, while the test set consisted of 89 proteins from CASP11 (all non-cancelled targets). Several proteins have been excl ...
metabolism - Garland Science
... nitrogen only from organic compounds and thus are completely dependent on plants for their nutrition. Plants obtain the major elements that make up the plant body—carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen—mainly as carbon dioxide, water, and nitrate. They also take up and use many other minerals and el ...
... nitrogen only from organic compounds and thus are completely dependent on plants for their nutrition. Plants obtain the major elements that make up the plant body—carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen—mainly as carbon dioxide, water, and nitrate. They also take up and use many other minerals and el ...
Why nature chose phosphate to modify proteins
... triphosphates was the key to the formation of polynucleotides, and the encoding of genetic information. The selection of ATP as the major energy storage compound also meant the ready availability of activated phosphate groups for transfer to other molecules. Because of its energy storage function, A ...
... triphosphates was the key to the formation of polynucleotides, and the encoding of genetic information. The selection of ATP as the major energy storage compound also meant the ready availability of activated phosphate groups for transfer to other molecules. Because of its energy storage function, A ...
Proteins and enzymes - Delivery guide
... reading about the ‘clotting cascade’ will challenge them to think in more depth. It is common for students to misunderstand the concept of the product from one reaction being the enzyme needed for the next. ...
... reading about the ‘clotting cascade’ will challenge them to think in more depth. It is common for students to misunderstand the concept of the product from one reaction being the enzyme needed for the next. ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.