Chemical Equilibrium - Chemistry with Mrs. Caruso Let the Bonding
... The shift in equilibrium position that occurs because of the addition of an __ion_ already involved in the equilibrium reaction. Its addition will result in a shift away from the side where it was added. Ex. BaSO4 (s) ⇌ Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq). If add Na2SO4, what ion will be added? As a result, equili ...
... The shift in equilibrium position that occurs because of the addition of an __ion_ already involved in the equilibrium reaction. Its addition will result in a shift away from the side where it was added. Ex. BaSO4 (s) ⇌ Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq). If add Na2SO4, what ion will be added? As a result, equili ...
Experiment 16: Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant
... Click on the Configure Spectrometer button in the toolbar: In the dialog box that appears, click in the circle next to Absorbance vs. Concentration. On the left-hand side of the box, type in Concentration under Column Name:, Conc under Short Name: and mol/L under Units:. Scroll through the listing i ...
... Click on the Configure Spectrometer button in the toolbar: In the dialog box that appears, click in the circle next to Absorbance vs. Concentration. On the left-hand side of the box, type in Concentration under Column Name:, Conc under Short Name: and mol/L under Units:. Scroll through the listing i ...
Equilibria PPT
... OCR’s resources are provided to support the teaching of OCR specifications, but in no way constitute an endorsed teaching method that is required by the Board, and the decision to use them lies with the individual teacher. Whilst every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the content, OCR cannot ...
... OCR’s resources are provided to support the teaching of OCR specifications, but in no way constitute an endorsed teaching method that is required by the Board, and the decision to use them lies with the individual teacher. Whilst every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the content, OCR cannot ...
Equilibrium - Clayton State University
... - Amount of products formed or reactants consumed cannot be predicted from stoichiometry alone - These reactions achieve a condition of equilibrium ...
... - Amount of products formed or reactants consumed cannot be predicted from stoichiometry alone - These reactions achieve a condition of equilibrium ...
Chapter 6 - Department of Chemical Engineering
... Vapor/liquid equilibrium (VLE) designates a static condition where no change occurs in the macroscopic properties of a system with time. If enough time passes for an isolated system, where liquid and vapor phases are in contact, eventually the mixture will reach an equilibrium state. At microscopic ...
... Vapor/liquid equilibrium (VLE) designates a static condition where no change occurs in the macroscopic properties of a system with time. If enough time passes for an isolated system, where liquid and vapor phases are in contact, eventually the mixture will reach an equilibrium state. At microscopic ...
K c
... experimental conditions may disturb the balance and shift the equilibrium position so that more or less of the desired product is formed. • In this section we will study 5 factor which can effect chemical equilibrium namely : concentration, pressure, volume, temperature, and catalyst. • Le Châtelier ...
... experimental conditions may disturb the balance and shift the equilibrium position so that more or less of the desired product is formed. • In this section we will study 5 factor which can effect chemical equilibrium namely : concentration, pressure, volume, temperature, and catalyst. • Le Châtelier ...
Lab announcements – 2 lab quiz week before spring break
... Most chemical reactions do not go to completion. chemical equilibrium – two opposing reactions occur simultaneously at the same rate ‘equilibrium’ doesn’t necessarily mean ‘equal’ amounts of reactants and products – in fact, it usually doesn’t. Equilibrium constant – measure of this balance aA + Kc ...
... Most chemical reactions do not go to completion. chemical equilibrium – two opposing reactions occur simultaneously at the same rate ‘equilibrium’ doesn’t necessarily mean ‘equal’ amounts of reactants and products – in fact, it usually doesn’t. Equilibrium constant – measure of this balance aA + Kc ...
dx cx dx and x - Cameron University
... 1.1 Define and apply the terms system, surroundings, universe, permeable, impermeable, reversible, irreversible, equilibrium, adiabatic, nonadiabatic, extensive properties, intensive properties, open, and closed systems 2.1 Define temperature 2.2 State the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics 3.1 Work with ...
... 1.1 Define and apply the terms system, surroundings, universe, permeable, impermeable, reversible, irreversible, equilibrium, adiabatic, nonadiabatic, extensive properties, intensive properties, open, and closed systems 2.1 Define temperature 2.2 State the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics 3.1 Work with ...
[A], [B], [C], [D] - Wits Structural Chemistry
... The systematic treatment of equilibrium gives us the tool to deal with all types of complicated chemical equilibria. The systematic procedure is to write as many ...
... The systematic treatment of equilibrium gives us the tool to deal with all types of complicated chemical equilibria. The systematic procedure is to write as many ...
Review Unit 8 Test (Chp 15,17)
... A is half true, but “decreases”, decreases to become a constant nonzero rate at equilibrium. not “increases.” decreases to become zero at equilibrium. Greater pressure of reactant initially (Q = 0/1.00 = 0) so forward rate is faster due to greater collision frequency of reactant particles. The forwa ...
... A is half true, but “decreases”, decreases to become a constant nonzero rate at equilibrium. not “increases.” decreases to become zero at equilibrium. Greater pressure of reactant initially (Q = 0/1.00 = 0) so forward rate is faster due to greater collision frequency of reactant particles. The forwa ...
Worksheet Key
... g) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) 2 HCl (g): volume is doubled. No change; changing volume or pressure will not affect this system; same # moles on both sides. h) Using the same system as above, some neon is added to the system. No change; neon is an inert gas; it won’t react with or affect the system. ...
... g) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) 2 HCl (g): volume is doubled. No change; changing volume or pressure will not affect this system; same # moles on both sides. h) Using the same system as above, some neon is added to the system. No change; neon is an inert gas; it won’t react with or affect the system. ...
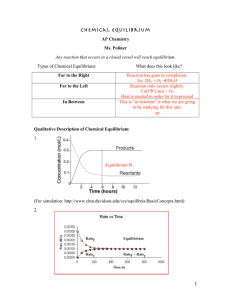
What is equilibrium?
... Nonreversible chemical reactions: the reaction proceeds until all of the reactants are used up and the products are formed A+B C+D • Nonreversible reactions often produce – a gas that escapes – Insoluble solid product (precipitate) ...
... Nonreversible chemical reactions: the reaction proceeds until all of the reactants are used up and the products are formed A+B C+D • Nonreversible reactions often produce – a gas that escapes – Insoluble solid product (precipitate) ...
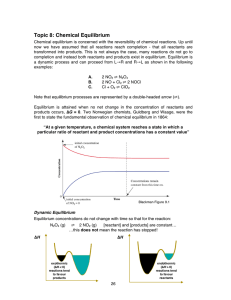
Topic 8: Chemical Equilibrium
... The pressure of a system can be changed in three ways: • Add or remove a gaseous reactant or product (same as changing concentration) • Add an inert gas (one not involved in the reaction) This changes total pressure but not partial pressure – this means that if an inert gas is added at constant volu ...
... The pressure of a system can be changed in three ways: • Add or remove a gaseous reactant or product (same as changing concentration) • Add an inert gas (one not involved in the reaction) This changes total pressure but not partial pressure – this means that if an inert gas is added at constant volu ...
Notes - Text
... It is used for the preparation of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. • The process is carried out at high temperature (500°C) and pressure (200 atm) in the presence of a catalyst. • Ammonia is a good source of fixed nitrogen for plants. • Much of the NH3 produced industrially is used as a fertilize ...
... It is used for the preparation of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. • The process is carried out at high temperature (500°C) and pressure (200 atm) in the presence of a catalyst. • Ammonia is a good source of fixed nitrogen for plants. • Much of the NH3 produced industrially is used as a fertilize ...
111 Exam III OUTLINE TRO 1-3-11
... 1. The forward reaction (⇀ ) and reverse (↽ ) reactions are occurring simultaneously. 2. The rate for the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction and a dynamic equilibrium is achieved. 3. The ratio of the concentrations of the products to reactants is constant. B. THE EQUILIBRI ...
... 1. The forward reaction (⇀ ) and reverse (↽ ) reactions are occurring simultaneously. 2. The rate for the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction and a dynamic equilibrium is achieved. 3. The ratio of the concentrations of the products to reactants is constant. B. THE EQUILIBRI ...






![[A], [B], [C], [D] - Wits Structural Chemistry](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000095863_1-918f0427052f54159a7c908528a2e159-300x300.png)