Balanced Equations And Equilibrium Constants
... Given overall reaction (need to REVERSE first reaction, see Rule 2 for how this changes the equilibrium constant): N2O(g) + (1/2)O2(g) <---> 2NO(g) K = (1/K1)*(K2) = 8.5*10-13 2) When we reverse an equation we invert the value of K. Kreverse reaction = 1/(Kforward reaction) 3) When we multiply coeff ...
... Given overall reaction (need to REVERSE first reaction, see Rule 2 for how this changes the equilibrium constant): N2O(g) + (1/2)O2(g) <---> 2NO(g) K = (1/K1)*(K2) = 8.5*10-13 2) When we reverse an equation we invert the value of K. Kreverse reaction = 1/(Kforward reaction) 3) When we multiply coeff ...
Flame Temperature and Chemical Equilibrium
... Flame Temperature at Complete Conversion • First law of thermodynamics for an adiabaEc system at constant pressure (δq = 0, dp = 0) ...
... Flame Temperature at Complete Conversion • First law of thermodynamics for an adiabaEc system at constant pressure (δq = 0, dp = 0) ...
Equilibrium Review True/False Indicate whether the statement is
... 3. (1 point) Explain why equilibrium will be unaffected if the pressure of the system below is tripled under constant temperature. H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI(g) 4. (1 point) Use the following information to answer the next question. Consider the following equilibrium reaction: 3O2(g) + 64 kcal 2O3(g) How ...
... 3. (1 point) Explain why equilibrium will be unaffected if the pressure of the system below is tripled under constant temperature. H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI(g) 4. (1 point) Use the following information to answer the next question. Consider the following equilibrium reaction: 3O2(g) + 64 kcal 2O3(g) How ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... • The equilibrium constant (K) is the ratio of the mathematical product of the concentrations of substances formed at equilibrium to the mathematical product of the concentrations of reacting substances. Each concentration is raised to a power equal to the coefficient of that substance in the chemic ...
... • The equilibrium constant (K) is the ratio of the mathematical product of the concentrations of substances formed at equilibrium to the mathematical product of the concentrations of reacting substances. Each concentration is raised to a power equal to the coefficient of that substance in the chemic ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... 5. What three things must be taken into account when determining if a reaction has enough energy to overcome the activation energy (Ea)? 6. What does a catalyst do to a reaction? Explain. Something that is added to a reaction to speed up the reaction – it lowers the activation energy (energy necessa ...
... 5. What three things must be taken into account when determining if a reaction has enough energy to overcome the activation energy (Ea)? 6. What does a catalyst do to a reaction? Explain. Something that is added to a reaction to speed up the reaction – it lowers the activation energy (energy necessa ...
Physical Chemistry
... University Rule: Come to class minimum 80% during one semester meeting or you will miss FINAL EXAM ...
... University Rule: Come to class minimum 80% during one semester meeting or you will miss FINAL EXAM ...
System stability
... The increasing monotony of the function S(U)|V implies the positiveness of 1/T=S/U|V. Furthermore, energy itself has to be also a monotonic increasing function of temperature at constant volume, U/T|V>0 because otherwise the system would be thermally unstable (energy would flow from colder to ho ...
... The increasing monotony of the function S(U)|V implies the positiveness of 1/T=S/U|V. Furthermore, energy itself has to be also a monotonic increasing function of temperature at constant volume, U/T|V>0 because otherwise the system would be thermally unstable (energy would flow from colder to ho ...
Le Chatelier`s Principle in Iron Thiocyanate Equilibrium
... Introduction Chemical equilibrium exists when two opposing reactions occur simultaneously at the same rate. Changes in experimental conditions such as concentration, pressure, volume, and temperature disturb the balance and shift the equilibrium position so that more or less of the desired product i ...
... Introduction Chemical equilibrium exists when two opposing reactions occur simultaneously at the same rate. Changes in experimental conditions such as concentration, pressure, volume, and temperature disturb the balance and shift the equilibrium position so that more or less of the desired product i ...
Equilibrium
... catastrophism had been succeeded by the understanding that gradual land-forming processes were responsible for the shape of the Earth’s surface, and the idea of a ‘balance of nature’ prevailed. This was expressed first through the graded profile of rivers for time-bound studies, and subsequently by ...
... catastrophism had been succeeded by the understanding that gradual land-forming processes were responsible for the shape of the Earth’s surface, and the idea of a ‘balance of nature’ prevailed. This was expressed first through the graded profile of rivers for time-bound studies, and subsequently by ...
Chapter 1 Introduction and Definition of Terms
... If body A and B are each in thermal equilibrium with a third body C, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. TA = TC and TB = TC => TA = TB The aim of classical thermodynamics is to establish the relationships which exist between equilibrium state of a given system and the influences w ...
... If body A and B are each in thermal equilibrium with a third body C, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. TA = TC and TB = TC => TA = TB The aim of classical thermodynamics is to establish the relationships which exist between equilibrium state of a given system and the influences w ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 1 Introduction
... Isolated Systems – matter and energy may not cross the boundary. Adiabatic Systems – heat must not cross the boundary. Diathermic Systems - heat may cross boundary. ...
... Isolated Systems – matter and energy may not cross the boundary. Adiabatic Systems – heat must not cross the boundary. Diathermic Systems - heat may cross boundary. ...
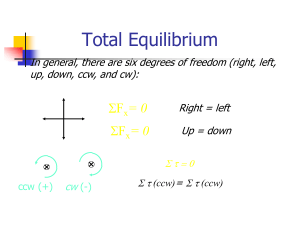
5. STATIC EQUILIBRIUM. Key words: Static Equilibrium, First
... with respect to any axis of rotation. Therefore, solving problems, we can choose any axis of rotation that makes our calculation easier. For example, we can choose as axis of rotation point at which unknown force is applied. In this case, the torque of this force will be zero. The number of unknown ...
... with respect to any axis of rotation. Therefore, solving problems, we can choose any axis of rotation that makes our calculation easier. For example, we can choose as axis of rotation point at which unknown force is applied. In this case, the torque of this force will be zero. The number of unknown ...
KUKUM*s - Portal UniMAP
... Pusat Pengajian Kejuruteraan Bioproses COURSE OUTLINE (1) Kod kursus/ Course code: ...
... Pusat Pengajian Kejuruteraan Bioproses COURSE OUTLINE (1) Kod kursus/ Course code: ...
Exam Review Chapter 18-Equilibrium
... 10. Which of the following is true concerning the impact of increasing temperature on reaction rates? a. The number of collisions between reactant atoms is increased. b. The energy of each reactant atom is increased. c. The percentage of collisions with sufficient energy to cross the activation ener ...
... 10. Which of the following is true concerning the impact of increasing temperature on reaction rates? a. The number of collisions between reactant atoms is increased. b. The energy of each reactant atom is increased. c. The percentage of collisions with sufficient energy to cross the activation ener ...
Advanced Placement Chemistry Test
... same as the number of moles of SO2 present, regardless of the temperature. Changing the volume of the vessel changes the amount of oxygen in the system. Changing the temperature changes the amount of oxygen in the system. Injecting helium gas into the vessel, but keeping the volume of the vessel unc ...
... same as the number of moles of SO2 present, regardless of the temperature. Changing the volume of the vessel changes the amount of oxygen in the system. Changing the temperature changes the amount of oxygen in the system. Injecting helium gas into the vessel, but keeping the volume of the vessel unc ...
Chem 480A
... (There is an interesting problem in going from Equation 5a to Equation 5b which is not usually discussed. In Equation 5a the coefficients of the balanced chemical equation, a, b, etc. have units of moles, so that, for example, cC is moles times Joules per mole which leaves just units of Joules. How ...
... (There is an interesting problem in going from Equation 5a to Equation 5b which is not usually discussed. In Equation 5a the coefficients of the balanced chemical equation, a, b, etc. have units of moles, so that, for example, cC is moles times Joules per mole which leaves just units of Joules. How ...
solving equilibrium problems with the ti-92
... the correct answer. Remember the computer maxim, Garbage in, garbage out! The key to correctly solving equilibrium problems is in setting up the ICE table, or reaction stoichiometry matrix. This will be covered in detail by your instructor, and the textbook; here, we are only interested in solving t ...
... the correct answer. Remember the computer maxim, Garbage in, garbage out! The key to correctly solving equilibrium problems is in setting up the ICE table, or reaction stoichiometry matrix. This will be covered in detail by your instructor, and the textbook; here, we are only interested in solving t ...