Physics 130 - University of North Dakota
... Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Real objects are “elastic” (to some extent) Elastic: Object returns to original shape after deformation Original shape called “Equilibrium” Object resists deformation with force Force called “Restoring Force” Force proportional to deformation Force is in opposit ...
... Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Real objects are “elastic” (to some extent) Elastic: Object returns to original shape after deformation Original shape called “Equilibrium” Object resists deformation with force Force called “Restoring Force” Force proportional to deformation Force is in opposit ...
Chapter 19, part II Notes
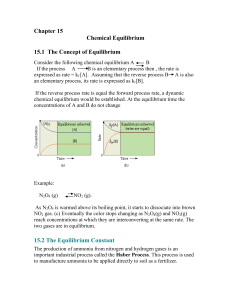
... Equilibrium Reactions LeChatelier’s Principle Equilibrium Constants ...
... Equilibrium Reactions LeChatelier’s Principle Equilibrium Constants ...
The Equilibrium Constant
... use stoichiometry to find the change in the other parts. 2) If not given, let x be the change in concentration of the reactant with the smallest coefficient (to avoid fractions) 3) You will usually need to do one of these steps in order to solve: ...
... use stoichiometry to find the change in the other parts. 2) If not given, let x be the change in concentration of the reactant with the smallest coefficient (to avoid fractions) 3) You will usually need to do one of these steps in order to solve: ...
DOC
... had come to equilibrium, the concentration of PCl3 was found to be 0.12 mole/L. Determine the Kc value. (b) Given K and one or more initial concentrations, determine the equilibrium concentrations General Method: Set up a "concentration table" based on an unknown "x" -- usually one of the equilibriu ...
... had come to equilibrium, the concentration of PCl3 was found to be 0.12 mole/L. Determine the Kc value. (b) Given K and one or more initial concentrations, determine the equilibrium concentrations General Method: Set up a "concentration table" based on an unknown "x" -- usually one of the equilibriu ...
RTF
... 2. For systems involving gases, the equilibrium constant is often determined by using partial pressure instead of concentration. Given the following reaction at equilibrium at the partial pressures of the ...
... 2. For systems involving gases, the equilibrium constant is often determined by using partial pressure instead of concentration. Given the following reaction at equilibrium at the partial pressures of the ...
Chemistry 341
... familiarity with differential and integral calculus. The first part of the course focuses on the basic concepts, principles, and laws of classical thermodynamics, with emphasis on formulations and operational definitions most relevant to chemical systems and chemical processes. These concepts, princ ...
... familiarity with differential and integral calculus. The first part of the course focuses on the basic concepts, principles, and laws of classical thermodynamics, with emphasis on formulations and operational definitions most relevant to chemical systems and chemical processes. These concepts, princ ...
Document
... 8. Use Table I data to determine the stability of the compounds listed. (The more exothermic the reaction is, the lower in energy the products are. Low energy corresponds to high stability.) 9. State the two fundamental thermodynamic drives in nature. (Memorize: “Nature is lazy and disorganized.) 10 ...
... 8. Use Table I data to determine the stability of the compounds listed. (The more exothermic the reaction is, the lower in energy the products are. Low energy corresponds to high stability.) 9. State the two fundamental thermodynamic drives in nature. (Memorize: “Nature is lazy and disorganized.) 10 ...
Kc and Kp Conversions Hess`s Law in Equilibrium Constants
... The equilibrium constant of a reaction that has been multiplied by a number is the equilibrium constant raised to a power that is equal to that number. ...
... The equilibrium constant of a reaction that has been multiplied by a number is the equilibrium constant raised to a power that is equal to that number. ...
Topics 7 and 17 Outlines
... • The reaction quotient (Q) measures the relative amount of products and reactants present during a reaction at a particular point in time. Q is the equilibrium expression with non-equilibrium concentrations. The position of the equilibrium changes with changes in concentration, pressure, and temper ...
... • The reaction quotient (Q) measures the relative amount of products and reactants present during a reaction at a particular point in time. Q is the equilibrium expression with non-equilibrium concentrations. The position of the equilibrium changes with changes in concentration, pressure, and temper ...
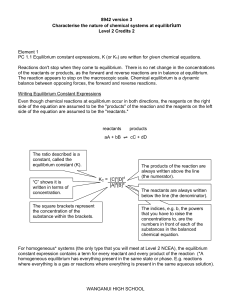
Wanganui High School
... asked to write K expressions use K, if KC then write KC! o Do I need the state symbols? Not for this Unit Standard but if you are putting them in, put them ALL in, and put them in the right place, inside the ] bracket eg [H2(g)]3 9 [H2)](g)3 8, [FeSCN]2+(aq) PC 1.2 Changes in equilibrium position ar ...
... asked to write K expressions use K, if KC then write KC! o Do I need the state symbols? Not for this Unit Standard but if you are putting them in, put them ALL in, and put them in the right place, inside the ] bracket eg [H2(g)]3 9 [H2)](g)3 8, [FeSCN]2+(aq) PC 1.2 Changes in equilibrium position ar ...
ChE 215, Physical Chemistry
... The objective of this course is to introduce the basic topics in Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics. In fact this course present collection of distinct topics particularly useful to chemical engineering students. The basic principles in the course are demonstrated by six experiments ...
... The objective of this course is to introduce the basic topics in Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics. In fact this course present collection of distinct topics particularly useful to chemical engineering students. The basic principles in the course are demonstrated by six experiments ...
Equilibrium Review worksheet
... substances involved in this equilibrium. The vessel is heated to 650 °C. Determine the equilibrium amount concentrations of each substance, organizing your values in an ICE table. (Hint: use the value of Kc to determine which side of the reaction is favored, and therefore which substances will incre ...
... substances involved in this equilibrium. The vessel is heated to 650 °C. Determine the equilibrium amount concentrations of each substance, organizing your values in an ICE table. (Hint: use the value of Kc to determine which side of the reaction is favored, and therefore which substances will incre ...