
chem 102 class notes - Louisiana Tech University
... long period of time, the contents of the reaction vessel do not become colorless. Instead, the intensity of the brown color eventually becomes constant, which means that the concentration of NO2 is no longer changing. Making the container colder makes equilibrium to shift to left and warming shift ...
... long period of time, the contents of the reaction vessel do not become colorless. Instead, the intensity of the brown color eventually becomes constant, which means that the concentration of NO2 is no longer changing. Making the container colder makes equilibrium to shift to left and warming shift ...
text page 117 2.4 Entropy Change versus
... information for you to reliably determine whether entropy increases or decreases during the reaction but: Entropy usually decreases when gas particles combine into fewer particles. ...
... information for you to reliably determine whether entropy increases or decreases during the reaction but: Entropy usually decreases when gas particles combine into fewer particles. ...
Chemical Equilibrium - 2012 Book Archive
... Consider the following reaction occurring in a closed container (so that no material can go in or out): H2 + I2 → 2HI This is simply the reaction between elemental hydrogen and elemental iodine to make hydrogen iodide. The way the equation is written, we are led to believe that the reaction goes to ...
... Consider the following reaction occurring in a closed container (so that no material can go in or out): H2 + I2 → 2HI This is simply the reaction between elemental hydrogen and elemental iodine to make hydrogen iodide. The way the equation is written, we are led to believe that the reaction goes to ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... Write ksp expression for each of the following: AgI(s) Ag1+ (aq) + I1- (aq) Ag2S(s) 2Ag1+ (aq) + S2- (aq) PbI2(s) Pb2+ (aq) + 2I1- (aq) MgCO3(s) Mg2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) Ca3(PO4)2(s) 3Ca2+(aq) + 2PO43- (aq) ...
... Write ksp expression for each of the following: AgI(s) Ag1+ (aq) + I1- (aq) Ag2S(s) 2Ag1+ (aq) + S2- (aq) PbI2(s) Pb2+ (aq) + 2I1- (aq) MgCO3(s) Mg2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) Ca3(PO4)2(s) 3Ca2+(aq) + 2PO43- (aq) ...
Document
... the species in a reaction and asked to determine in which direction the reaction must proceed to achieve equilibrium. Plan We can determine the starting concentration of each species in the reaction mixture. We can then substitute the starting concentrations into the equilibrium-constant expression ...
... the species in a reaction and asked to determine in which direction the reaction must proceed to achieve equilibrium. Plan We can determine the starting concentration of each species in the reaction mixture. We can then substitute the starting concentrations into the equilibrium-constant expression ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... the reverse reaction continue to occur. They both occur at the same rate, so any overall change by one reaction is cancelled by the reverse reaction. We say that chemical equilibrium is dynamic, rather than static. Also, because both reactions are occurring simultaneously, the equilibrium can be wri ...
... the reverse reaction continue to occur. They both occur at the same rate, so any overall change by one reaction is cancelled by the reverse reaction. We say that chemical equilibrium is dynamic, rather than static. Also, because both reactions are occurring simultaneously, the equilibrium can be wri ...
Unit 3: 1 Equilibrium and the Constant, K
... Learning objective 6.1 The student is able to, given a set of experimental observations regarding physical, chemical, biological, or environmental processes that are reversible, construct an explanation that connects the observations to the reversibility of the underlying chemical reactions or proc ...
... Learning objective 6.1 The student is able to, given a set of experimental observations regarding physical, chemical, biological, or environmental processes that are reversible, construct an explanation that connects the observations to the reversibility of the underlying chemical reactions or proc ...
Equilibrium
... It may be tempting to think that once equilibrium has been reached, the reaction stops. However, chemical equilibrium is a dynamic process. The forward and reverse reactions continue to occur even after equilibrium has been reached, but, because the rates of the two reactions are equal, there is no ...
... It may be tempting to think that once equilibrium has been reached, the reaction stops. However, chemical equilibrium is a dynamic process. The forward and reverse reactions continue to occur even after equilibrium has been reached, but, because the rates of the two reactions are equal, there is no ...
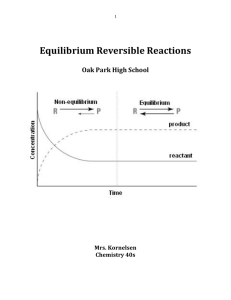
Equilibrium Reversible Reactions
... For example, in a class of 20 students, 10 students could represent sodium ions and 10 students could represent chloride ions. Have 4 sodium ions and 4 chloride ions link arms on the left side of the room to represent sodium chloride particles. Have the remaining 12 students stand on the right side ...
... For example, in a class of 20 students, 10 students could represent sodium ions and 10 students could represent chloride ions. Have 4 sodium ions and 4 chloride ions link arms on the left side of the room to represent sodium chloride particles. Have the remaining 12 students stand on the right side ...
Chapter 15: Chemical Equilibrium
... of the reaction products is physically separated from a reaction mixture as a gas (the reaction of a metal carbonate with acid, for example, Figure 15.X), a single reaction arrow is used. The Equilibrium State In Chapter 12, we described the nature of a dynamic equilibrium between a liquid and its v ...
... of the reaction products is physically separated from a reaction mixture as a gas (the reaction of a metal carbonate with acid, for example, Figure 15.X), a single reaction arrow is used. The Equilibrium State In Chapter 12, we described the nature of a dynamic equilibrium between a liquid and its v ...
Chapter 15
... of the reaction products is physically separated from a reaction mixture as a gas (the reaction of a metal carbonate with acid, for example, Figure 15.X), a single reaction arrow is used. The Equilibrium State In Chapter 12, we described the nature of a dynamic equilibrium between a liquid and its v ...
... of the reaction products is physically separated from a reaction mixture as a gas (the reaction of a metal carbonate with acid, for example, Figure 15.X), a single reaction arrow is used. The Equilibrium State In Chapter 12, we described the nature of a dynamic equilibrium between a liquid and its v ...
Chapter 16 Controlling the yield of reactions
... The volume of the container was increased at constant temperature and a new equilbrium was established. Predict how each of the following quantities would change at the new equilibrium compared with the initial equilibrium: a concentration of NO2 b mass of NO2 A12. ...
... The volume of the container was increased at constant temperature and a new equilbrium was established. Predict how each of the following quantities would change at the new equilibrium compared with the initial equilibrium: a concentration of NO2 b mass of NO2 A12. ...
Ch16 - WordPress.com
... The volume of the container was increased at constant temperature and a new equilbrium was established. Predict how each of the following quantities would change at the new equilibrium compared with the initial equilibrium: a concentration of NO2 b mass of NO2 A12. An increase in volume will cause a ...
... The volume of the container was increased at constant temperature and a new equilbrium was established. Predict how each of the following quantities would change at the new equilibrium compared with the initial equilibrium: a concentration of NO2 b mass of NO2 A12. An increase in volume will cause a ...
File - IB CHEM NINJA
... consequence, macroscopic properties of the system (that is those that can be observed or measured, such as its colour, density, pH) are constant, even though on a molecular scale there is continual interconversion of reactants and products. The concentrations of the species at equilibrium will refle ...
... consequence, macroscopic properties of the system (that is those that can be observed or measured, such as its colour, density, pH) are constant, even though on a molecular scale there is continual interconversion of reactants and products. The concentrations of the species at equilibrium will refle ...
Ch16
... The volume of the container was increased at constant temperature and a new equilbrium was established. Predict how each of the following quantities would change at the new equilibrium compared with the initial equilibrium: a concentration of NO2 b mass of NO2 A12. An increase in volume will cause a ...
... The volume of the container was increased at constant temperature and a new equilbrium was established. Predict how each of the following quantities would change at the new equilibrium compared with the initial equilibrium: a concentration of NO2 b mass of NO2 A12. An increase in volume will cause a ...
ENTROPY
... the extreme consideration of a single distinguishable quantum state (identified by its quantum numbers). The distribution is characterised by the amounts of extensive magnitudes belonging to each subsystem. Let P={p1,p2,...pn}, with pi≥0 and Σpi=1, be a probability distribution function, such that p ...
... the extreme consideration of a single distinguishable quantum state (identified by its quantum numbers). The distribution is characterised by the amounts of extensive magnitudes belonging to each subsystem. Let P={p1,p2,...pn}, with pi≥0 and Σpi=1, be a probability distribution function, such that p ...
Slide 1
... proposed the law of chemical equilibrium, which states that at a given temperature, a chemical system may reach a state in which a particular ratio of reactant and product concentrations has a constant value. ...
... proposed the law of chemical equilibrium, which states that at a given temperature, a chemical system may reach a state in which a particular ratio of reactant and product concentrations has a constant value. ...
Physical and Chemical equilibrium
... concentration of reactants or product, but actually reaction takes place in both the directions with same speed (iv)Catalyst does not affect the equilibrium, it only fastens the chemical reaction to attain the state of equilibrium (v) Chemical equilibrium can be attended in either direction (vi) Cha ...
... concentration of reactants or product, but actually reaction takes place in both the directions with same speed (iv)Catalyst does not affect the equilibrium, it only fastens the chemical reaction to attain the state of equilibrium (v) Chemical equilibrium can be attended in either direction (vi) Cha ...
Physcal Chemistry ERT 108 semester II 2010/2011
... A system may be separated from its surroundings by various kinds of wall: ...
... A system may be separated from its surroundings by various kinds of wall: ...
(K c ) [A] - Knockhardy
... the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other examination boards. Individual students may use the material at home for revision purposes or it may be used for classroom teaching if an interactive white board is available. Accompanying notes on this, and the full range of AS and A2 topics, ...
... the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other examination boards. Individual students may use the material at home for revision purposes or it may be used for classroom teaching if an interactive white board is available. Accompanying notes on this, and the full range of AS and A2 topics, ...


















![(K c ) [A] - Knockhardy](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011755527_1-914ea907d1ff7656ef398ad87316c94c-300x300.png)