Module 3 Nature vs. Nurture
... Do you think that those people who reproduce in large numbers in our society today should really be the ones reproducing at such rates? Why or why not? What correlation does economic status have with reproduction rates worldwide if any? ...
... Do you think that those people who reproduce in large numbers in our society today should really be the ones reproducing at such rates? Why or why not? What correlation does economic status have with reproduction rates worldwide if any? ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... Children learn the probability that any given word or syllable will follow another. Although there are commonalities in language acquisition, there are also many differences. Parents respond to children’s sentence errors by restating or elaborating on the phrase. Children imitate these adult recasts ...
... Children learn the probability that any given word or syllable will follow another. Although there are commonalities in language acquisition, there are also many differences. Parents respond to children’s sentence errors by restating or elaborating on the phrase. Children imitate these adult recasts ...
Old Final Exam WITH ANSWERS!!
... __C__ 3. What is the term for mating pairs being more different (‘opposites attract’) than would be expected by chance? A. attraction of the fittest B. positive assortative mating C. negative assortative mating D. founder effect E. heritability. _D___ 4. Which genetic variance component is most impo ...
... __C__ 3. What is the term for mating pairs being more different (‘opposites attract’) than would be expected by chance? A. attraction of the fittest B. positive assortative mating C. negative assortative mating D. founder effect E. heritability. _D___ 4. Which genetic variance component is most impo ...
An except from Nesse Evolution and Mental Disorders, in press Sept
... 11. Experiences shared within a culture and whose effects are incorporated into values and emotional proclivities that may be difficult to change later (such as values or attitudes about sex) 12. Experiences shared within a culture whose effects account for variation, but these effects are not media ...
... 11. Experiences shared within a culture and whose effects are incorporated into values and emotional proclivities that may be difficult to change later (such as values or attitudes about sex) 12. Experiences shared within a culture whose effects account for variation, but these effects are not media ...
chapter_22
... Francis Galton and Karl Pearson (late 1800s): Recognized that continuous traits are statistically correlated between parents and offspring, but could not determine how transmission occurs. ...
... Francis Galton and Karl Pearson (late 1800s): Recognized that continuous traits are statistically correlated between parents and offspring, but could not determine how transmission occurs. ...
Adoption Studies
... Adoptive studies strongly point to the simple fact that biologically related children turn out to be different in a family. So investigators ask: Do siblings have differing experiences? Do siblings, despite sharing half of their genes, have different combinations of the other half of their genes? ...
... Adoptive studies strongly point to the simple fact that biologically related children turn out to be different in a family. So investigators ask: Do siblings have differing experiences? Do siblings, despite sharing half of their genes, have different combinations of the other half of their genes? ...
Adoption Studies
... Adoptive studies strongly point to the simple fact that biologically related children turn out to be different in a family. So investigators ask: Do siblings have differing experiences? Do siblings, despite sharing half of their genes, have different combinations of the other half of their genes? ...
... Adoptive studies strongly point to the simple fact that biologically related children turn out to be different in a family. So investigators ask: Do siblings have differing experiences? Do siblings, despite sharing half of their genes, have different combinations of the other half of their genes? ...
Unit III: Biological Bases of Behavior
... • Molecular genetics studies the molecular structure and function of genes • Find the genes that together orchestrate traits or reveal at-risk populations for diseases ...
... • Molecular genetics studies the molecular structure and function of genes • Find the genes that together orchestrate traits or reveal at-risk populations for diseases ...
Uses of heritability
... A corn breeder chooses to breed from plants that have large cobs. The average cob length in his crop is 15 cm, but he breeds from plants that average 18 cm cobs. Next year, he measures cob length in the offspring of the selected plants and discovers that the mean is 16 cm What is the heritability of ...
... A corn breeder chooses to breed from plants that have large cobs. The average cob length in his crop is 15 cm, but he breeds from plants that average 18 cm cobs. Next year, he measures cob length in the offspring of the selected plants and discovers that the mean is 16 cm What is the heritability of ...
Module 3PPT
... happening based on our genes The environment may or may not trigger the predisposition Example – disease (i.e. cancer) ...
... happening based on our genes The environment may or may not trigger the predisposition Example – disease (i.e. cancer) ...
Genetics - the science of heredity and variation
... Genes - the smallest unit of inheritance; a portion of a DNA molecule, occur in pairs on chromosomes in the nucleus of every cell Haploid - refers to the number of chromosomes in a sex cell which is half of the original number Heritability - proportion of observed variation in a particular trait whi ...
... Genes - the smallest unit of inheritance; a portion of a DNA molecule, occur in pairs on chromosomes in the nucleus of every cell Haploid - refers to the number of chromosomes in a sex cell which is half of the original number Heritability - proportion of observed variation in a particular trait whi ...
Development Through the Lifespan
... Third Parties Adapting to Change Changes from within and outside the family Socioeconomic Status and Family Functioning Timing of Family Life Cycle Values and Expectations Father’s Involvement Communication and Discipline Styles Children’s Cognitive Development Who is Poor? 12% of ...
... Third Parties Adapting to Change Changes from within and outside the family Socioeconomic Status and Family Functioning Timing of Family Life Cycle Values and Expectations Father’s Involvement Communication and Discipline Styles Children’s Cognitive Development Who is Poor? 12% of ...
The Biological Research
... psychiatric disorders has been established Human characteristics are polygenetic, establish by more than one gene, a fact which affects the study of heritability Other procedures compare adopted children to their biological parents and adoptive parents, finding more similarities between the adopted ...
... psychiatric disorders has been established Human characteristics are polygenetic, establish by more than one gene, a fact which affects the study of heritability Other procedures compare adopted children to their biological parents and adoptive parents, finding more similarities between the adopted ...
Chapter 3: Genes, Environment and Development
... How are traits passed from parents to offspring? What is an example of how a child could inherit a trait through each of the mechanisms? ...
... How are traits passed from parents to offspring? What is an example of how a child could inherit a trait through each of the mechanisms? ...
File
... chromosome 15 that contains several genes involved in the movement of a brain chemical called GABA between neurons. One version of the gene, GABRG3, was found statistically linked (associated) with alcoholism in the affected families. (Washington University, 2004) A study conducted looked at thirty ...
... chromosome 15 that contains several genes involved in the movement of a brain chemical called GABA between neurons. One version of the gene, GABRG3, was found statistically linked (associated) with alcoholism in the affected families. (Washington University, 2004) A study conducted looked at thirty ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
... Finland study is a longitudinal, genome-wide association study looking for genes associated with height at different ages in a cohort born in 1966. The Connecticut study compared different groups and didn’t follow genes. The Finland study followed the same individuals and did consider genetic inform ...
... Finland study is a longitudinal, genome-wide association study looking for genes associated with height at different ages in a cohort born in 1966. The Connecticut study compared different groups and didn’t follow genes. The Finland study followed the same individuals and did consider genetic inform ...
Course Outline - North Carolina State University
... • Heritability describes the relative contributions of genotype and environment to phenotypic variation. • Heritability is a measure of a population, not an individual, and does not say anything about the genetic difference between populations. • There are three common approaches to measuring herita ...
... • Heritability describes the relative contributions of genotype and environment to phenotypic variation. • Heritability is a measure of a population, not an individual, and does not say anything about the genetic difference between populations. • There are three common approaches to measuring herita ...
Adoption Studies
... Adoptive studies strongly point to the simple fact that biologically related children turn out to be different in a family. So investigators ask: Do siblings have differing experiences? Do siblings, despite sharing half of their genes, have different combinations of the other half of their genes? ...
... Adoptive studies strongly point to the simple fact that biologically related children turn out to be different in a family. So investigators ask: Do siblings have differing experiences? Do siblings, despite sharing half of their genes, have different combinations of the other half of their genes? ...
Behavioral Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences
... - Example: nutrition affecting if you’ll reach your genetic potential for height - See Nature & Nurture: The Study of Twins (4 min) – Prenatal environmental differences can have long term effects but environment can help one reach their potential. • Environment acts in response to what genes have gi ...
... - Example: nutrition affecting if you’ll reach your genetic potential for height - See Nature & Nurture: The Study of Twins (4 min) – Prenatal environmental differences can have long term effects but environment can help one reach their potential. • Environment acts in response to what genes have gi ...
Quantitative Genetics and Multifactorial Traits
... o We can also use individuals with different degrees of relatedness o Can compare results for monozygotic (MZ) twins vs. dizygotic (DZ) o H2 = 2(rMZ - rDZ) o Chromosomal regions that contain genes influencing quantitative traits are called quantitative trait loci (QTLs) o Mapping QTLs o This is a c ...
... o We can also use individuals with different degrees of relatedness o Can compare results for monozygotic (MZ) twins vs. dizygotic (DZ) o H2 = 2(rMZ - rDZ) o Chromosomal regions that contain genes influencing quantitative traits are called quantitative trait loci (QTLs) o Mapping QTLs o This is a c ...
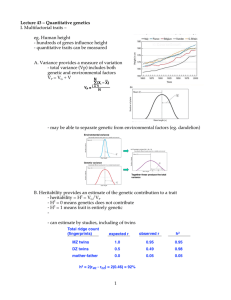
1 Lecture 43 â Quantitative genetics I. Multifactorial traits â eg
... - hundreds of genes influence height - quantitative traits can be measured A. Variance provides a measure of variation - total variance (Vp) includes both genetic and environmental factors V P = VG + V ...
... - hundreds of genes influence height - quantitative traits can be measured A. Variance provides a measure of variation - total variance (Vp) includes both genetic and environmental factors V P = VG + V ...
Document
... characters is continuous. • Such quantitative variation is studied with statistical techniques. • Continuous variation may be the result of segregation of interacting alleles at several loci with cumulative effect on phenotype. • Environmental interaction with genotype contributes to phenotypic vari ...
... characters is continuous. • Such quantitative variation is studied with statistical techniques. • Continuous variation may be the result of segregation of interacting alleles at several loci with cumulative effect on phenotype. • Environmental interaction with genotype contributes to phenotypic vari ...
Document
... characters is continuous. • Such quantitative variation is studied with statistical techniques. • Continuous variation may be the result of segregation of interacting alleles at several loci with cumulative effect on phenotype. • Environmental interaction with genotype contributes to phenotypic vari ...
... characters is continuous. • Such quantitative variation is studied with statistical techniques. • Continuous variation may be the result of segregation of interacting alleles at several loci with cumulative effect on phenotype. • Environmental interaction with genotype contributes to phenotypic vari ...
7.1 The Inheritance of Traits Offspring resemble their parents, but not
... Heritability: proportion of the variation within a population due to genetic differences among individuals ...
... Heritability: proportion of the variation within a population due to genetic differences among individuals ...