CHAPTER I
... While genetic causes of schizophrenia have been supported with evidence from behavioral genetics research, environmental factors can be just as important. Often 50 percent or more of the variance among individuals is due to nongenetic factors. One goal of psychologists is to study the “nonshared” a ...
... While genetic causes of schizophrenia have been supported with evidence from behavioral genetics research, environmental factors can be just as important. Often 50 percent or more of the variance among individuals is due to nongenetic factors. One goal of psychologists is to study the “nonshared” a ...
Quantitative Genomics slides
... Questions for the Study of 1) Is this trait influenced by genetic factors? How strong are these genetic influences? 2) Which traits are influenced by the same genes? 3) Where are the genes that influence a trait? 4) What are the specific genes that influence the trait? 5) What specific genetic vari ...
... Questions for the Study of 1) Is this trait influenced by genetic factors? How strong are these genetic influences? 2) Which traits are influenced by the same genes? 3) Where are the genes that influence a trait? 4) What are the specific genes that influence the trait? 5) What specific genetic vari ...
Chapter 3 Nature
... • To summarize the countless amount of studies: Twins (especially identical), whether or not they are raised in the same environment are very much alike in many ways. ...
... • To summarize the countless amount of studies: Twins (especially identical), whether or not they are raised in the same environment are very much alike in many ways. ...
Heredity and Environment
... • There is no schizo-gene, or depression gene, or leadership gene • Most psychological traits are complex, depending on… – Multiple genes interacting – Numerous environmental effects ...
... • There is no schizo-gene, or depression gene, or leadership gene • Most psychological traits are complex, depending on… – Multiple genes interacting – Numerous environmental effects ...
03-Study Guide
... #2-Discuss the human genome and elaborate on the differences between genotype and phenotype. ...
... #2-Discuss the human genome and elaborate on the differences between genotype and phenotype. ...
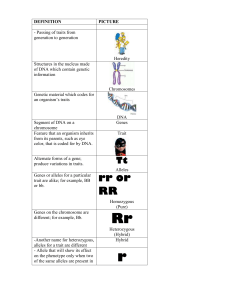
definition - Humble ISD
... -Another name for heterozygous, alleles for a trait are different - Allele that will show its effect on the phenotype only when two of the same alleles are present in ...
... -Another name for heterozygous, alleles for a trait are different - Allele that will show its effect on the phenotype only when two of the same alleles are present in ...
Ch.03 Nature Nurture
... Evolutionary Psychology E.g. Men more likely than women to initiate casual sex. Why? Biologically, it is a more successful reproductive strategy for men than women. ...
... Evolutionary Psychology E.g. Men more likely than women to initiate casual sex. Why? Biologically, it is a more successful reproductive strategy for men than women. ...
DNA and Gene Expression
... • QTL mapping and knockout studies identify 5 genes for dopamine D2 receptor – Each gene accounts for 20 minutes of sleep; five about 130 minutes of total 170 minute difference between LS and SS ...
... • QTL mapping and knockout studies identify 5 genes for dopamine D2 receptor – Each gene accounts for 20 minutes of sleep; five about 130 minutes of total 170 minute difference between LS and SS ...
3-8-heredity_and_environment
... about 40% of the individual differences that we observe in, say, shyness may in some way be attributable to genetic individual difference. • It does NOT mean that 40% of any person's shyness is due to his/her genes and the other 60% is due to his/her environment. ...
... about 40% of the individual differences that we observe in, say, shyness may in some way be attributable to genetic individual difference. • It does NOT mean that 40% of any person's shyness is due to his/her genes and the other 60% is due to his/her environment. ...
Genetics - MrGalusha.org
... about 40% of the individual differences that we observe in, say, shyness may in some way be attributable to genetic individual difference. • It does NOT mean that 40% of any person's shyness is due to his/her genes and the other 60% is due to his/her environment. ...
... about 40% of the individual differences that we observe in, say, shyness may in some way be attributable to genetic individual difference. • It does NOT mean that 40% of any person's shyness is due to his/her genes and the other 60% is due to his/her environment. ...
ANS 95433 Animal Breeding - An
... 5. --------- Standard error of the heritability estimate from the regression of offspring on one parent is equal to the standard error of the regression coefficient. 6. --------- At a biallelic locus with no dominance, the additive variance is maximum when allele frequency is 0.5. 7. --------- Three ...
... 5. --------- Standard error of the heritability estimate from the regression of offspring on one parent is equal to the standard error of the regression coefficient. 6. --------- At a biallelic locus with no dominance, the additive variance is maximum when allele frequency is 0.5. 7. --------- Three ...
Nature VS nurture
... likelihood toward certain characteristics Does not mean “Born with” Usually needs something from the environment to activate- (diathesis-stress model) Common genetic predispositions….body weight-alcoholismAlzheimer’s-Schizophrenia ...
... likelihood toward certain characteristics Does not mean “Born with” Usually needs something from the environment to activate- (diathesis-stress model) Common genetic predispositions….body weight-alcoholismAlzheimer’s-Schizophrenia ...
Quantitative Genetics
... A heritability index close to 1.0 indicates that environmental conditions had little impact on phenotypic variation in the population observed. A heritability index close to 0 indicates that environmental conditions were almost solely responsible for the phenotypic variation observed in the sample p ...
... A heritability index close to 1.0 indicates that environmental conditions had little impact on phenotypic variation in the population observed. A heritability index close to 0 indicates that environmental conditions were almost solely responsible for the phenotypic variation observed in the sample p ...
The Genetic Basis of Complex Inheritance
... range of phenotypes can be accounted for by cumulative effect of many alleles. Polygenes: Additive allele; nonadditive allele 1 phenotypic traits can be measured eg. weight or height 2 two or more loci (genes) could account for phenotype in an additive or cumulative way 3 each loci may be occupied b ...
... range of phenotypes can be accounted for by cumulative effect of many alleles. Polygenes: Additive allele; nonadditive allele 1 phenotypic traits can be measured eg. weight or height 2 two or more loci (genes) could account for phenotype in an additive or cumulative way 3 each loci may be occupied b ...
Biol 258: PP seminar
... b. Evolution: need genetic variation for trait. Deals with variation: not genetic, not environmental, but interaction. Must take account of both Plasticity is property of genotype. GxE property of population. What are consequences for evolution? What are consequences for heritability? c. Cha ...
... b. Evolution: need genetic variation for trait. Deals with variation: not genetic, not environmental, but interaction. Must take account of both Plasticity is property of genotype. GxE property of population. What are consequences for evolution? What are consequences for heritability? c. Cha ...
Study Material
... As shown in Figure 24.3b, Nilsson-Ehle discovered that the colors fell into a 1:4:6:4:1 ratio He concluded that this species is diploid for two different genes that control hull color ...
... As shown in Figure 24.3b, Nilsson-Ehle discovered that the colors fell into a 1:4:6:4:1 ratio He concluded that this species is diploid for two different genes that control hull color ...
2.2 To what extent does genetics influence behavior?
... Evolutionary Psychologist attempt to explain how certain human behaviors explain the development of our species over time. Natural selection does not select the behavior – it only selects the mechanisms that produces the ...
... Evolutionary Psychologist attempt to explain how certain human behaviors explain the development of our species over time. Natural selection does not select the behavior – it only selects the mechanisms that produces the ...
BSC 219
... One standard deviation from mean covers 66% of area Two standard deviations from mean covers 95% of area Three standard deviations from mean covers 99% of area Correlation Correlation: when two characteristics are correlated, a change in one characteristic is likely to be associated with a change in ...
... One standard deviation from mean covers 66% of area Two standard deviations from mean covers 95% of area Three standard deviations from mean covers 99% of area Correlation Correlation: when two characteristics are correlated, a change in one characteristic is likely to be associated with a change in ...
SR6e Chapter 3
... Single gene-pair inheritance ◦ Dominant gene = dominant trait ◦ Recessive genes Trait expressed if paired with a similar gene (Homozygous) Trait not expressed if paired with dissimilar gene (Heterozygous) ◦ Recessive traits: homozygous recessive ◦ Dominant traits: hetero or homozygous gene pair ...
... Single gene-pair inheritance ◦ Dominant gene = dominant trait ◦ Recessive genes Trait expressed if paired with a similar gene (Homozygous) Trait not expressed if paired with dissimilar gene (Heterozygous) ◦ Recessive traits: homozygous recessive ◦ Dominant traits: hetero or homozygous gene pair ...
Nature vs Nurture and Psychological Development
... became known as the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Test. Studies have shown that twins who were raised in different homes have a statistically significant similarity in their IQs. Studies have also shown that environmental factors such as nutrition and schooling can influence IQ scores. ...
... became known as the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Test. Studies have shown that twins who were raised in different homes have a statistically significant similarity in their IQs. Studies have also shown that environmental factors such as nutrition and schooling can influence IQ scores. ...
Module 03_lecture
... from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms • Called monozygotic twins ...
... from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms • Called monozygotic twins ...
Psychology - HGunnWikiMHS
... single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms • Called monozygotic twins ...
... single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms • Called monozygotic twins ...