Clinical genomics - University of Toledo
... • The number, indications, and complexity of genetic tests offered have been increasing, and will continue to do so for the foreseeable future. • It is therefore not surprising that mistakes often occur in the ordering of complex genetic tests. • Incorrect ordering of genetic tests results in unnece ...
... • The number, indications, and complexity of genetic tests offered have been increasing, and will continue to do so for the foreseeable future. • It is therefore not surprising that mistakes often occur in the ordering of complex genetic tests. • Incorrect ordering of genetic tests results in unnece ...
Lecture 3: More Transmission Genetics
... The diseased individuals are present in every generation (indicates a dominant disease) and males and females are both about equally affected (indicates autosomal inheritance) ...
... The diseased individuals are present in every generation (indicates a dominant disease) and males and females are both about equally affected (indicates autosomal inheritance) ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... Will it happen again if I have more children? What can I do to prevent it from happening again? ...
... Will it happen again if I have more children? What can I do to prevent it from happening again? ...
Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia Clefting (EEC) Syndrome
... (EEC) Syndrome One of the relatively common ectodermal dysplasia (ED) syndromes that is more complex than others is the ectrodactyly-ectodermal dysplasia-cleft lip and palate syndrome. It is often called the EEC syndrome. The word ectrodactyly is derived from the Greek, and means congenital absence ...
... (EEC) Syndrome One of the relatively common ectodermal dysplasia (ED) syndromes that is more complex than others is the ectrodactyly-ectodermal dysplasia-cleft lip and palate syndrome. It is often called the EEC syndrome. The word ectrodactyly is derived from the Greek, and means congenital absence ...
Molecular Genetics 2 - New York University
... Definition: “Mutations in each of two (or more) unlinked genes are present in a single individual. The combination of the two genetic hits causes a disease phenotype that is not apparent when an individual carries only one of these gene alterations” * Proposed Disorders where this form of inheritanc ...
... Definition: “Mutations in each of two (or more) unlinked genes are present in a single individual. The combination of the two genetic hits causes a disease phenotype that is not apparent when an individual carries only one of these gene alterations” * Proposed Disorders where this form of inheritanc ...
Biological and Environmental Factors
... carried on the X-Chromosome – Males more likely to be affected (sex chromosomes don’t match) – Hemophilia ...
... carried on the X-Chromosome – Males more likely to be affected (sex chromosomes don’t match) – Hemophilia ...
Human Heredity and Sex
... *Most chromosomal disorders are caused by mutations. *The most common form of mutation that results in chromosomal disorders is Nondisjunction – the addition or loss of a whole chromosome when the chromosomes are supposed to separate in meiosis. ...
... *Most chromosomal disorders are caused by mutations. *The most common form of mutation that results in chromosomal disorders is Nondisjunction – the addition or loss of a whole chromosome when the chromosomes are supposed to separate in meiosis. ...
How Are Traits Passed From Generation to Generation
... Inheritance- the process by which traits are passed from one generation to the next. Monohybrid cross- a genetic cross that involves only one trait Multiple alleles- Three or more alleles for the same gene Gametes-Male and female sex cells Nucleotide- monomer of nucleic acids Pedigree- a genetic ana ...
... Inheritance- the process by which traits are passed from one generation to the next. Monohybrid cross- a genetic cross that involves only one trait Multiple alleles- Three or more alleles for the same gene Gametes-Male and female sex cells Nucleotide- monomer of nucleic acids Pedigree- a genetic ana ...
GENES AND CHROMOSOMES
... A. alleles carried on homologs (sketch these) 1. homologs segregate during meiosis 2. gametes carry one allele or the other, but not both B. when two pairs of alternate alleles carried on two pairs of homologs 1. homologs separate during meiosis I 2. chromatids separate during meiosis II 3. alleles ...
... A. alleles carried on homologs (sketch these) 1. homologs segregate during meiosis 2. gametes carry one allele or the other, but not both B. when two pairs of alternate alleles carried on two pairs of homologs 1. homologs separate during meiosis I 2. chromatids separate during meiosis II 3. alleles ...
All About Genetics Webquest
... “Intermediate Expression” is also known as CODOMINANCE (this is the term our textbook uses). What is different about heterozygous offspring if the trait is codominant rather than completely dominant (like Mendel’s pea plants)? ...
... “Intermediate Expression” is also known as CODOMINANCE (this is the term our textbook uses). What is different about heterozygous offspring if the trait is codominant rather than completely dominant (like Mendel’s pea plants)? ...
Complementation
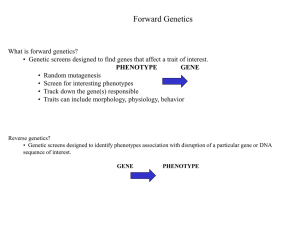
... What is forward genetics? • Genetic screens designed to find genes that affect a trait of interest. ...
... What is forward genetics? • Genetic screens designed to find genes that affect a trait of interest. ...
adaptability. These studies look first, into the extent to which
... differences in the environment? For example, differences due to mirror imaging, to asymmetrical defects such as ptosis, to embryological errors of one or both twins, or to changes of chromosome number or structure such as arise from errors of mitosis at the first or later cleavage divisions. It is t ...
... differences in the environment? For example, differences due to mirror imaging, to asymmetrical defects such as ptosis, to embryological errors of one or both twins, or to changes of chromosome number or structure such as arise from errors of mitosis at the first or later cleavage divisions. It is t ...
File
... zygotes: the fertilized egg. 2 week period of rapid development & grows into an…. embryo: weeks 2 through 8. organs are primitive, but identifiable. baby is 1 inch long. arms, legs & face are distinct fetus: developing human organism from 9 weeks to birth (pregnancy is 40 weeks) ...
... zygotes: the fertilized egg. 2 week period of rapid development & grows into an…. embryo: weeks 2 through 8. organs are primitive, but identifiable. baby is 1 inch long. arms, legs & face are distinct fetus: developing human organism from 9 weeks to birth (pregnancy is 40 weeks) ...
Understanding hereditary disease. Mutts DO have genetic diseases
... Genetics: To explain what is going on we are going to simplify what happens. Genes come in pairs - one from each parent. Either of these genes can then be passed to the next generation. Lets say that we have a dog with a gene for hip dysplasia ( this is actually a multi-gene problem). Hip dysplasia ...
... Genetics: To explain what is going on we are going to simplify what happens. Genes come in pairs - one from each parent. Either of these genes can then be passed to the next generation. Lets say that we have a dog with a gene for hip dysplasia ( this is actually a multi-gene problem). Hip dysplasia ...
7.1 Study Guide
... 9. The verb carry means “to transport.” This meaning is related to the term carrier in genetics, because a carrier is a person who “transports” a disease-causing allele to offspring / parents. 10. With X chromosome inactivation, which occurs in males / females, one of the two X chromosomes in every ...
... 9. The verb carry means “to transport.” This meaning is related to the term carrier in genetics, because a carrier is a person who “transports” a disease-causing allele to offspring / parents. 10. With X chromosome inactivation, which occurs in males / females, one of the two X chromosomes in every ...
The right to a child
... Write down one thing you have learnt Write down one thing that you disagreed with / would challenge. Write down a question that the article left you asking ...
... Write down one thing you have learnt Write down one thing that you disagreed with / would challenge. Write down a question that the article left you asking ...
Essays for Chapters 16, 17, and 18
... a. Describe the four main types of genetic material (six classes) found in viruses and their mode of replication (focus mainly on those described in class.) b. Explain how each of the four main types of genetic material code for making proteins necessary for viral coats or metabolism. c. Explain the ...
... a. Describe the four main types of genetic material (six classes) found in viruses and their mode of replication (focus mainly on those described in class.) b. Explain how each of the four main types of genetic material code for making proteins necessary for viral coats or metabolism. c. Explain the ...
Chapter 7 sections 1,2,4
... not play a role in sex determination. You have two alleles for each gene; one from each parent. Most traits are the result of autosomal genes. Curly or straight hair ...
... not play a role in sex determination. You have two alleles for each gene; one from each parent. Most traits are the result of autosomal genes. Curly or straight hair ...
Drugs of Abuse - Teach Genetics (Utah)
... online activity of the same title located in The New Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain module on our website (url above). Students learn about the short and long-term effect of a number of drugs of abuse. ...
... online activity of the same title located in The New Science of Addiction: Genetics and the Brain module on our website (url above). Students learn about the short and long-term effect of a number of drugs of abuse. ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 5 TEST: HEREDITY
... 1. heredity: passing of traits from one generation to another 2. allele: different forms a gene may have for a trait 3. genetics: study of how alleles affect offspring 4. purebred: organism that produces same traits in offspring 5. cross pollinate: pollinate a flower or plant with pollen from anothe ...
... 1. heredity: passing of traits from one generation to another 2. allele: different forms a gene may have for a trait 3. genetics: study of how alleles affect offspring 4. purebred: organism that produces same traits in offspring 5. cross pollinate: pollinate a flower or plant with pollen from anothe ...
Chapter 3 Genetics
... Gregor Mendel: a priest who studied how physical characteristics were passed down to offspring in pea plants. -his work/ideas formed the foundation of genetics. -he is known as the Father of Genetics ...
... Gregor Mendel: a priest who studied how physical characteristics were passed down to offspring in pea plants. -his work/ideas formed the foundation of genetics. -he is known as the Father of Genetics ...