12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes 12.3
... highest possible value, (b) lowest possible value, (c) average value, (d) none of the preceding. (a) It has been proposed that temperature differences in the ocean could be used to run a heat engine to generate electricity. In tropical regions, the water temperature is about 25°C at the surface an ...
... highest possible value, (b) lowest possible value, (c) average value, (d) none of the preceding. (a) It has been proposed that temperature differences in the ocean could be used to run a heat engine to generate electricity. In tropical regions, the water temperature is about 25°C at the surface an ...
Comparison of entropy difference in the cooling process
... and ethanol are the best substances for cooling by evaporation at room temperature. These data refer to specific conditions, which does not mean they are the same at different temperatures. As an interesting fact, the Δs/R value for the refrigerant R-134a at 170 K is 19.01, much higher than the value ...
... and ethanol are the best substances for cooling by evaporation at room temperature. These data refer to specific conditions, which does not mean they are the same at different temperatures. As an interesting fact, the Δs/R value for the refrigerant R-134a at 170 K is 19.01, much higher than the value ...
ESO201A: Thermodynamics
... reversible processes and their examples, internally reversible iso-thermal process, heat transfer processes, The Carnot’s heat engine cycle. Lecture #20 Carnot cycle implications, The Carnot principles, Thermodynamic temperature scale, Thermal efficiency of a reversible engine as a function of high ...
... reversible processes and their examples, internally reversible iso-thermal process, heat transfer processes, The Carnot’s heat engine cycle. Lecture #20 Carnot cycle implications, The Carnot principles, Thermodynamic temperature scale, Thermal efficiency of a reversible engine as a function of high ...
The Use and Misuse of the LUWS of Thermodynamics
... physics, such as the "energy" E = Q21/2eA of charging a condenser is actually a change in free energy and not of energy. The free energy turns out to be the thermodynamic analogue of the electromechanical potential energy, and is both a more familiar and less complicated quantity than the energy U. ...
... physics, such as the "energy" E = Q21/2eA of charging a condenser is actually a change in free energy and not of energy. The free energy turns out to be the thermodynamic analogue of the electromechanical potential energy, and is both a more familiar and less complicated quantity than the energy U. ...
Thermodynamics: Heat and Work
... • As a system goes from orderly to disorderly the amount of work you can get out of the system decreases. • Well since the entropy of the universe is always increasing, the logical conclusion is that eventually the universe will be a uniform mixture at thermal equilibrium. • No work can happen and n ...
... • As a system goes from orderly to disorderly the amount of work you can get out of the system decreases. • Well since the entropy of the universe is always increasing, the logical conclusion is that eventually the universe will be a uniform mixture at thermal equilibrium. • No work can happen and n ...
12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes 12.3
... preceding. CQ In Fig. 12.20, the plunger of a syringe is pushed in quickly, and the small pieces of paper in the syringe catch fire. Explain this phenomenon, using the first law of thermodynamics. (Similarly, in a diesel engine, there are no spark plugs. How can the air–fuel mixture ignite?) Whil ...
... preceding. CQ In Fig. 12.20, the plunger of a syringe is pushed in quickly, and the small pieces of paper in the syringe catch fire. Explain this phenomenon, using the first law of thermodynamics. (Similarly, in a diesel engine, there are no spark plugs. How can the air–fuel mixture ignite?) Whil ...
AP Physics – Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The argument goes like this: the universe must go from an ordered state to a disordered state according to the second law of thermodynamics. Yet for life to have evolved as Darwin said it has would require that life have gone from a low state of order to a higher state of order. This is clearly proh ...
... The argument goes like this: the universe must go from an ordered state to a disordered state according to the second law of thermodynamics. Yet for life to have evolved as Darwin said it has would require that life have gone from a low state of order to a higher state of order. This is clearly proh ...
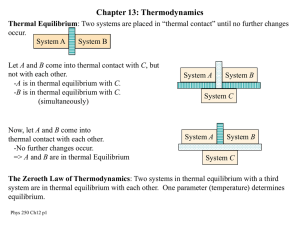
Last time
... transitions? Suppose we perform a constant pressure calorimetry experiment, passing through the melting point of a sample. The heat released on melting is the enthalpy of melting: ...
... transitions? Suppose we perform a constant pressure calorimetry experiment, passing through the melting point of a sample. The heat released on melting is the enthalpy of melting: ...
1 Lecture: 2 Thermodynamic equilibrium 1
... it completely converted into heat at the system, we see that the final temperature T2 can be reached after some time. Once the system has reached T2 it is indistinguishable from the system at T2 obtained by lowering the mass m through a difference in height of h. We can also supply some mechanical w ...
... it completely converted into heat at the system, we see that the final temperature T2 can be reached after some time. Once the system has reached T2 it is indistinguishable from the system at T2 obtained by lowering the mass m through a difference in height of h. We can also supply some mechanical w ...
Energy Flow in Marine Ecosystem
... Work: mechanical work is the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance In thermodynamics, work is the quantity of energy transferred from one system to another without an accompanying transfer of entropy Thermodynamics: is the study of the conversion of heat energy into ...
... Work: mechanical work is the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance In thermodynamics, work is the quantity of energy transferred from one system to another without an accompanying transfer of entropy Thermodynamics: is the study of the conversion of heat energy into ...
p250c13
... Example: What is the maximum possible thermal efficiency of a steam engine that takes in steam at 160ºC and exhausts it at 100ºC? ...
... Example: What is the maximum possible thermal efficiency of a steam engine that takes in steam at 160ºC and exhausts it at 100ºC? ...
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The second law of thermodynamics gives information concerning the direction of spontaneous change. If the second law says that a certain process is impossible, you will not be able to get the process to go. On the other hand, note that if the second law says that a process is possible, you still hav ...
... The second law of thermodynamics gives information concerning the direction of spontaneous change. If the second law says that a certain process is impossible, you will not be able to get the process to go. On the other hand, note that if the second law says that a process is possible, you still hav ...
Identification of an average temperature and a dynamical
... own temperature. The introduction of an average temperature together with the entropy principle dictates the classical Fick law for diffusion and also novel constitutive equations associated with the difference of temperatures between the components. The constitutive equations fit with results recen ...
... own temperature. The introduction of an average temperature together with the entropy principle dictates the classical Fick law for diffusion and also novel constitutive equations associated with the difference of temperatures between the components. The constitutive equations fit with results recen ...
Using the “Clicker” - Boston University: Physics
... A heat engine is a device that uses heat to do work. A gasoline-powered car engine is a good example. To be useful, the engine must go through cycles, with work being done every cycle. Two temperatures are required. The higher temperature causes the system to expand, doing work, and the lower temper ...
... A heat engine is a device that uses heat to do work. A gasoline-powered car engine is a good example. To be useful, the engine must go through cycles, with work being done every cycle. Two temperatures are required. The higher temperature causes the system to expand, doing work, and the lower temper ...
process
... A heat engine is a device that uses heat to do work. A gasoline-powered car engine is a good example. To be useful, the engine must go through cycles, with work being done every cycle. Two temperatures are required. The higher temperature causes the system to expand, doing work, and the lower temper ...
... A heat engine is a device that uses heat to do work. A gasoline-powered car engine is a good example. To be useful, the engine must go through cycles, with work being done every cycle. Two temperatures are required. The higher temperature causes the system to expand, doing work, and the lower temper ...
Carnot Cycle - University of Wyoming
... • e = 1 (100% efficiency) only if Qc = 0 – No energy expelled to cold reservoir ...
... • e = 1 (100% efficiency) only if Qc = 0 – No energy expelled to cold reservoir ...
Announcements
... l Heat can be made to flow the other way only when work is done on the system, as for example with a heat pump or an air conditioner ...
... l Heat can be made to flow the other way only when work is done on the system, as for example with a heat pump or an air conditioner ...
ET 11-08-14 SET 2
... 7. A system contains 0.2 m3 of a gas at a pressure of 4 bar and 150°C. It is expanded adiabatically till the pressure falls to 1 bar. The gas is then heated at a constant pressure till its enthalpy increases by 100 kJ. Determine the total work done. Take Cp =1 kJ/kgK and Cv = 0.714 kJ/kgK. Or 8. 12 ...
... 7. A system contains 0.2 m3 of a gas at a pressure of 4 bar and 150°C. It is expanded adiabatically till the pressure falls to 1 bar. The gas is then heated at a constant pressure till its enthalpy increases by 100 kJ. Determine the total work done. Take Cp =1 kJ/kgK and Cv = 0.714 kJ/kgK. Or 8. 12 ...
ph202_overhead_ch15
... • A measure of the disorder (or randomness) of a system • For a reversible the change in entropy is measured as the ratio of heat gained to temperature DS = (Q/T)R = Sfinal - Sinitial – When heat energy is gained by a system, entropy is gained by the system (and lost by the surrounding environment) ...
... • A measure of the disorder (or randomness) of a system • For a reversible the change in entropy is measured as the ratio of heat gained to temperature DS = (Q/T)R = Sfinal - Sinitial – When heat energy is gained by a system, entropy is gained by the system (and lost by the surrounding environment) ...
heat engine
... temperature, and all the rejected heat goes into a cold reservoir at a single temperature. Since the efficiency can only depend on the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. QC QH ...
... temperature, and all the rejected heat goes into a cold reservoir at a single temperature. Since the efficiency can only depend on the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. QC QH ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... temperature, and all the rejected heat goes into a cold reservoir at a single temperature. Since the efficiency can only depend on the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. QC QH ...
... temperature, and all the rejected heat goes into a cold reservoir at a single temperature. Since the efficiency can only depend on the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. QC QH ...
L14
... The cycle starts where you take a mass of cold air in a piston, compress it adiabatically. Since the temperature is low, then the pressure will be low, and it doesn’t take much work to compress it. Then you add heat to the compressed gas, increasing its temperature substantially. Now the pressure is ...
... The cycle starts where you take a mass of cold air in a piston, compress it adiabatically. Since the temperature is low, then the pressure will be low, and it doesn’t take much work to compress it. Then you add heat to the compressed gas, increasing its temperature substantially. Now the pressure is ...
Thermodynamics of ideal gases
... take place in an isolated system which is not allowed to exchange heat with or perform work on the environment. The First Law states that the energy is unchanged under any process in an isolated system. This implies that the energy of an open system can only change by exchange of heat or work with t ...
... take place in an isolated system which is not allowed to exchange heat with or perform work on the environment. The First Law states that the energy is unchanged under any process in an isolated system. This implies that the energy of an open system can only change by exchange of heat or work with t ...