CB4 – Natural Selection and GM
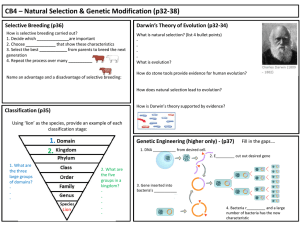
... How is selective breeding carried out? 1. Decide which ______________are important 2. Choose _____________ that show these characteristics 3. Select the best ____________ from parents to breed the next generation 4. Repeat the process over many ___________ ...
... How is selective breeding carried out? 1. Decide which ______________are important 2. Choose _____________ that show these characteristics 3. Select the best ____________ from parents to breed the next generation 4. Repeat the process over many ___________ ...
Spring Break Worksheet on Evolution
... 5) Because the trees of England turned black because of soot, the white moths increased in numbers. 6) An organism’s phenotype is a physical trait. Natural selection only works on an organism’s genotype. ...
... 5) Because the trees of England turned black because of soot, the white moths increased in numbers. 6) An organism’s phenotype is a physical trait. Natural selection only works on an organism’s genotype. ...
Population Genetics ppt - Liberty Union High School District
... split into 2 or more species A species may evolve into a new species Requires very long periods of time ...
... split into 2 or more species A species may evolve into a new species Requires very long periods of time ...
How Evolution Works
... combinations Any change in allele frequency = Evolution Peppered Moth Simulation ...
... combinations Any change in allele frequency = Evolution Peppered Moth Simulation ...
Chapter 15: Evolution
... __________ __________ operates to eliminate extreme expressions of a trait when the average expression leads to higher fitness. __________ __________ makes an organism more fit. __________ __________ is a process that splits a population into two groups. __________ __________ operates in pop ...
... __________ __________ operates to eliminate extreme expressions of a trait when the average expression leads to higher fitness. __________ __________ makes an organism more fit. __________ __________ is a process that splits a population into two groups. __________ __________ operates in pop ...
11.3 Other Mechanisms of Evolution
... 11.3 Other Mechanisms of Evolution • Genetic drift has negative effects on a population. – less likely to have some individuals that can adapt to a changing environment due to loss of genetic variation – harmful alleles can become more common due to chance Example of Genetic Drift Cheetahs exhibit ...
... 11.3 Other Mechanisms of Evolution • Genetic drift has negative effects on a population. – less likely to have some individuals that can adapt to a changing environment due to loss of genetic variation – harmful alleles can become more common due to chance Example of Genetic Drift Cheetahs exhibit ...
Green Chapter 17 Test Review
... How is incomplete dominance different from regular genetics? What would it look like? ...
... How is incomplete dominance different from regular genetics? What would it look like? ...
File
... adapt to changes in the environment and why some species become extinct. Natural Selection is the process of organisms best adapted to an environment surviving in that environment. Traits are a form of inherited characteristics. An adaptation is a characteristic that helps an organism survive and re ...
... adapt to changes in the environment and why some species become extinct. Natural Selection is the process of organisms best adapted to an environment surviving in that environment. Traits are a form of inherited characteristics. An adaptation is a characteristic that helps an organism survive and re ...
math
... Compute fitness of each individual ; LOOP Select individuals from old generations for mating ; Create offspring by applying recombination and/or mutation to the selected individuals ; Compute fitness of the new individuals ; Kill old individuals ,insert offspring in new generation ; IF Population ha ...
... Compute fitness of each individual ; LOOP Select individuals from old generations for mating ; Create offspring by applying recombination and/or mutation to the selected individuals ; Compute fitness of the new individuals ; Kill old individuals ,insert offspring in new generation ; IF Population ha ...
Biology Chapter 13 and 14
... will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. 2. If allele frequencies remained constant then there would be genetic equilibrium. ...
... will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. 2. If allele frequencies remained constant then there would be genetic equilibrium. ...
Random Genetic Drift
... All populations started out with identical gene pools, but with time, the gene frequencies will change. The populations will become different from each other over time. DRIFT CAUSES AN INCREASE OF GENETIC VARIABILITY BETWEEN POPULATIONS ...
... All populations started out with identical gene pools, but with time, the gene frequencies will change. The populations will become different from each other over time. DRIFT CAUSES AN INCREASE OF GENETIC VARIABILITY BETWEEN POPULATIONS ...
Factors that Cause Evolutionary Change
... populations are the small events that lead to evolution within a population, or microevolution. When the frequency of an allele in a population changes, microevolution has occurred. The following table lists the five common factors that lead to microevolution: Factor ...
... populations are the small events that lead to evolution within a population, or microevolution. When the frequency of an allele in a population changes, microevolution has occurred. The following table lists the five common factors that lead to microevolution: Factor ...
File
... 13) The following five conditions can upset genetic equilibrium. a. Nonrandom mating – If mates are selected for a particular trait, the ______________________ of the trait will increase. i. Define sex selection. ______________________________________________________ ________________________________ ...
... 13) The following five conditions can upset genetic equilibrium. a. Nonrandom mating – If mates are selected for a particular trait, the ______________________ of the trait will increase. i. Define sex selection. ______________________________________________________ ________________________________ ...
Biodiversity
... Because organisms with certain traits have greater chance of reproducing, there offspring will make up a larger part of the population ...
... Because organisms with certain traits have greater chance of reproducing, there offspring will make up a larger part of the population ...
7.1 Solutions File
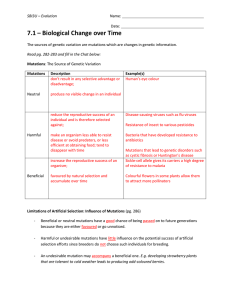
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
Population Genetics
... – What frequency of the population will be homozygous dominant, heterozygous, and homozygous recessive? – What frequency of the population will demonstrate the dominant phenotype? ...
... – What frequency of the population will be homozygous dominant, heterozygous, and homozygous recessive? – What frequency of the population will demonstrate the dominant phenotype? ...
Organisms, Life History and Evolutionary Fitness
... Allelic variation arises from MUTATION Central Dogma: ...
... Allelic variation arises from MUTATION Central Dogma: ...
Notes: Other Evolutionary Mechanisms
... • If the five Hardy Weinberg conditions are MET, then the population is in ________ (not changing) • If any ONE of them is affected, then the population will evolve Population Size Effects • In small populations, there are less options for mating, therefore any evolutionary changes occur more ______ ...
... • If the five Hardy Weinberg conditions are MET, then the population is in ________ (not changing) • If any ONE of them is affected, then the population will evolve Population Size Effects • In small populations, there are less options for mating, therefore any evolutionary changes occur more ______ ...
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
... • Intrasexual selection- selection within the same sex, individuals of one sex compete directly for mates of the opposite sex. • Intersexual selection- “mate choice”, individuals of one sex (usually females) are choosy in selecting their mates from the other sex. ...
... • Intrasexual selection- selection within the same sex, individuals of one sex compete directly for mates of the opposite sex. • Intersexual selection- “mate choice”, individuals of one sex (usually females) are choosy in selecting their mates from the other sex. ...
Ch 023 evolupop
... allele allowing for better reproduction success. •Chromosomal Mutation: disrupts development may have benefits. •Bacteria: reproduce every 20 minutes, mutation in one may produce millions in an hour. Antibiotic resistant bacteria ...
... allele allowing for better reproduction success. •Chromosomal Mutation: disrupts development may have benefits. •Bacteria: reproduce every 20 minutes, mutation in one may produce millions in an hour. Antibiotic resistant bacteria ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.