What can affect the effective population size? Genetic bottlenecks
... 1) What can affect the effective population size? a) Genetic bottlenecks b) Unequal number of males & females c) Population size through generations d) Variance in reproductive success e) Founder effect f) All the above 2) Under which circumstance is gene flow stronger than genetic drift? a) Ne*m = ...
... 1) What can affect the effective population size? a) Genetic bottlenecks b) Unequal number of males & females c) Population size through generations d) Variance in reproductive success e) Founder effect f) All the above 2) Under which circumstance is gene flow stronger than genetic drift? a) Ne*m = ...
TODAY. . . Selection Directional Stabilizing Disruptive More HW
... alleles that are incompletely dominant exist for a gene that affects shell thickness and weight (S – thick, heavy shell; s – thin, light shell). You sample 100 individuals from the population: 37 are SS, 8 are ss, and 55 are Ss. A)Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? Why or why not? B) ...
... alleles that are incompletely dominant exist for a gene that affects shell thickness and weight (S – thick, heavy shell; s – thin, light shell). You sample 100 individuals from the population: 37 are SS, 8 are ss, and 55 are Ss. A)Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? Why or why not? B) ...
Charlesworth B. Evolution in age-structured populations. Cambridge
... the ways in which natural selection can shape life history. This is the subject of the final chapter. One result of wide generalsignificance is thefact that the intensity of natural selection is a function ofthe age at which genes affecting the trait are expressed. Other things being equal,genes wit ...
... the ways in which natural selection can shape life history. This is the subject of the final chapter. One result of wide generalsignificance is thefact that the intensity of natural selection is a function ofthe age at which genes affecting the trait are expressed. Other things being equal,genes wit ...
A1989T880700001
... the ways in which natural selection can shape life history. This is the subject of the final chapter. One result of wide generalsignificance is thefact that the intensity of natural selection is a function ofthe age at which genes affecting the trait are expressed. Other things being equal,genes wit ...
... the ways in which natural selection can shape life history. This is the subject of the final chapter. One result of wide generalsignificance is thefact that the intensity of natural selection is a function ofthe age at which genes affecting the trait are expressed. Other things being equal,genes wit ...
Mechanisms of Change
... the idea of selection to cause major changes in the features of their plants and animals over the course of decades. Farmers and breeders allowed only the plants and animals with desirable characteristics to reproduce, causing the evolution of farm stock. This process is called artificial selection ...
... the idea of selection to cause major changes in the features of their plants and animals over the course of decades. Farmers and breeders allowed only the plants and animals with desirable characteristics to reproduce, causing the evolution of farm stock. This process is called artificial selection ...
Evolution Review - rosedale11universitybiology
... e. all of the above. 11. The primary evolutionary unit is the: a. individual b. population c. germ cell d. gene e. cell Short Answer 12. Differentiate between the terms “evolution” and “natural selection.” Evolution: “change in allele frequency” for inherited characteristics over successive generati ...
... e. all of the above. 11. The primary evolutionary unit is the: a. individual b. population c. germ cell d. gene e. cell Short Answer 12. Differentiate between the terms “evolution” and “natural selection.” Evolution: “change in allele frequency” for inherited characteristics over successive generati ...
evolution of populations
... descendants than other individuals, just by chance. Over time, a series of chance occurrences of this type can cause an allele to become common in population o ________ ______---a random change in the frequency of a gene---occurs most efficiently in small populations. o Genetic drift may occur when ...
... descendants than other individuals, just by chance. Over time, a series of chance occurrences of this type can cause an allele to become common in population o ________ ______---a random change in the frequency of a gene---occurs most efficiently in small populations. o Genetic drift may occur when ...
Study Guide Evolution Chapter 14
... 1. Species change over time. 2. Ancestral Species of past gave rise to new species of today. 3. Lamarck proposed the 1st important theory of evolution in 1809 4. Darwin explained evolution by natural selection by ‘Descent with Modification’ in 1859 5. Microevolution is favorable change in a populati ...
... 1. Species change over time. 2. Ancestral Species of past gave rise to new species of today. 3. Lamarck proposed the 1st important theory of evolution in 1809 4. Darwin explained evolution by natural selection by ‘Descent with Modification’ in 1859 5. Microevolution is favorable change in a populati ...
Biology II Notes - Wando High School
... 3. random fertilization of sperm and egg XI. Diploidy and Balancing Selection Preserve Variation A. An ancestral population is varied, with individuals having characteristics suited for many types of environments. B. Over successive generations, those individuals with the characteristics best suited ...
... 3. random fertilization of sperm and egg XI. Diploidy and Balancing Selection Preserve Variation A. An ancestral population is varied, with individuals having characteristics suited for many types of environments. B. Over successive generations, those individuals with the characteristics best suited ...
Microevolution involves the evolutionary changes within a population.
... Random mating must occur No genetic drift No natural selection ...
... Random mating must occur No genetic drift No natural selection ...
Phenotype Genotype and the Environment
... Babies that are too small are not strong enough, but if too large, complications in delivery. ...
... Babies that are too small are not strong enough, but if too large, complications in delivery. ...
Natural Selection does not produce perfection, just *good
... squirrels evolve new breeding times in response to climate change, a fish species evolve resistance to toxins dumped into the Hudson River, and a host of microbes evolve resistance to new drugs we've developed ...
... squirrels evolve new breeding times in response to climate change, a fish species evolve resistance to toxins dumped into the Hudson River, and a host of microbes evolve resistance to new drugs we've developed ...
CH 13 * Microevolution - Chadwick School: Haiku Learning
... – The founder effect • Is genetic drift in a new colony. ...
... – The founder effect • Is genetic drift in a new colony. ...
File
... inflicted on them in the 1890s. Hunting reduced their population size to as few as 20 individuals at the end of the 19th century. Their population has since rebounded to over 30,000 but their genes still carry the marks of this bottleneck. They have much less genetic variation than a population of s ...
... inflicted on them in the 1890s. Hunting reduced their population size to as few as 20 individuals at the end of the 19th century. Their population has since rebounded to over 30,000 but their genes still carry the marks of this bottleneck. They have much less genetic variation than a population of s ...
Slide 1
... • Can only be passed on to offspring only if they occur in the germ line • Are the ultimate source of genetic variation (new genes and alleles) • But are NOT considered a significant source of genetic change, especially in slowly reproducing plants and animals ...
... • Can only be passed on to offspring only if they occur in the germ line • Are the ultimate source of genetic variation (new genes and alleles) • But are NOT considered a significant source of genetic change, especially in slowly reproducing plants and animals ...
Microevolution involves the evolutionary changes within a population.
... Random mating must occur No genetic drift No natural selection ...
... Random mating must occur No genetic drift No natural selection ...
Variationand geneticdrift12
... relative frequency are. In evolution what happens to the relative frequency? 2. Explain why variation in a gene poll is important and what the two sources of variation are? 3. Describe genetic drift and the three causes of genetic drift. ...
... relative frequency are. In evolution what happens to the relative frequency? 2. Explain why variation in a gene poll is important and what the two sources of variation are? 3. Describe genetic drift and the three causes of genetic drift. ...
Evolution of Populations
... All of genes found within a population Relative frequency of alleles- proportion of gene pool that the allele makes up ...
... All of genes found within a population Relative frequency of alleles- proportion of gene pool that the allele makes up ...
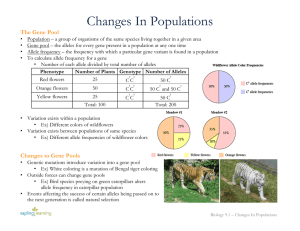
Changes In Populations
... • Ex) Different colors of wildflowers • Variation exists between populations of same species • Ex) Different allele frequencies of wildflower colors ...
... • Ex) Different colors of wildflowers • Variation exists between populations of same species • Ex) Different allele frequencies of wildflower colors ...
ch 4 notes
... Random change in allele frequency over time Can lead to one allele being lost and the other fixed in a population May occur in a group that is endogamous (reproducing only within the group) Gene Flow: Spread of Genes across Population Boundaries Gene flow often refers to migration, though influenced ...
... Random change in allele frequency over time Can lead to one allele being lost and the other fixed in a population May occur in a group that is endogamous (reproducing only within the group) Gene Flow: Spread of Genes across Population Boundaries Gene flow often refers to migration, though influenced ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.