27_3 The Process of Evolution - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... ii. Gene pool – (following Mendel’s laws) the total number of alleles at all the gene loci in all members (that are capable of sexual reproduction) d. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium i. p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 1. p2 = frequency of DD genotype (homozygous dominant) 2. 2pq = frequency of Dd genotype (heterozygou ...
... ii. Gene pool – (following Mendel’s laws) the total number of alleles at all the gene loci in all members (that are capable of sexual reproduction) d. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium i. p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 1. p2 = frequency of DD genotype (homozygous dominant) 2. 2pq = frequency of Dd genotype (heterozygou ...
Lesson Overview Evolution and Ecology
... genotypes. - The result of natural selection is evolution. ...
... genotypes. - The result of natural selection is evolution. ...
Chapter 7.1 , 7.2, and 7.3
... Evolution is the process in which inherited characteristics within a population change over generations, sometimes developing into new species. Scientists continue to develop theories to explain how evolution happens. Evidence that organisms evolve can be found by comparing living organisms to ...
... Evolution is the process in which inherited characteristics within a population change over generations, sometimes developing into new species. Scientists continue to develop theories to explain how evolution happens. Evidence that organisms evolve can be found by comparing living organisms to ...
AP Biology - farishapbio
... 3. Describe the conditions that a population must meet in order to maintain HardyWeinberg equilibrium. Extremely large population size – The smaller the population, the greater the role played by chance fluctuations in allele frequencies from one generation to the next (genetic drift) No gene f ...
... 3. Describe the conditions that a population must meet in order to maintain HardyWeinberg equilibrium. Extremely large population size – The smaller the population, the greater the role played by chance fluctuations in allele frequencies from one generation to the next (genetic drift) No gene f ...
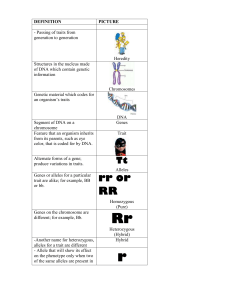
definition - Humble ISD
... -Another name for heterozygous, alleles for a trait are different - Allele that will show its effect on the phenotype only when two of the same alleles are present in ...
... -Another name for heterozygous, alleles for a trait are different - Allele that will show its effect on the phenotype only when two of the same alleles are present in ...
biology Ch. 13 Notes Part b Evolution
... o less common #’s go up from greater food 13.16 Explain what is meant by neutral variation. ✍ Mutations that have no effect, + or -, on the individual ✍ Mutation occurs in __________ region of DNA ✍ Occurs but doesn’t change ___________ significantly 13.17 Give four reasons why natural selec ...
... o less common #’s go up from greater food 13.16 Explain what is meant by neutral variation. ✍ Mutations that have no effect, + or -, on the individual ✍ Mutation occurs in __________ region of DNA ✍ Occurs but doesn’t change ___________ significantly 13.17 Give four reasons why natural selec ...
Evolution and Diversity: Sometimes, differences between organisms
... kind provide advantages for surviving and reproducing in different environments. These selective differences may lead to dramatic changes in characteristics of organisms in a population over extremely long periods of time. KEY IDEA: The diversity and changing of life forms over many generations is t ...
... kind provide advantages for surviving and reproducing in different environments. These selective differences may lead to dramatic changes in characteristics of organisms in a population over extremely long periods of time. KEY IDEA: The diversity and changing of life forms over many generations is t ...
Evolution Learning Objectives
... 6. Describe the four ways that natural selection causes evolution. 7. What is meant by the phrases ‘survival of the fittest”? 8. How do mutations play a role in natural selection? 9. Why is variability (variations) important in populations? 10. Why does natural selection act on phenotype rather than ...
... 6. Describe the four ways that natural selection causes evolution. 7. What is meant by the phrases ‘survival of the fittest”? 8. How do mutations play a role in natural selection? 9. Why is variability (variations) important in populations? 10. Why does natural selection act on phenotype rather than ...
Population Genetics I.
... Gene frequencies will reach an equilibrium when the following conditions are met: •Diploid organism (copy of gene from each parent) •Sexual reproduction •Non-overlapping generations •Random mating •Large population •Equal allele frequencies in the sexes •NO migration, mutation, or selection ...
... Gene frequencies will reach an equilibrium when the following conditions are met: •Diploid organism (copy of gene from each parent) •Sexual reproduction •Non-overlapping generations •Random mating •Large population •Equal allele frequencies in the sexes •NO migration, mutation, or selection ...
Examples of Genetic Drift File
... The last green-eyed person in a small town dies, leaving only brown-eyed and blue-eyed people. An airplane crash introduces the white heron, which loves spotted mackerel, into a population of spotted and unspotted mackerel. Over time, fewer mackerel are born with spots. A man steps on a group of bee ...
... The last green-eyed person in a small town dies, leaving only brown-eyed and blue-eyed people. An airplane crash introduces the white heron, which loves spotted mackerel, into a population of spotted and unspotted mackerel. Over time, fewer mackerel are born with spots. A man steps on a group of bee ...
4Modern Evolution Regents
... – Therefore theories to how variations occur were created. • Mutation Theory • Modern Theory of Natural Selection ...
... – Therefore theories to how variations occur were created. • Mutation Theory • Modern Theory of Natural Selection ...
Powerpoint
... • Now monera (prokaryotes) is divided into two separate kingdoms based on their biochemistry. ...
... • Now monera (prokaryotes) is divided into two separate kingdoms based on their biochemistry. ...
1. a. In allopatric speciation, a physical barrier splits a single
... 1. a. In allopatric speciation, a physical barrier splits a single ancestral population into two or more populations that are no longer able to exchange genes. Because gene flow between the populations is prevented, each population acts as an independent evolutionary lineage. Different mutations wil ...
... 1. a. In allopatric speciation, a physical barrier splits a single ancestral population into two or more populations that are no longer able to exchange genes. Because gene flow between the populations is prevented, each population acts as an independent evolutionary lineage. Different mutations wil ...
Behavioral Objectives:
... o How does misuse of antibiotics affect evolution of disease-causing bacteria like tuberucolosis (PBS video clip) Influence of genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and natural selection on allele frequency in a gene pool. o Bottle neck effect & founder effect Genetic equilibrium – What is it? What co ...
... o How does misuse of antibiotics affect evolution of disease-causing bacteria like tuberucolosis (PBS video clip) Influence of genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and natural selection on allele frequency in a gene pool. o Bottle neck effect & founder effect Genetic equilibrium – What is it? What co ...
Population Genetics
... environment (with certain genetic-based traits have greater reproductive success than others – 3. Individuals with phenotypes that are better adapted to the environment pass more copies of their alleles into next generation – 4. As a result, there is a change in allele frequency overtime ( = microev ...
... environment (with certain genetic-based traits have greater reproductive success than others – 3. Individuals with phenotypes that are better adapted to the environment pass more copies of their alleles into next generation – 4. As a result, there is a change in allele frequency overtime ( = microev ...
Lecture #10 Date
... Microevolution, IV • 2- Gene Flow: genetic exchange due to the migration of fertile individuals or gametes between populations (reduces differences between populations) ...
... Microevolution, IV • 2- Gene Flow: genetic exchange due to the migration of fertile individuals or gametes between populations (reduces differences between populations) ...
Ch.16 Notes - Green Local Schools
... • p = freq. of dominant allele • q = freq. of recessive allele • Phenotype frequency: # of individuals w/ a particular phenotype / total # of individuals ...
... • p = freq. of dominant allele • q = freq. of recessive allele • Phenotype frequency: # of individuals w/ a particular phenotype / total # of individuals ...
Document
... – The population is large • If the population is small, only a small number of organisms may have a certain trait and that trait could easily disappear. Also the addition of a new trait has a higher probability of becoming dominant in a small population • Genetic drift (allele frequency changes in a ...
... – The population is large • If the population is small, only a small number of organisms may have a certain trait and that trait could easily disappear. Also the addition of a new trait has a higher probability of becoming dominant in a small population • Genetic drift (allele frequency changes in a ...
Evolution II Task Review Answers
... 1. Adaptive radiation: a type of divergent evolution that occurs very quickly in a given area, the ancestral finches came from South America and spread to the different islands and adapted to their new environments 2. Double bubble gradualism and punctuated equilibrium Similarity: used to describe t ...
... 1. Adaptive radiation: a type of divergent evolution that occurs very quickly in a given area, the ancestral finches came from South America and spread to the different islands and adapted to their new environments 2. Double bubble gradualism and punctuated equilibrium Similarity: used to describe t ...
Genetic Variation is the Key to Natural Selection
... inbred varieties are crossed, the hybrids show a greater survivorship and growth pattern. • Recessive alleles are hidden. ...
... inbred varieties are crossed, the hybrids show a greater survivorship and growth pattern. • Recessive alleles are hidden. ...
File
... structures illustrate this. They do the same job (have similar appearance and function) but arose from different internal structures. E.g. wings of the bat, insect ...
... structures illustrate this. They do the same job (have similar appearance and function) but arose from different internal structures. E.g. wings of the bat, insect ...
AS90459 Version 2 Describe genetic variation and change Level 2
... Describe requires the student to define, give characteristics of, or an account of. Explain requires the student to provide a reason as to how or why something occurs. Discuss requires the student to show understanding by linking biological ideas. It may involve justifying, relating, evaluating, com ...
... Describe requires the student to define, give characteristics of, or an account of. Explain requires the student to provide a reason as to how or why something occurs. Discuss requires the student to show understanding by linking biological ideas. It may involve justifying, relating, evaluating, com ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.