GETE0305
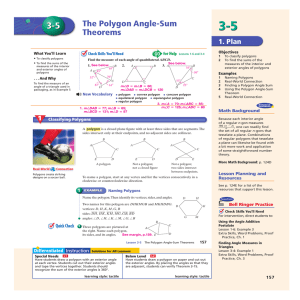
... To name a polygon, start at any vertex and list the vertices consecutively in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. ...
... To name a polygon, start at any vertex and list the vertices consecutively in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. ...
Chapter 13: Geometry: Angles and Polygons
... Many road signs are geometric in shape. In fact, they are often shaped like squares, rectangles, and triangles. You can use geometric properties to classify the shapes of road signs, determine the types of angles found in road signs, and list the similarities and differences among their shapes. You ...
... Many road signs are geometric in shape. In fact, they are often shaped like squares, rectangles, and triangles. You can use geometric properties to classify the shapes of road signs, determine the types of angles found in road signs, and list the similarities and differences among their shapes. You ...
Lesson 3.5 The Polygon Angle
... Convex Polygon: A polygon with no diagonal with points outside the polygon Concave Polygon: A polygon with at least one diagonal with points outside the polygon. ...
... Convex Polygon: A polygon with no diagonal with points outside the polygon Concave Polygon: A polygon with at least one diagonal with points outside the polygon. ...
All the corresponding sides are congruent. All the corresponding
... How many ways can you name pentagon DCBAE? ...
... How many ways can you name pentagon DCBAE? ...
Packet 2 for Unit 2 M2 Geo
... b. What is the sum of one pair of interior and exterior angles for any polygon? c. What is the sum of all of the interior and exterior angles for a polygon with n sides? d. What is the sum of all interior angles for a polygon with n sides? e. Substitute your answers from (c) and (d) into the equatio ...
... b. What is the sum of one pair of interior and exterior angles for any polygon? c. What is the sum of all of the interior and exterior angles for a polygon with n sides? d. What is the sum of all interior angles for a polygon with n sides? e. Substitute your answers from (c) and (d) into the equatio ...
Area of Polygons
... The rectangle is made of the same parts as the parallelogram, so their areas are the same. The area of the rectangle is bh, so the area of the parallelogram is also bh. Warning: Notice that the height h of the parallelogram is the perpendicular distance between two parallel sides of the parallelogra ...
... The rectangle is made of the same parts as the parallelogram, so their areas are the same. The area of the rectangle is bh, so the area of the parallelogram is also bh. Warning: Notice that the height h of the parallelogram is the perpendicular distance between two parallel sides of the parallelogra ...
feb3-7 geometry week3 quads and symmetry
... earned a B.S. degree in Mechanical Engineering in 1972 and a M.S. degree in Nuclear Engineering in 1974. After college he joined the Air Force and later went to work for NASA, where he earned many awards, including awardwinning work for the Galileo Jupiter probe and the Mars Observer project. One of ...
... earned a B.S. degree in Mechanical Engineering in 1972 and a M.S. degree in Nuclear Engineering in 1974. After college he joined the Air Force and later went to work for NASA, where he earned many awards, including awardwinning work for the Galileo Jupiter probe and the Mars Observer project. One of ...
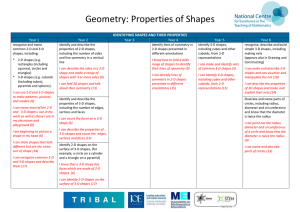
Progression Map: Geometry properties of shapes with
... I can describe the properties of 3-D shapes and count the edges, vertices and faces (13) identify 2-D shapes on the surface of 3-D shapes, [for example, a circle on a cylinder and a triangle on a pyramid] I know that a 3-D shape has faces which are made of 2-D shapes. (6) I can identify 2-D shapes o ...
... I can describe the properties of 3-D shapes and count the edges, vertices and faces (13) identify 2-D shapes on the surface of 3-D shapes, [for example, a circle on a cylinder and a triangle on a pyramid] I know that a 3-D shape has faces which are made of 2-D shapes. (6) I can identify 2-D shapes o ...
Similarity - MrsMcFadin
... When two objects are congruent, they have the same shape and size. Two objects are similar if they have the same shape, but different sizes. Their corresponding parts are all proportional. Any kind of polygon can have two that are similar to each other. ...
... When two objects are congruent, they have the same shape and size. Two objects are similar if they have the same shape, but different sizes. Their corresponding parts are all proportional. Any kind of polygon can have two that are similar to each other. ...
4.1
... • Name corresponding parts of congruent polygons (4-7) • State whether 2 figures are congruent or not (8-9) • Provide reasons in proofs ...
... • Name corresponding parts of congruent polygons (4-7) • State whether 2 figures are congruent or not (8-9) • Provide reasons in proofs ...
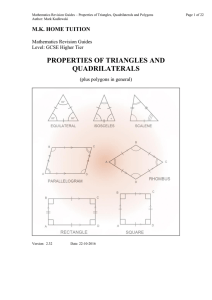
Triangles, quadrilaterals and polygons
... A square also has greater symmetry than a rectangle or a rhombus. There are now four lines of symmetry; two passing through the diagonals AC and BD, and the other two passing through the midpoints of opposite sides at PQ and RS. A square also has rotational symmetry of order 4. The diagonals bisect ...
... A square also has greater symmetry than a rectangle or a rhombus. There are now four lines of symmetry; two passing through the diagonals AC and BD, and the other two passing through the midpoints of opposite sides at PQ and RS. A square also has rotational symmetry of order 4. The diagonals bisect ...
GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT
... By dividing each of the following figures into triangles, show that the formula S = (n – 2) × 180o for the sum of the measures of all interior angles of an n-sided polygon is valid for each of the following polygons: ...
... By dividing each of the following figures into triangles, show that the formula S = (n – 2) × 180o for the sum of the measures of all interior angles of an n-sided polygon is valid for each of the following polygons: ...
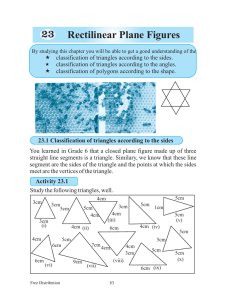
Rectilinear Plane Figures 23 - e
... « Considering the length of the sides of each triangle, separate the triangles on the page 83 into three groups indicating the relevant number of each triangle. « Discuss the characteristics of the triangles in each group. «Accordingly, propose a suitable name for each group. You would have discove ...
... « Considering the length of the sides of each triangle, separate the triangles on the page 83 into three groups indicating the relevant number of each triangle. « Discuss the characteristics of the triangles in each group. «Accordingly, propose a suitable name for each group. You would have discove ...
S1 Lines, angles and polygons
... We can prove this by constructing a line parallel to this side. These alternate angles are equal. These corresponding angles are equal. 5 of 67 ...
... We can prove this by constructing a line parallel to this side. These alternate angles are equal. These corresponding angles are equal. 5 of 67 ...
Progression In Geometry - Woodlands Primary and Nursery School
... Explore line symmetry through regular and irregular polygons – use mirrors to view and be convinced that you have the same shape through reflection. Quadrilateral: A shape with 4 sides, these include: squares, oblongs, trapeziums, rhombus, parallelogram ...
... Explore line symmetry through regular and irregular polygons – use mirrors to view and be convinced that you have the same shape through reflection. Quadrilateral: A shape with 4 sides, these include: squares, oblongs, trapeziums, rhombus, parallelogram ...
Pairs of Angles - St. Landry Parish School Board
... Once the measure of an angle is known, the angle can be classified as one of three types of angles. These types are defined in relation to a right angle. Types of Angles ...
... Once the measure of an angle is known, the angle can be classified as one of three types of angles. These types are defined in relation to a right angle. Types of Angles ...
2.2 Angles and proof - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... A All its sides are equal. B It has four lines of symmetry. C It has four right angles. Copy this table. Complete it by writing each shape name in the correct position. Number of pairs of parallel sides ...
... A All its sides are equal. B It has four lines of symmetry. C It has four right angles. Copy this table. Complete it by writing each shape name in the correct position. Number of pairs of parallel sides ...
Regular polytope
In mathematics, a regular polytope is a polytope whose symmetry is transitive on its flags, thus giving it the highest degree of symmetry. All its elements or j-faces (for all 0 ≤ j ≤ n, where n is the dimension of the polytope) — cells, faces and so on — are also transitive on the symmetries of the polytope, and are regular polytopes of dimension ≤ n. Regular polytopes are the generalized analog in any number of dimensions of regular polygons (for example, the square or the regular pentagon) and regular polyhedra (for example, the cube). The strong symmetry of the regular polytopes gives them an aesthetic quality that interests both non-mathematicians and mathematicians.Classically, a regular polytope in n dimensions may be defined as having regular facets [(n − 1)-faces] and regular vertex figures. These two conditions are sufficient to ensure that all faces are alike and all vertices are alike. Note, however, that this definition does not work for abstract polytopes.A regular polytope can be represented by a Schläfli symbol of the form {a, b, c, ...., y, z}, with regular facets as {a, b, c, ..., y}, and regular vertex figures as {b, c, ..., y, z}.







![arXiv:1007.3607v1 [cs.CG] 21 Jul 2010 On k](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014301021_1-0b834295d3acb0403d454bb0d0019afe-300x300.png)






