* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Packet 2 for Unit 2 M2 Geo
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Surface (topology) wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Shapley–Folkman lemma wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
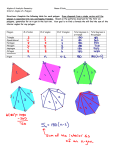
M2 GEOMETRY PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 2 – SECTIONS 1-6 & 6-1 SUM OF ANGLES IN A POLYGON 1. Watch the video at this location, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZIKHV1bvRQ4, for a physical demonstration of the sum of the three angles in a triangle. 2. The diagonals of a polygon are segments connecting any two non-consecutive vertices. a. Name all the diagonals of polygon DEFG shown at right. b. Name all the diagonals of polygon HIJKL shown at right. c. We can define the words convex and concave using diagonals. In a convex polygons, all of the diagonals are inside the figure. What happens with one or more of the diagonals in a concave polygon? 3. Now we’ll find a pattern between the number of sides in a convex polygon and the sum of its angles. Divide the rows up among your group instead of doing them all yourself. a. In the chart on the next page, write the type of polygon that has the given number of sides in the “Type of Polygon” column. b. Find the number of triangles that are formed by drawing all diagonals from the labelled point in each polygon below. Then write this number in the “Number of Triangles” column on the next page. Only the first 5 rows will be used. B A C E D 3 M2 GEOMETRY PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 2 – SECTIONS 1-6 & 6-1 c. The sum of angles in each triangle is 180 ° . Use this fact to find the sum of angles in each polygon in part (b). Write these answers in the first 5 rows of Sum of Interior Angles column of the chart. d. How is the Number of Triangles related to the Number of Sides in each row of the chart? Use this pattern to fill in the number of triangles for 8, 9, and 10 sides. e. Write a formula for the number of triangles in a polygon with n sides. Write this answer in the last row of the Number of Triangles column. f. How is the Sum of Interior Angles related to the Number of Triangles in each row of the chart? Write this as a formula in the last row of the Sum of Interior Angles column, and use your formula to complete the rows for 8, 9, and 10 sides. Chart for #3: Number of Sides Type of Polygon 3 Triangle Number of Triangles 180° 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 n Sum of Interior Angles n-gon 4 M2 GEOMETRY PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 2 – SECTIONS 1-6 & 6-1 The formula you found on the previous page can be used to solve problems involving angles in a polygon. Here are 2 examples: Ex 1: A convex polygon has 13 sides. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles. Ex 2: The measure of an interior angle of a regular polygon is 120. Find the number of sides. (n – 2) ⋅ 180 Let n be the number of sides. Then there are n angles. In a regular polygon, each angle has the same measure (120 in this case). The sum of the measures of all n angles is 120n. (13 – 2) ⋅ 180 Substitute 13 for n. 11 ⋅ 180 1980 120n = (n – 2) ⋅ 180 Both describe the sum of angles. 120n = 180n – 360 Distribute. – 60n = –360 Subtract 180n from both sides. n=6 Divide both sides by – 60. 4. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex polygon with 30 sides. Show your work. 5. Find the number of sides of a regular polygon in which each angle measures 160 ° . Show your work. 6. Find the value of x. 5 M2 GEOMETRY PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 2 – SECTIONS 1-6 & 6-1 EXTERIOR ANGLES OF A POLYGON Exterior angles of a polygon are formed by extending each side of the polygon, as shown in the diagrams on this page. Is there a pattern in the sum of these angles? Let’s find out. 1. Use the diagram of the triangle at right to complete the proof: Given: Triangle with interior angles measuring a°, b°, and c° and exterior angles, ∠1, ∠2, and ∠3 . Prove: ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 = ______ STATEMENTS REASONS 1. a + b + c = 180 1. 2. a + ∠1 = 180 , __ + __ = ____, __ + __ = ____ 2. 3. a + b + c + ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 = 540 3. 4. 180 + ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 = 540 4. 5. 5. Subtraction 2. Complete the proof for the sum of the exterior angles of the quadrilateral at right: Given: Quadrilateral with interior angles measuring a°, b°, c° , and d° and exterior angles, ∠1, ∠2, ∠3 , and ∠4 . Prove: ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 + ∠4 = ______ STATEMENTS REASONS 1. 1. Sum of int ∠ s in a quadrilateral is 360 2. 2. Lin. pairs add up to 180 3. 3. Addition 4. 4. Substitution 5. 5. Subtraction 6 M2 GEOMETRY PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 2 – SECTIONS 1-6 & 6-1 3. Follow the steps to find the sum of the exterior angles of any convex n-gon: a. How many angles are in a polygon with n sides? b. What is the sum of one pair of interior and exterior angles for any polygon? c. What is the sum of all of the interior and exterior angles for a polygon with n sides? d. What is the sum of all interior angles for a polygon with n sides? e. Substitute your answers from (c) and (d) into the equation below. Use x for “sum of ext angles.” sum of all sum of sum of int and ext = + int angles ext angles angles f. Use algebra to solve for x, the sum of the exterior angles of any polygon. g. Complete this statement: The sum of the exterior angles of any convex polygon is ______. 4. Use your rule to find the measure of each exterior angle of a regular polygon with 20 sides. 7 M2 GEOMETRY PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 2 – SECTIONS 1-6 & 6-1 PRACTICE FOR 1-6 & 6-1 Name each polygon by its number of sides and then classify it as convex or concave and regular or irregular. (See p. 1-2 in this packet.) 1. 2. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of each convex polygon. (See p. 4-5 of this packet.) 3. nonagon 4. heptagon The measure of an interior angle of a regular polygon is given. Find the number of sides in the polygon. (See p. 4-5 of this packet.) 5. 108 ° 6. 150 ° Classify the polygon by number of sides, and find the measure of each interior angle. (See p. 4-5 of this packet.) 7. 8. 8 M2 GEOMETRY PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 2 – SECTIONS 1-6 & 6-1 Find the measures of each interior angle of each regular polygon. (See p. 4-5 in this packet.) 9. pentagon 10. Dodecagon (12 sides) Find the measures of each exterior angle of each regular polygon. (See p. 7 in this packet.) 11. octagon 12. nonagon 13. Write an equation, and solve to find the measures of the interior angles in the figure at right. Then find the measures of each exterior angle. 9 M2 GEOMETRY PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 2 – SECTIONS 1-6 & 6-1 Review of 1-6 & 6-1 Name each polygon by its number of sides and then classify it as convex or concave and regular or irregular. 1. 2. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of each convex polygon. 3. 11-gon 4. 14-gon The measure of an interior angle of a regular polygon is given. Find the number of sides in the polygon. 5. 144 ° 6. 156 ° Find the measure of each interior angle. 7. 8. 10 M2 GEOMETRY PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 2 – SECTIONS 1-6 & 6-1 Find the measure of the angle labeled “x” in each diagram. 9. 10. Find the measures of one exterior angle and one interior angle given the number of sides of each regular polygon. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 11. 16 sides 12. 40 sides 11 M2 GEOMETRY PACKET 2 FOR UNIT 2 – SECTIONS 1-6 & 6-1 Answers to review problems: 1. Hexagon, concave, irregular 2. Nonagon, convex, regular 3. 1620 ° 4. 2160 ° 5. 10 sides 6. 15 sides 7. ∠J = 115°, ∠K = 130°, ∠M = 50°, ∠N = 65° 8. ∠R = 128°, ∠T = 128°, ∠S = 52°, ∠U = 52° 9. 78 ° 10. 150 ° 11. Exterior 22.5 ° , interior 157.5 ° 12. Exterior 9 ° , interior 171 ° 12