chapter-3-understanding-quadrilaterals
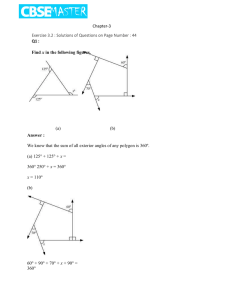
... 78) ABCD is a rhombus. If < ACB = 40°, then < ADB is ___ (a) 40° (b) 45° (c) 50° (d) 60° 79) Four angles of quadrilateral are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 7 : 9 . The greates angle is __ ...
... 78) ABCD is a rhombus. If < ACB = 40°, then < ADB is ___ (a) 40° (b) 45° (c) 50° (d) 60° 79) Four angles of quadrilateral are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 7 : 9 . The greates angle is __ ...
Chapter 3
... b) Not congruent. Many similar triangles can have the same three angles. 4. a) to c) Measure two sides and the contained angle, two angles and any one side, or three sides. Could use a ruler and/or a protractor. d) The triangle are congruent because the chosen measurements were sufficient to describ ...
... b) Not congruent. Many similar triangles can have the same three angles. 4. a) to c) Measure two sides and the contained angle, two angles and any one side, or three sides. Could use a ruler and/or a protractor. d) The triangle are congruent because the chosen measurements were sufficient to describ ...
Answer - CBSEMASTER
... with this condition, the following conditions should also be fulfilled. The sum of the measures of adjacent angles should be 180º. Opposite angles should also be of same measures. (ii) No. Opposite sides AD and BC are of different lengths. (iii) No. Opposite angles A and C have different measures. ...
... with this condition, the following conditions should also be fulfilled. The sum of the measures of adjacent angles should be 180º. Opposite angles should also be of same measures. (ii) No. Opposite sides AD and BC are of different lengths. (iii) No. Opposite angles A and C have different measures. ...
- Triumph Learning
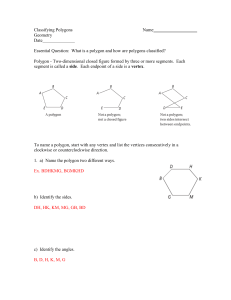
... Look at the polygon on the left of the previous page. All the diagonals of that polygon lie inside the polygon. In fact, any line segment drawn between any two points of that polygon would lie inside the polygon. That is because the polygon on the left is convex. Notice that the polygon on the right ...
... Look at the polygon on the left of the previous page. All the diagonals of that polygon lie inside the polygon. In fact, any line segment drawn between any two points of that polygon would lie inside the polygon. That is because the polygon on the left is convex. Notice that the polygon on the right ...
The Polygon Angle-Sum Theorems
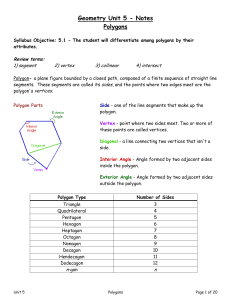
... Essential Understanding The sum of the interior angle measures of a polygon depends on the number of sides the polygon has. By dividing a polygon with n sides into (n - 2) triangles, you can show that the sum of the interior angle measures of any polygon is a multiple of 180. ...
... Essential Understanding The sum of the interior angle measures of a polygon depends on the number of sides the polygon has. By dividing a polygon with n sides into (n - 2) triangles, you can show that the sum of the interior angle measures of any polygon is a multiple of 180. ...
Chapter Four Polygons
... quadrilateral and a circle, will we always be able to draw a quadrilateral inside the circle, whose corners are all on the circumference, and whose angles are the same as the given quadrilateral? What must be true about the quadrilateral for it to be possible? ...
... quadrilateral and a circle, will we always be able to draw a quadrilateral inside the circle, whose corners are all on the circumference, and whose angles are the same as the given quadrilateral? What must be true about the quadrilateral for it to be possible? ...
Regular polytope
In mathematics, a regular polytope is a polytope whose symmetry is transitive on its flags, thus giving it the highest degree of symmetry. All its elements or j-faces (for all 0 ≤ j ≤ n, where n is the dimension of the polytope) — cells, faces and so on — are also transitive on the symmetries of the polytope, and are regular polytopes of dimension ≤ n. Regular polytopes are the generalized analog in any number of dimensions of regular polygons (for example, the square or the regular pentagon) and regular polyhedra (for example, the cube). The strong symmetry of the regular polytopes gives them an aesthetic quality that interests both non-mathematicians and mathematicians.Classically, a regular polytope in n dimensions may be defined as having regular facets [(n − 1)-faces] and regular vertex figures. These two conditions are sufficient to ensure that all faces are alike and all vertices are alike. Note, however, that this definition does not work for abstract polytopes.A regular polytope can be represented by a Schläfli symbol of the form {a, b, c, ...., y, z}, with regular facets as {a, b, c, ..., y}, and regular vertex figures as {b, c, ..., y, z}.