Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Introduction to Cells
... 13. The cell theory makes several fascinating statements about cells! What are three statements mentioned in the video that are included in the cell theory? ...
... 13. The cell theory makes several fascinating statements about cells! What are three statements mentioned in the video that are included in the cell theory? ...
2. a) Protein channels help to move material across the cell
... allowing cells to identify one another 3. The plasma membrane is described to be fluid because of its lipids and membrane proteins that move laterally or sideways throughout the membrane. That means the membrane is not solid, but more like a 'fluid'. The membrane is depicted as mosaic because li ...
... allowing cells to identify one another 3. The plasma membrane is described to be fluid because of its lipids and membrane proteins that move laterally or sideways throughout the membrane. That means the membrane is not solid, but more like a 'fluid'. The membrane is depicted as mosaic because li ...
Cell Size Limitations
... Movement from higher concentration to lower concentration Larger the distance, slower the diffusion rate A cell 20 cm would require months for nutrients to get to the center ...
... Movement from higher concentration to lower concentration Larger the distance, slower the diffusion rate A cell 20 cm would require months for nutrients to get to the center ...
Exercise and Sport Science (BOIL121) Lecture notes
... - has nuclear pores → exchange material with rest of cell - centre of nucleus - one or more nucleoli - site of ribosome production - ribosomes then → cytoplasm through nuclear pores RIBOSOMES: messenger and photocopy of genes - divides into 2 cells - DNA and protein - scattered throughout nucleus - ...
... - has nuclear pores → exchange material with rest of cell - centre of nucleus - one or more nucleoli - site of ribosome production - ribosomes then → cytoplasm through nuclear pores RIBOSOMES: messenger and photocopy of genes - divides into 2 cells - DNA and protein - scattered throughout nucleus - ...
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
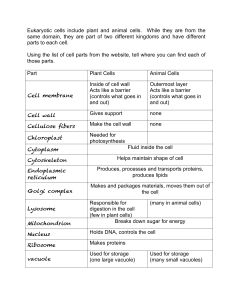
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
1 06 Parts of Cell E.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... special structures called organelles. Many of these tiny structures can be seen only with a transmission electron microscope. The organelles described below are found in both plant and animal cells, although Figure 1 shows an animal cell. ...
... special structures called organelles. Many of these tiny structures can be seen only with a transmission electron microscope. The organelles described below are found in both plant and animal cells, although Figure 1 shows an animal cell. ...
Sections 3
... 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic cells to eukaryotic cells. Discuss what they have in common and what is different between them. ...
... 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic cells to eukaryotic cells. Discuss what they have in common and what is different between them. ...
Chapter 7 1. ______ is a selectively permeable
... 11. When a cell with a cell wall gains water, it is considered ______________ which is normal since the cell is made to withstand pressure. When that same cell loses water, it undergoes __________________. 12. Active transport requires ______________ to keep concentration gradient. For example, the ...
... 11. When a cell with a cell wall gains water, it is considered ______________ which is normal since the cell is made to withstand pressure. When that same cell loses water, it undergoes __________________. 12. Active transport requires ______________ to keep concentration gradient. For example, the ...
PowerPoint
... • PRESSURE: increased pressure (make area smaller) increases transport • CONCENTRATION: increased amounts of solute will increase the transport ...
... • PRESSURE: increased pressure (make area smaller) increases transport • CONCENTRATION: increased amounts of solute will increase the transport ...
Document
... A large, membrane-bound, usually spherical protoplasmic structure within a living cell, containing the cell's hereditary material and controlling its metabolism, growth, and ...
... A large, membrane-bound, usually spherical protoplasmic structure within a living cell, containing the cell's hereditary material and controlling its metabolism, growth, and ...
Homework 1-6 Classifying Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes File
... Biology Homework 1-6 Classifying Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Instructions: Use the clues to decide whether the organism is a Prokaryote or Eukaryote. 1. ___________ - This organism is made of many cells. Each cell has a nucleus, mitochondria and many chloroplasts. It can grow to over 100 ft tall and ...
... Biology Homework 1-6 Classifying Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Instructions: Use the clues to decide whether the organism is a Prokaryote or Eukaryote. 1. ___________ - This organism is made of many cells. Each cell has a nucleus, mitochondria and many chloroplasts. It can grow to over 100 ft tall and ...
Honors Biology Midterm
... 26. Catalase, ligase, polymerase, etc. These are all examples of: 27. Is water a polar compound? 28. Is fructose a monosaccharide? 29. The bonding of water molecules on one another is called: 30. The _________________ of DNA is a nucleotide. 31. Does a decrease in hydrogen ions leads to a decrease i ...
... 26. Catalase, ligase, polymerase, etc. These are all examples of: 27. Is water a polar compound? 28. Is fructose a monosaccharide? 29. The bonding of water molecules on one another is called: 30. The _________________ of DNA is a nucleotide. 31. Does a decrease in hydrogen ions leads to a decrease i ...
Cells Test What do I need to know???? Know the parts of a plant
... Know the parts of a plant and animal cell and their functions or jobs in the cell. Study flash cards and reading. Animal Cell ...
... Know the parts of a plant and animal cell and their functions or jobs in the cell. Study flash cards and reading. Animal Cell ...
Biology_Semester_2_Learning_Targets
... a. Describe properties of water that makes it important to life. b. Explain what chemical compounds are and why they are important to living organisms. c. Describe the composition and role of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. d. Identify biomolecules with the use of indicators. e. ...
... a. Describe properties of water that makes it important to life. b. Explain what chemical compounds are and why they are important to living organisms. c. Describe the composition and role of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. d. Identify biomolecules with the use of indicators. e. ...
Life Science
... Composed of a network of protein fibers called microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Cytoskeleton Function 1. gives cells support and helps the cell keep its shape 2. anchors organelles into a certain position or allows them to move around in the cell 3. allows cells to move by ...
... Composed of a network of protein fibers called microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Cytoskeleton Function 1. gives cells support and helps the cell keep its shape 2. anchors organelles into a certain position or allows them to move around in the cell 3. allows cells to move by ...
Cell Processes Study Guide
... How things move into and out of cells Know the following terms: Diffusion – movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Osmosis – the diffusion of water through a membrane Active/Passive transport – diffusion of molecules through a protein channel that ar ...
... How things move into and out of cells Know the following terms: Diffusion – movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Osmosis – the diffusion of water through a membrane Active/Passive transport – diffusion of molecules through a protein channel that ar ...
Chapter 4
... e) Five main components of eukaryotic cells include nucleus, organelles, cytosol, cytoskeleton, and plasma membrane: Figure 4.3 ...
... e) Five main components of eukaryotic cells include nucleus, organelles, cytosol, cytoskeleton, and plasma membrane: Figure 4.3 ...
Cell Transport - Bartlett High School
... ●Regulates what comes in and out of the cell ●Main components: proteins and phospholipids ...
... ●Regulates what comes in and out of the cell ●Main components: proteins and phospholipids ...
L4 Prokaryotes eukaryotes and onion cheek preps
... Much simpler in structure, lack membrane bound organelles (mitochondria, chloroplasts). Lack complex structures such as Golgi bodies, cytoskeleton and lysosomes. • Nucleotide (or Nuclear Zone). The region of the cytoplasm that contains DNA. It is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. • DNA. Always c ...
... Much simpler in structure, lack membrane bound organelles (mitochondria, chloroplasts). Lack complex structures such as Golgi bodies, cytoskeleton and lysosomes. • Nucleotide (or Nuclear Zone). The region of the cytoplasm that contains DNA. It is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. • DNA. Always c ...
Rough ER Ribosome Protein
... a. The “distribution center” of the cell b. Made of many flattened sacks of membrane c. Proteins are sorted for export or use d. Vesicles bud off as transport boxes i. ...
... a. The “distribution center” of the cell b. Made of many flattened sacks of membrane c. Proteins are sorted for export or use d. Vesicles bud off as transport boxes i. ...
Chapter 1.3 cell processes_1
... and waxes are all lipids our bodies store for later use. • Proteins : made of carbon, hydrogen, • Oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Great for increasing the cell’s functions and speeding up the enzymes for metabolism. ...
... and waxes are all lipids our bodies store for later use. • Proteins : made of carbon, hydrogen, • Oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Great for increasing the cell’s functions and speeding up the enzymes for metabolism. ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.