STUDY GUIDE Cells/Membrane Transport Cell Organelles What`s
... shrinks = more water inside the cell, so water will leave it ...
... shrinks = more water inside the cell, so water will leave it ...
Diffusion - Union High School
... Aquaporins- Water channel proteins that allow water to pass through them. ...
... Aquaporins- Water channel proteins that allow water to pass through them. ...
BIOL108 LECTURE NOTES
... o Hydrogen bonding keeps water liquid – between 0 and 100C o Water is a universal solvent – facilitates chemical reactions o Hydrogen bonding gives water cohesion – used for transport o Hydrogen bonding means that large amounts of energy must be gained or lost for water temperature to change signifi ...
... o Hydrogen bonding keeps water liquid – between 0 and 100C o Water is a universal solvent – facilitates chemical reactions o Hydrogen bonding gives water cohesion – used for transport o Hydrogen bonding means that large amounts of energy must be gained or lost for water temperature to change signifi ...
Unit 7 Diffusion and Osmosis
... water and eliminate wastes. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable – it will allow some things to pass through, while blocking other things. ...
... water and eliminate wastes. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable – it will allow some things to pass through, while blocking other things. ...
File osmosis @ diffusion guided notes 6b
... 3. Active ________________Diffusion – is the process by which _________________________ of __________________________ to an area of lower concentration – diffusion is the main method by which small molecules move across the cell membrane! What causes diffusion? Molecules are always moving and as a r ...
... 3. Active ________________Diffusion – is the process by which _________________________ of __________________________ to an area of lower concentration – diffusion is the main method by which small molecules move across the cell membrane! What causes diffusion? Molecules are always moving and as a r ...
Organelles - Fcusd.org
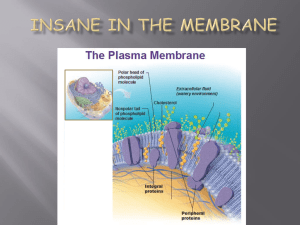
... proteins embedded in the layers. Proteins can act as channels for molecules to move through membrane & allow communication with environment. ...
... proteins embedded in the layers. Proteins can act as channels for molecules to move through membrane & allow communication with environment. ...
Unit 4: Cells and Transport Short Answer Five of
... Five of the following will be chosen for the Short Answer portion of the exam. 1. What do all cells have in common? 2. How can you tell the difference between a plant and an animal cell? List at least 3 differences. ...
... Five of the following will be chosen for the Short Answer portion of the exam. 1. What do all cells have in common? 2. How can you tell the difference between a plant and an animal cell? List at least 3 differences. ...
Animal Cell - Eagan High School
... Helps the cell maintain its shape. Assists with movement of materials Serve as “tracks” along which organelles move Form cilia & flagella too Assist in movement of DNA (chromosomes) in mitosis ...
... Helps the cell maintain its shape. Assists with movement of materials Serve as “tracks” along which organelles move Form cilia & flagella too Assist in movement of DNA (chromosomes) in mitosis ...
CellMembranes - Mexico Central School District
... -Not attracted to the water -Also called NON-POLAR A Phospholipid AS Biology. Foundation. Cell membranes and Transport ...
... -Not attracted to the water -Also called NON-POLAR A Phospholipid AS Biology. Foundation. Cell membranes and Transport ...
Cell Organelles BioH
... What is the difference between the two parts of the ER? Rough ER – has ribosomes and process proteins Smooth ER – no ribosomes, makes lipids ...
... What is the difference between the two parts of the ER? Rough ER – has ribosomes and process proteins Smooth ER – no ribosomes, makes lipids ...
Ch 3 Notes Outline
... Biologists classify cells into two broad categories: Both have: Internal Structure of Eukaryotic Cells: Evolutionary History of the Animal Cell The first cells to arise were: _________________ which is lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus. Prokaryotic cells today are represented by __________________ ...
... Biologists classify cells into two broad categories: Both have: Internal Structure of Eukaryotic Cells: Evolutionary History of the Animal Cell The first cells to arise were: _________________ which is lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus. Prokaryotic cells today are represented by __________________ ...
Cellular Structures and Organelles
... HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID Bilayer (two layers) with POLAR heads facing the water and NON-POLAR tails facing away from the water ...
... HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID Bilayer (two layers) with POLAR heads facing the water and NON-POLAR tails facing away from the water ...
Document
... enzymes to break down macromolecules -destroy cells or foreign matter that the cell has engulfed by phagocytosis ...
... enzymes to break down macromolecules -destroy cells or foreign matter that the cell has engulfed by phagocytosis ...
File
... What is a centriole? In what type of cell (plant or animal) is it found? What does it do for the cell? ...
... What is a centriole? In what type of cell (plant or animal) is it found? What does it do for the cell? ...
CELLS UNIT 1 Learning Targets - Milton
... Draw/create a bacteria, plant, and animal cell and place the appropriate organelles in each cell type. Name the four cell structures in common to all cell types. Describe Anton Van Leeuwen hoek’s contribution to cellular biology. List the three principles of the cell theory. Describe the function of ...
... Draw/create a bacteria, plant, and animal cell and place the appropriate organelles in each cell type. Name the four cell structures in common to all cell types. Describe Anton Van Leeuwen hoek’s contribution to cellular biology. List the three principles of the cell theory. Describe the function of ...
CELL TRANSPORT - Oncourse : Gateway : Home
... across the cell membrane Requires no energy from the cell Diffusion is the simplest type of passive transport ...
... across the cell membrane Requires no energy from the cell Diffusion is the simplest type of passive transport ...
CLONING
... An electric shock is used to start the cell dividing to form embryo cells These embryo cells contain the same genetic information as the adult skin cell When the embryo has developed into a ball of cells, it is inserted into the womb of an adult female to continue its development ...
... An electric shock is used to start the cell dividing to form embryo cells These embryo cells contain the same genetic information as the adult skin cell When the embryo has developed into a ball of cells, it is inserted into the womb of an adult female to continue its development ...
File
... Capsule- Outside the cell wall. For additional protection. Plasma membrane- Regulates what crosses into the cell Nucleiod Region- where circular DNA is found Ribosomes- Workbench, where proteins are made ...
... Capsule- Outside the cell wall. For additional protection. Plasma membrane- Regulates what crosses into the cell Nucleiod Region- where circular DNA is found Ribosomes- Workbench, where proteins are made ...
cell functions for chart File
... - stores water, wastes, and sometimes, fat. - more than one per animal cell. ...
... - stores water, wastes, and sometimes, fat. - more than one per animal cell. ...
Cell Labeling Worksheet Instructions: Using the Organelle List
... Instructions: Using the Organelle List below, write each organelle term next to its function description. By doing so, you will also be labeling the cell parts in your model. “DNA,” “nucleus,” and “flagellum” are already filled in for you as an example. Organelle List: DNA, nucleus, flagellum, cell ...
... Instructions: Using the Organelle List below, write each organelle term next to its function description. By doing so, you will also be labeling the cell parts in your model. “DNA,” “nucleus,” and “flagellum” are already filled in for you as an example. Organelle List: DNA, nucleus, flagellum, cell ...
Transport across cell membranes
... Channel proteins and carrier proteins help larger molecules cross the membrane Many channels are gated for regulation Carrier proteins change shape to move molecules through More specific than simple diffusion but still does not require energy ...
... Channel proteins and carrier proteins help larger molecules cross the membrane Many channels are gated for regulation Carrier proteins change shape to move molecules through More specific than simple diffusion but still does not require energy ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.