eprint_10_27669_1347
... Cytology : is the study of the structure and function of cells. Cytoplasm : is the area of space outside the nucleus but which is contained within the cell membrane. It contains the organelles and fluid. The organelles are tiny structures in the cytoplasm which perform various jobs for the cel ...
... Cytology : is the study of the structure and function of cells. Cytoplasm : is the area of space outside the nucleus but which is contained within the cell membrane. It contains the organelles and fluid. The organelles are tiny structures in the cytoplasm which perform various jobs for the cel ...
Cell practice problem
... B. store wastes in both plants and animals C. use energy from the sun to make food D. are in the nuclei of plant and animal cells 2. While viewing a slide of rapidly moving sperm cells, a student concludes that these cells require a large amount of energy to maintain their activity. The organelles t ...
... B. store wastes in both plants and animals C. use energy from the sun to make food D. are in the nuclei of plant and animal cells 2. While viewing a slide of rapidly moving sperm cells, a student concludes that these cells require a large amount of energy to maintain their activity. The organelles t ...
Chapter 3 THE CELL
... o Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes. o Eukaryotes are usually made up of many cells, like people, dogs, fish, plants, etc. o Sometimes though they are living one cell organisms like fungi or protist. ...
... o Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes. o Eukaryotes are usually made up of many cells, like people, dogs, fish, plants, etc. o Sometimes though they are living one cell organisms like fungi or protist. ...
Plant Cells - New Brigden School
... Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. The organelles are only found in plant cells and some protests such as algae. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts work to convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells. The entire process is called photosynthesi ...
... Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. The organelles are only found in plant cells and some protests such as algae. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts work to convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells. The entire process is called photosynthesi ...
Understanding Our Environment
... - Contain stroma - Enzyme-filled matrix. - Contain grana made up of thylakoids. Thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll. Chromoplasts and Leucoplasts are additional plastids found in many plants. ...
... - Contain stroma - Enzyme-filled matrix. - Contain grana made up of thylakoids. Thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll. Chromoplasts and Leucoplasts are additional plastids found in many plants. ...
Cell Biology FR Review
... Explain how the plasma membrane contributes to the regulation of the cell. • Membrane proteins allow for large polar molecules and ions to enter the cell via specific channels. • Non-polar molecules are free to diffuse into the cell. • Pump proteins are able to “grab” substances using active transp ...
... Explain how the plasma membrane contributes to the regulation of the cell. • Membrane proteins allow for large polar molecules and ions to enter the cell via specific channels. • Non-polar molecules are free to diffuse into the cell. • Pump proteins are able to “grab” substances using active transp ...
Cell Structure & Function
... • Site of protein synthesis • Made up of rRNA and proteins • Not surrounded by a membrane • Located in the cytoplasm or attached to ...
... • Site of protein synthesis • Made up of rRNA and proteins • Not surrounded by a membrane • Located in the cytoplasm or attached to ...
Homeostasis Keystone Questions of the Day Key
... concentration of carbon dioxide inside the cell is greater than the concentration outside the cell. How are the small molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide moving through the cell membrane? A. passive transport by diffusion B. active transport by endocytosis C. passive transport by osmosis D. activ ...
... concentration of carbon dioxide inside the cell is greater than the concentration outside the cell. How are the small molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide moving through the cell membrane? A. passive transport by diffusion B. active transport by endocytosis C. passive transport by osmosis D. activ ...
1.2 Notes
... goes in and out of cell Directs cell’s activities Protects nucleus by controlling what goes in and out of nucleus Contains genetic material ...
... goes in and out of cell Directs cell’s activities Protects nucleus by controlling what goes in and out of nucleus Contains genetic material ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide - Conackamack Middle School
... a. Eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes i. Definitions of each ii. Differences between the two b. Organelles of the plant and animal cells i. Structure of each ii. Function of each c. Similarities/Differences of plant and animal cells d. Vocabulary to include – organelle, cell membrane, cell wall, vacuole, ly ...
... a. Eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes i. Definitions of each ii. Differences between the two b. Organelles of the plant and animal cells i. Structure of each ii. Function of each c. Similarities/Differences of plant and animal cells d. Vocabulary to include – organelle, cell membrane, cell wall, vacuole, ly ...
Cells: Organelles, Membranes and Communication Test Review
... Know what each of the organelles covered in your class and book does and why the cell needs it - why would it have more than average number of them? What would happen if you got rid of them? Be able to recognize and explain where and how each of the organelles formed (endosymbiosis or invaginati ...
... Know what each of the organelles covered in your class and book does and why the cell needs it - why would it have more than average number of them? What would happen if you got rid of them? Be able to recognize and explain where and how each of the organelles formed (endosymbiosis or invaginati ...
Cellular Movement and Cell Energy Worksheets
... Passive transport is the movement of substances through a cell membrane without using the cell’s ___________________. ...
... Passive transport is the movement of substances through a cell membrane without using the cell’s ___________________. ...
Unit Three
... All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells Cells are the smallest living things, the basic unit of organization of all organisms Cells arise only by the division of a previously existing cell ...
... All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells Cells are the smallest living things, the basic unit of organization of all organisms Cells arise only by the division of a previously existing cell ...
Review Puzzle
... 7. Converts light energy for plants 8. Holds genetic information 9. Where proteins are made 10. Tissues working together 11. Digests waste material 12. Tool used to view cells 13. Stores water, food, & waste 14. Organs working together 15. Package and secrete proteins 16. Cells working together 17. ...
... 7. Converts light energy for plants 8. Holds genetic information 9. Where proteins are made 10. Tissues working together 11. Digests waste material 12. Tool used to view cells 13. Stores water, food, & waste 14. Organs working together 15. Package and secrete proteins 16. Cells working together 17. ...
CHAPTER 3 CELLS unit of life
... It is a container of chemicals. But, it's different than non-living containers of chemicals. Cells (living containers of chemicals) : are very organized and made of complex chemicals (eg. proteins, carbohydrates, DNA, fats) take nutrients from the environment for their own use can repair themselves ...
... It is a container of chemicals. But, it's different than non-living containers of chemicals. Cells (living containers of chemicals) : are very organized and made of complex chemicals (eg. proteins, carbohydrates, DNA, fats) take nutrients from the environment for their own use can repair themselves ...
Types of Transport
... • bind to a specific type of diffusing molecule. • have a highly specific hydrophilic region to which the solute molecule binds. • binding cause the protein to undergo a change in shape that moves the solute across the bilayer and release it on the other side ...
... • bind to a specific type of diffusing molecule. • have a highly specific hydrophilic region to which the solute molecule binds. • binding cause the protein to undergo a change in shape that moves the solute across the bilayer and release it on the other side ...
The Cell: Organelles and Functions
... Cilia and Flagella Form: “Hair” or “Whip-like” extensions from the cell made of microtubules Function: ...
... Cilia and Flagella Form: “Hair” or “Whip-like” extensions from the cell made of microtubules Function: ...
Cells - Wsfcs
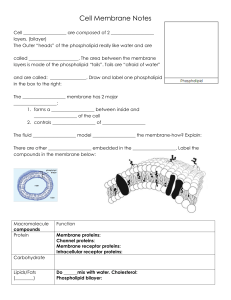
... 17. Why can cells not survive if they are totally isolated from their environment? 18. What controls what enters or leaves a cell? 19. Define selectively permeable. 20. Describe the phospholipid make up of cell membranes. 21. Cells are bathed in an aqueous environment. What does this mean? 22. Sketc ...
... 17. Why can cells not survive if they are totally isolated from their environment? 18. What controls what enters or leaves a cell? 19. Define selectively permeable. 20. Describe the phospholipid make up of cell membranes. 21. Cells are bathed in an aqueous environment. What does this mean? 22. Sketc ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.