The Cell Theory consists of three main points: What is Biology?
... What is Biology? ______________________________________________________________ Inside a Cell An ______________________ is a cell ___________________ in which functions are ...
... What is Biology? ______________________________________________________________ Inside a Cell An ______________________ is a cell ___________________ in which functions are ...
Introduction to Cell Structure and Function.
... Cilia - short and numerous • Flagella - long, single (Moveable portions of the cytoskeleton that project from the surface of the cell) ...
... Cilia - short and numerous • Flagella - long, single (Moveable portions of the cytoskeleton that project from the surface of the cell) ...
CELL DIVISION
... 2. Mitosis: Cell reproduces itself; get two daughter cells 3. Cytokinesis: Cell’s cytoplasm divides, creating a new cell -Prior to cell division, must always have a duplication of genetic material DNA Replication Chromosome: Structure that contains genetic material passed from generation to genera ...
... 2. Mitosis: Cell reproduces itself; get two daughter cells 3. Cytokinesis: Cell’s cytoplasm divides, creating a new cell -Prior to cell division, must always have a duplication of genetic material DNA Replication Chromosome: Structure that contains genetic material passed from generation to genera ...
The Diversity of Cells Note-taking Guide (Chapter 3: Section 1
... Mattheis Schleiden Theodor Schwann Rudolf Virchow ...
... Mattheis Schleiden Theodor Schwann Rudolf Virchow ...
Section 3: Cell Organelles
... Summarize the importance of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells. Identify three structure in plant cells that are absent from animal cells. ...
... Summarize the importance of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells. Identify three structure in plant cells that are absent from animal cells. ...
Cheek Cell Lab
... 7. Once you think you have located a cell, switch to high power and refocus. (Remember, do NOT use the coarse adjustment knob at this point) ...
... 7. Once you think you have located a cell, switch to high power and refocus. (Remember, do NOT use the coarse adjustment knob at this point) ...
Cell Vocabulary
... 9. Golgi Apparatus (Body)- Receives material from Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) like the mailroom because it stacks, ships, and sends parts from ER to the other parts of cell. Both Cells. 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum- Ribosomes are attached giving it a bumpy look. Used for protein synthesis and brea ...
... 9. Golgi Apparatus (Body)- Receives material from Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) like the mailroom because it stacks, ships, and sends parts from ER to the other parts of cell. Both Cells. 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum- Ribosomes are attached giving it a bumpy look. Used for protein synthesis and brea ...
Cell Transport
... the concentration of solute is lower outside the cell than inside the cell Have more water outside the cell so water moves into the cell Causes an increase in pressure inside the cell: called turgor pressure (plants) or osmotic pressure (animals). Increase in pressure in animal cells causes them to ...
... the concentration of solute is lower outside the cell than inside the cell Have more water outside the cell so water moves into the cell Causes an increase in pressure inside the cell: called turgor pressure (plants) or osmotic pressure (animals). Increase in pressure in animal cells causes them to ...
cell organelle vocabulary quiz
... 1. Any living thing. Some may exist as a single cell (unicellular) but most are made of many cells (multicellular) such as plants and animals. ...
... 1. Any living thing. Some may exist as a single cell (unicellular) but most are made of many cells (multicellular) such as plants and animals. ...
Cells
... features to help a cell carry out its functions. Cell membrane: Surrounds the cell and controls movement of substances in and out. Nucleus: Contains genetic material (DNA) which controls the cell's activities. Vacuole: Area in a cell that contains liquid, and can be used by plants to keep the cell r ...
... features to help a cell carry out its functions. Cell membrane: Surrounds the cell and controls movement of substances in and out. Nucleus: Contains genetic material (DNA) which controls the cell's activities. Vacuole: Area in a cell that contains liquid, and can be used by plants to keep the cell r ...
Unit 2: Multi-cellular organisms
... 17. DNA can be transferred naturally from one cell to another. DNA can also be transferred by genetic ENGINEERING. 18. During GENETIC engineering, the section of DNA that contains the required GENE is identified and cut out of the source CHROMOSOME. Then the gene is inserted into a vector such as a ...
... 17. DNA can be transferred naturally from one cell to another. DNA can also be transferred by genetic ENGINEERING. 18. During GENETIC engineering, the section of DNA that contains the required GENE is identified and cut out of the source CHROMOSOME. Then the gene is inserted into a vector such as a ...
Cells - Educator Pages
... Function - All cell contents that lie between the cell membrane and the nucleus. (organelles + cytosol) Cytosol - liquid portion/non-organelles. Structure - made up of fluid and organelles except for nucleus ...
... Function - All cell contents that lie between the cell membrane and the nucleus. (organelles + cytosol) Cytosol - liquid portion/non-organelles. Structure - made up of fluid and organelles except for nucleus ...
Cell Structure and Function There are two types of cells: Prokaryotes
... diameter, the smallest Mycoplasma bacteria are only 0.2 micrometers across, and even the best light microscopes can barely see so small them. The biggest cell, a giant amoeba Chaos chaos may be 1000 micrometers in diameter, which is large enough to be seen unaided as a tiny speck in pond water. Desp ...
... diameter, the smallest Mycoplasma bacteria are only 0.2 micrometers across, and even the best light microscopes can barely see so small them. The biggest cell, a giant amoeba Chaos chaos may be 1000 micrometers in diameter, which is large enough to be seen unaided as a tiny speck in pond water. Desp ...
sept-9-cells-bread-on
... 3. (4 pts.) The differences between Matt and Maria in The House of the Scorpion are much like the differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the missing blanks below with either the word “plant” or “animal” then fully describe (using complete sentences) why you paired each character with e ...
... 3. (4 pts.) The differences between Matt and Maria in The House of the Scorpion are much like the differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the missing blanks below with either the word “plant” or “animal” then fully describe (using complete sentences) why you paired each character with e ...
What is the difference in the functioning between rough ER and
... Rough ER is used by animal cells, while smooth ER is only used by plant cells. ...
... Rough ER is used by animal cells, while smooth ER is only used by plant cells. ...
Chapter 5
... to stimulus (chemical or electrical) – 3 conditions determine direction • Relative concentration on either side of membrane • Voltage differences across membrane • Gated channels – channel open or closed ...
... to stimulus (chemical or electrical) – 3 conditions determine direction • Relative concentration on either side of membrane • Voltage differences across membrane • Gated channels – channel open or closed ...
klathrop/Plasma Membrane unit Vocabulary
... Diffusion - the movement of molecules in a fluid from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration, (driven by a concentration gradient.) Example: If you put a drop of food coloring in pure water, with out siring or shaking the dye will eventually become distributed even throughout ...
... Diffusion - the movement of molecules in a fluid from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration, (driven by a concentration gradient.) Example: If you put a drop of food coloring in pure water, with out siring or shaking the dye will eventually become distributed even throughout ...
Lesson 1 study sheet
... Study Sheet How Do Plant and Animal Cells Differ? Chapter 1, Lesson 1 Page 50-59 Learning Targets (What must I be able to do to reach mastery?) 1. I can describe the functions of these organelles: chloroplast, cell wall, nucleus, chromosome, DNA, endoplasmic reticulum, membrane, vacuole, cytoplasm, ...
... Study Sheet How Do Plant and Animal Cells Differ? Chapter 1, Lesson 1 Page 50-59 Learning Targets (What must I be able to do to reach mastery?) 1. I can describe the functions of these organelles: chloroplast, cell wall, nucleus, chromosome, DNA, endoplasmic reticulum, membrane, vacuole, cytoplasm, ...
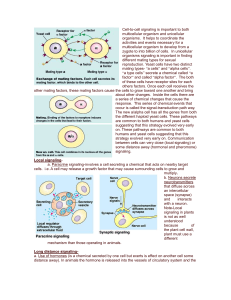
Long distance signaling
... b. Tyrosine-Kinase receptors-are receptors that when activated can activate more than one signal-transduction pathway at one time. This is important when an event like cell reproduction requires a number of biochemical pathways to be activated at once. The tyrosine-kinase receptor in the inactive fo ...
... b. Tyrosine-Kinase receptors-are receptors that when activated can activate more than one signal-transduction pathway at one time. This is important when an event like cell reproduction requires a number of biochemical pathways to be activated at once. The tyrosine-kinase receptor in the inactive fo ...
A View of the Cell
... • The observations + conclusions of these scientists are summarized as one fundamental idea of modern biology – the Cell Theory: – All organisms are composed of one or more cells – The cell is the basic unit of structure + organization of organisms – All cells come from preexisting cells ...
... • The observations + conclusions of these scientists are summarized as one fundamental idea of modern biology – the Cell Theory: – All organisms are composed of one or more cells – The cell is the basic unit of structure + organization of organisms – All cells come from preexisting cells ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.