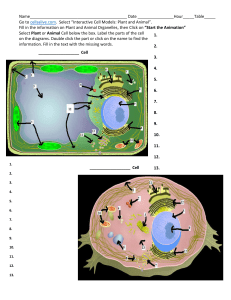
DW#4 CellsAlive Websearch
... Genes within the chromatin are made of 5. ____________________________ (DNA). The DNA stores the organism’s entire encoded genetic information. The DNA is similar in every cell of the body, but depending on the specific cell type, some genes may be turned on or off - that's why a liver cell is diffe ...
... Genes within the chromatin are made of 5. ____________________________ (DNA). The DNA stores the organism’s entire encoded genetic information. The DNA is similar in every cell of the body, but depending on the specific cell type, some genes may be turned on or off - that's why a liver cell is diffe ...
Study Guide, Section 2
... 6. Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers and line up along the equator of the cell during metaphase. 7. The nucleus reappears during prophase. 8. Centrioles migrate to the poles of the cell during telophase. 9. Chromatids are pulled apart during anaphase. 10. The first stage of mitosis is telophase. ...
... 6. Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers and line up along the equator of the cell during metaphase. 7. The nucleus reappears during prophase. 8. Centrioles migrate to the poles of the cell during telophase. 9. Chromatids are pulled apart during anaphase. 10. The first stage of mitosis is telophase. ...
Effects of electric field on mast cells Dan Zhu, Zu-Hui Wu, Ji
... Effects of electric field on mast cells Dan Zhu, Zu-Hui Wu, Ji-Yao Chen and Lu-Wei Zhou Soft-matter Laboratory, State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics, and Department of Physics Fudan Univiversity, Shanghai, China Mast cell is a kind of immune cells which is sensitive to physical stimuli such as el ...
... Effects of electric field on mast cells Dan Zhu, Zu-Hui Wu, Ji-Yao Chen and Lu-Wei Zhou Soft-matter Laboratory, State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics, and Department of Physics Fudan Univiversity, Shanghai, China Mast cell is a kind of immune cells which is sensitive to physical stimuli such as el ...
The Cell Membrane
... Membrane is a collage of proteins & other molecules embedded in the fluid matrix of the lipid bilayer ...
... Membrane is a collage of proteins & other molecules embedded in the fluid matrix of the lipid bilayer ...
Exercises - Tiwari Academy
... What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down? Answer 3: Plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane of the cell that maintains its homeostasis, i.e., constant internal composition of the cell. If it ruptures or breaks down the constant internal chemical composition of the ...
... What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down? Answer 3: Plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane of the cell that maintains its homeostasis, i.e., constant internal composition of the cell. If it ruptures or breaks down the constant internal chemical composition of the ...
Doellman, Cell Structure and Function Unit Exam
... 32. You have just discovered a mutant plant that no one else has ever seen before. This plant is very unusual because its cells do not contain a cell wall. Predict how the lack of cell wall will impact the plant’s survival on Earth. (Hint: What will it look like? What accommodations will it have to ...
... 32. You have just discovered a mutant plant that no one else has ever seen before. This plant is very unusual because its cells do not contain a cell wall. Predict how the lack of cell wall will impact the plant’s survival on Earth. (Hint: What will it look like? What accommodations will it have to ...
the - myndrs.com
... A stack of saccules that prepares secretory vesicles is known as a: A. Plastid. B. Lysosome. C. Nucleolus. D. Golgi body. ...
... A stack of saccules that prepares secretory vesicles is known as a: A. Plastid. B. Lysosome. C. Nucleolus. D. Golgi body. ...
Chapter 3
... no energy from the cell (diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and filtration). Where does the energy for passive transport come from? Is a cell required for these mechanisms to occur? diffusion: from area of ___________ concentration to area of ____________ concentration to reach _____________ ...
... no energy from the cell (diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and filtration). Where does the energy for passive transport come from? Is a cell required for these mechanisms to occur? diffusion: from area of ___________ concentration to area of ____________ concentration to reach _____________ ...
Cells 10th class
... • Ribosomes are small round organelles that make proteins based on the instructions provided by the DNA. • Ribosomes are located in the cytosol or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. ...
... • Ribosomes are small round organelles that make proteins based on the instructions provided by the DNA. • Ribosomes are located in the cytosol or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. ...
Cells and Their Organelles
... Mitochondria are spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections called cristae. The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell. Color and label the mitochond ...
... Mitochondria are spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections called cristae. The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell. Color and label the mitochond ...
Golgi apparatus
... • The basic processes necessary for living things to survive are the same for a single cell as they are for a more complex organism. • A single-celled organism has to conduct all life processes by itself. • A multi-cellular organism has groups of cells that specialize to perform specific functions. ...
... • The basic processes necessary for living things to survive are the same for a single cell as they are for a more complex organism. • A single-celled organism has to conduct all life processes by itself. • A multi-cellular organism has groups of cells that specialize to perform specific functions. ...
Cells
... regardless of internal and external conditions. Survival depends on the cell’s ability to maintain the proper conditions within itself. What is this called???? ...
... regardless of internal and external conditions. Survival depends on the cell’s ability to maintain the proper conditions within itself. What is this called???? ...
Cellular transport
... Plant cells like a hypotonic environment (water flows in) Their strong cell walls withstand the osmotic pressure that can cause animal cells to burst or shrivel ...
... Plant cells like a hypotonic environment (water flows in) Their strong cell walls withstand the osmotic pressure that can cause animal cells to burst or shrivel ...
August 24, 2010 Dr. Cynthia Smas Distinguish the major kinetic
... Dr. Cynthia Smas 1. Distinguish the major kinetic difference(s) between simple and facilitated diffusion a. Facilitated diffusion through transport-specific carriers acts to accelerate a reaction that is already thermodynamically favorable b. Facilitated diffusion (carrier- or ion channel-mediated) ...
... Dr. Cynthia Smas 1. Distinguish the major kinetic difference(s) between simple and facilitated diffusion a. Facilitated diffusion through transport-specific carriers acts to accelerate a reaction that is already thermodynamically favorable b. Facilitated diffusion (carrier- or ion channel-mediated) ...
Cells are often called the “building blocks of life”. They are the basic
... A large, membrane-bound sac filled with fluid that stores, water, food, waste, and other substances in which the cell processes. This gives the cell its shape. ...
... A large, membrane-bound sac filled with fluid that stores, water, food, waste, and other substances in which the cell processes. This gives the cell its shape. ...
chapter04
... Most eukaryotic cells are surrounded by a glycocalix, or cell coat, formed by polysaccharide side chains of proteins (glycoproteins) and lipids (glycolipids) that are part of the plasma membrane. Molecules of the ECM allow cells to recognize one another, make contact and form associations. Other mol ...
... Most eukaryotic cells are surrounded by a glycocalix, or cell coat, formed by polysaccharide side chains of proteins (glycoproteins) and lipids (glycolipids) that are part of the plasma membrane. Molecules of the ECM allow cells to recognize one another, make contact and form associations. Other mol ...
ch_03 - HCC Learning Web
... Three nonmembranous organelles are found in eukaryotes: ribosomes, a cytoskeleton, and centrioles. Eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S rather than 70S and are found within the cytosol as well as attached to the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum, discussed shortly. The cytoskeleton is extensive and is ...
... Three nonmembranous organelles are found in eukaryotes: ribosomes, a cytoskeleton, and centrioles. Eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S rather than 70S and are found within the cytosol as well as attached to the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum, discussed shortly. The cytoskeleton is extensive and is ...
cell structure packet
... 4. The cell wall is what makes plants __________. 5. List three important things that can pass through the cell wall of a plant. 6. Besides a plant, what other kind of cell has a cell wall? ...
... 4. The cell wall is what makes plants __________. 5. List three important things that can pass through the cell wall of a plant. 6. Besides a plant, what other kind of cell has a cell wall? ...
5cpptdd - Cell-as-a
... • Rough ER is found in both animals cells and in plant cells. Appears “pebble” by electron microscopy due to the presence of numerous ribosome on its surface. ...
... • Rough ER is found in both animals cells and in plant cells. Appears “pebble” by electron microscopy due to the presence of numerous ribosome on its surface. ...
Chloroplast Mitochondria Cell Membrane Golgi Apparatus Cell Wall
... structural unit of all life. All organisms are made up of cells and all the substances of an organism are products of the cell. More than three hundred years ago an English scientists Robert Hooke (1635-1703) observed some by the name of ________________ ...
... structural unit of all life. All organisms are made up of cells and all the substances of an organism are products of the cell. More than three hundred years ago an English scientists Robert Hooke (1635-1703) observed some by the name of ________________ ...
Study Guide for Test on Cells - Mercer Island School District
... surface area is critical for supporting the needs of the cell (notes and p. 128-129) Be able to explain the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and be able to name types of organisms composed of these cell types. Know that while prokaryotic cells do not have any membrane-bound organe ...
... surface area is critical for supporting the needs of the cell (notes and p. 128-129) Be able to explain the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and be able to name types of organisms composed of these cell types. Know that while prokaryotic cells do not have any membrane-bound organe ...
passive-and-active-transport
... are more crowded to where they are less crowded. It has a special name because of the importance of water to living cells. ...
... are more crowded to where they are less crowded. It has a special name because of the importance of water to living cells. ...
• Compare and contrast the organization of a living system (cell
... Adapted from Understanding by Design: Professional Development Handbook. McTighe and Wiggins. ASCD. 2004. ...
... Adapted from Understanding by Design: Professional Development Handbook. McTighe and Wiggins. ASCD. 2004. ...
ch8_sec1 - LeMars Community Schools
... conditions in a changing environment. Individual cells, as well as organisms, must maintain homeostasis in order to live. • One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. ...
... conditions in a changing environment. Individual cells, as well as organisms, must maintain homeostasis in order to live. • One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. ...
5 kingdoms
... • eukaryotic organisms – can be photosynthetic, absorptive or ingestive. • Complex 1 cell (many organelles) • some move (cilia, flagella, pseudopodia); others don't • Ex. amoeba, diatom, euglena, paramecium, some algae (unicellular), etc ...
... • eukaryotic organisms – can be photosynthetic, absorptive or ingestive. • Complex 1 cell (many organelles) • some move (cilia, flagella, pseudopodia); others don't • Ex. amoeba, diatom, euglena, paramecium, some algae (unicellular), etc ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.























