Elena Aragon
... Cells without walls that are immersed in an isotonic environment, there will be no net movement of water across the plasma membrane, because water is flowing across the membrane at the same rate in both directions. Thus, in an isotonic environment, the volume of a cell without walls is stable. In a ...
... Cells without walls that are immersed in an isotonic environment, there will be no net movement of water across the plasma membrane, because water is flowing across the membrane at the same rate in both directions. Thus, in an isotonic environment, the volume of a cell without walls is stable. In a ...
Cellular Transport - pams-hoey
... • Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane like the cell membrane Water diffuses across a membrane from an area of high concentration (crowded) to an area of low concentration (more space). ...
... • Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane like the cell membrane Water diffuses across a membrane from an area of high concentration (crowded) to an area of low concentration (more space). ...
Worksheet - Moore Public Schools
... Genes within the chromatin are made of 5. ____________________________ (DNA). The DNA stores the organism’s entire encoded genetic information. The DNA is similar in every cell of the body, but depending on the specific cell type, some genes may be turned on or off - that's why a liver cell is diffe ...
... Genes within the chromatin are made of 5. ____________________________ (DNA). The DNA stores the organism’s entire encoded genetic information. The DNA is similar in every cell of the body, but depending on the specific cell type, some genes may be turned on or off - that's why a liver cell is diffe ...
AP Biology: Fall Final Study Guide
... The monomer and polymer for all macromolecules The function of all macromolecules Interactions in protein structure that result in conformational shape ...
... The monomer and polymer for all macromolecules The function of all macromolecules Interactions in protein structure that result in conformational shape ...
Slide 1
... II. Unlike mitosis, the maternal (solid) and paternal (dotted) chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material. ...
... II. Unlike mitosis, the maternal (solid) and paternal (dotted) chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material. ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps energy from sunlight and gives plants their green color Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria Small bumps located on portio ...
... Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps energy from sunlight and gives plants their green color Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria Small bumps located on portio ...
Lecture 7: the cytoskeleton and cell movement
... Neurons have two types of processes extend from the cell body: Dendrites: short; receive stimuli from other nerve cells Axon; long; carries impulses from the cell body to other cells In dendrites, microtubules are bound to MAP2 and are oriented in both directions. Microtubules in axons are bound to ...
... Neurons have two types of processes extend from the cell body: Dendrites: short; receive stimuli from other nerve cells Axon; long; carries impulses from the cell body to other cells In dendrites, microtubules are bound to MAP2 and are oriented in both directions. Microtubules in axons are bound to ...
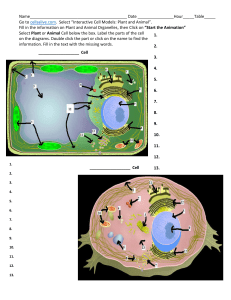
Name
... 12. Plants, algae, and many bacteria make their own food through the process of _________________. 13. What part of the cell helps control what enters and leaves the cell? ________________________ 14. What is the smallest unit of life in all living things called? _________________________ 15. Chloro ...
... 12. Plants, algae, and many bacteria make their own food through the process of _________________. 13. What part of the cell helps control what enters and leaves the cell? ________________________ 14. What is the smallest unit of life in all living things called? _________________________ 15. Chloro ...
Cell Membrane and Transport PPT
... The Cell (Plasma) Membrane • The cell membrane is made up of three organic parts: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. It has many parts but is still ...
... The Cell (Plasma) Membrane • The cell membrane is made up of three organic parts: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. It has many parts but is still ...
Macromolecules
... • A polymer consists of repeated, linked units, which can also bind forming large polymers called macromolecules (macro = LARGE) • Monomers link to form polymers through a chemical reaction called dehydration synthesis. During the formation of polymers, water is released or is a by-product. ...
... • A polymer consists of repeated, linked units, which can also bind forming large polymers called macromolecules (macro = LARGE) • Monomers link to form polymers through a chemical reaction called dehydration synthesis. During the formation of polymers, water is released or is a by-product. ...
Cell Cycle Notes
... A chromatid is basically one half of a chromosome Prior to cell division, each replicates and consists of two identical sister chromatids. When the cell divides, the chromatids separate from each other. One chromatid goes to each of the two new cells. Each pair of chromatids is attached at an area c ...
... A chromatid is basically one half of a chromosome Prior to cell division, each replicates and consists of two identical sister chromatids. When the cell divides, the chromatids separate from each other. One chromatid goes to each of the two new cells. Each pair of chromatids is attached at an area c ...
Y7 Cells - Marshfields School
... 14. The function of the _____________ is to digest (break down) food. 15. The function of the _____________ is to pump blood around the body. 16. Chloroplasts contain _____________ that absorbs sunlight and uses it in photosynthesis. 17. The _____________ gives support and is found in plant cells bu ...
... 14. The function of the _____________ is to digest (break down) food. 15. The function of the _____________ is to pump blood around the body. 16. Chloroplasts contain _____________ that absorbs sunlight and uses it in photosynthesis. 17. The _____________ gives support and is found in plant cells bu ...
Under what conditions do cells gain or lose water
... out. Such a membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane. Under normal conditions, water constantly passes in and out of this membrane. This diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. Like other substances, water diffuses from a region of higher concentrati ...
... out. Such a membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane. Under normal conditions, water constantly passes in and out of this membrane. This diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. Like other substances, water diffuses from a region of higher concentrati ...
Adhesion molecule
... Belts of proteins that close extracellular space between cells Prevent passage of water and water-soluble substances Account for electrical resistance across epithelia Leaky epithelia where there is need for some traffic Hormones Vasopressin Cytokines Lack of ATP causes “leak” Extravasa ...
... Belts of proteins that close extracellular space between cells Prevent passage of water and water-soluble substances Account for electrical resistance across epithelia Leaky epithelia where there is need for some traffic Hormones Vasopressin Cytokines Lack of ATP causes “leak” Extravasa ...
Diffusion and Osmosis
... Water molecules, of course, also diffuse. They move across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration. This process is called osmosis. It is important to recognize that the higher the concentration of dissolved particles in a solution, ...
... Water molecules, of course, also diffuse. They move across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration. This process is called osmosis. It is important to recognize that the higher the concentration of dissolved particles in a solution, ...
DW#4 CellsAlive Websearch
... Genes within the chromatin are made of 5. ____________________________ (DNA). The DNA stores the organism’s entire encoded genetic information. The DNA is similar in every cell of the body, but depending on the specific cell type, some genes may be turned on or off - that's why a liver cell is diffe ...
... Genes within the chromatin are made of 5. ____________________________ (DNA). The DNA stores the organism’s entire encoded genetic information. The DNA is similar in every cell of the body, but depending on the specific cell type, some genes may be turned on or off - that's why a liver cell is diffe ...
Fri. 9/19 and Wed. 9/24 Organelles
... except that it is coiled up tightly so that it can be separated cleanly into the two daughter cells ...
... except that it is coiled up tightly so that it can be separated cleanly into the two daughter cells ...
Reperfusion injury
... hepatocytes will tolerate ischemia much better than one that has just burned its last glucose molecule. Genetically determined diversity in metabolic pathways can also be important. For instance, when exposed to the same dose of a toxin, individuals who inherit variants in genes encoding cytochrome ...
... hepatocytes will tolerate ischemia much better than one that has just burned its last glucose molecule. Genetically determined diversity in metabolic pathways can also be important. For instance, when exposed to the same dose of a toxin, individuals who inherit variants in genes encoding cytochrome ...
Biochemistry
... Unsaturated fatty acids contain 1 or more __________________. These prevent them from holding the maximum number of hydrogens. This causes the carbon chain to bend into odd shapes so that they will _____ pack solidly. Thus unsaturated fats are generally ___________ at room temperature. ___________ o ...
... Unsaturated fatty acids contain 1 or more __________________. These prevent them from holding the maximum number of hydrogens. This causes the carbon chain to bend into odd shapes so that they will _____ pack solidly. Thus unsaturated fats are generally ___________ at room temperature. ___________ o ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.