I Have, Who Has_Photosynthesis_CellResp
... cells through their environment? I have cytoskeleton. Who has an extensive system of internal membranes that move proteins? I have vesicle. ...
... cells through their environment? I have cytoskeleton. Who has an extensive system of internal membranes that move proteins? I have vesicle. ...
All About Cells Review
... 2. Who was the first person to use a simple microscope and view microscopic organisms? 3.. What English scientist was first to view dead plant cells? 4. State the 3 parts to the cell theory. 5. Tell how each of these scientists contributed to the cell theory: (1)Matthias Schleiden, (2)Theodor Schwan ...
... 2. Who was the first person to use a simple microscope and view microscopic organisms? 3.. What English scientist was first to view dead plant cells? 4. State the 3 parts to the cell theory. 5. Tell how each of these scientists contributed to the cell theory: (1)Matthias Schleiden, (2)Theodor Schwan ...
syllabus - srm.cse.section-a
... INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES 1. To familiarize the students with the basic organization of organisms and subsequent building to a living being 2. To impart an understanding about the machinery of the cell functions that is ultimately responsible for various daily activities. 3. To provide knowledge abou ...
... INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES 1. To familiarize the students with the basic organization of organisms and subsequent building to a living being 2. To impart an understanding about the machinery of the cell functions that is ultimately responsible for various daily activities. 3. To provide knowledge abou ...
2014073000Ch1Test
... d. oxygen, simple sugars, carbon dioxide, and a cell wall 4. Animals get energy they need by a. absorbing sunlight b. drinking water c. breathing air d. eating food. 5. Cell theory states that a. the cell is the basic unit of all animals b. cells form from other living cells c. only living things ca ...
... d. oxygen, simple sugars, carbon dioxide, and a cell wall 4. Animals get energy they need by a. absorbing sunlight b. drinking water c. breathing air d. eating food. 5. Cell theory states that a. the cell is the basic unit of all animals b. cells form from other living cells c. only living things ca ...
Biology 9 - Unit 4b Meiosis Practice Name: 1. (a) Draw a
... _____2. Which processes always occur in meiosis but not normally in mitosis? I. ...
... _____2. Which processes always occur in meiosis but not normally in mitosis? I. ...
Cell Division
... MATCHING: Match the vocabulary word with its definition: _____ framework of microtubules to which chromosomes A. Chromatid attach during cell division to pull them to the poles _____ paired structures that appear next to the nucleus B. Centriole during prophase to separate chromosomes _____ constric ...
... MATCHING: Match the vocabulary word with its definition: _____ framework of microtubules to which chromosomes A. Chromatid attach during cell division to pull them to the poles _____ paired structures that appear next to the nucleus B. Centriole during prophase to separate chromosomes _____ constric ...
How Does a Cell Spend Most of it`s Life
... Hypothesis: Which stage do you think the cell spends most of its time in? Why? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________ ...
... Hypothesis: Which stage do you think the cell spends most of its time in? Why? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________ ...
Sections 3
... 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic cells to eukaryotic cells. Discuss what they have in common and what is different between them. ...
... 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic cells to eukaryotic cells. Discuss what they have in common and what is different between them. ...
Compare the size of these organisms
... What tissues in our body need to undergo a lot of cell division? Skin Why? ...
... What tissues in our body need to undergo a lot of cell division? Skin Why? ...
Compare the size of these organisms
... What tissues in our body need to undergo a lot of cell division? Skin Why? ...
... What tissues in our body need to undergo a lot of cell division? Skin Why? ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 8e
... Describe the life cycle of a cell (explain what happens in each phase of the life cycle) Describe the process of mitosis and state its function Explain the role that mitosis plays in transmitting genes from one cell to the next. ...
... Describe the life cycle of a cell (explain what happens in each phase of the life cycle) Describe the process of mitosis and state its function Explain the role that mitosis plays in transmitting genes from one cell to the next. ...
72. A foetal goat tongue cell line found highly sensitive for foot-and-mouth disease virus
... While infectious FMDV usually is present with high titres in fresh vesicular material, titres found in sera, nasal swabs, saliva and oropharyngeal samples (probang) are much lower, necessitating highly sensitive detection systems. The most sensitive cells for FMD virus isolation are primary bovine t ...
... While infectious FMDV usually is present with high titres in fresh vesicular material, titres found in sera, nasal swabs, saliva and oropharyngeal samples (probang) are much lower, necessitating highly sensitive detection systems. The most sensitive cells for FMD virus isolation are primary bovine t ...
Skeletal System Activities – Chapter 7
... 3.1.2 Differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. 3.1.3 Identify the structure and function of the parts of a typical eukaryotic cell. 3.1.4 Compare and contrast structures of plant and animal cells. 3.1.5 Describe how a cell’s plasma membrane functions. 3.1.6 Identify the roles of prot ...
... 3.1.2 Differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. 3.1.3 Identify the structure and function of the parts of a typical eukaryotic cell. 3.1.4 Compare and contrast structures of plant and animal cells. 3.1.5 Describe how a cell’s plasma membrane functions. 3.1.6 Identify the roles of prot ...
Virus and Kingdom Overview
... Finally, the RNA replicas leave the daughter cells after coating themselves with a protein. ...
... Finally, the RNA replicas leave the daughter cells after coating themselves with a protein. ...
Microbiology Terms
... Cell Terms Cell – a basic unit of structure and function in all organisms. Cell theory – states that all organisms are made up of one or more cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and all cells come from other cells Eukaryote – an organism whose cells have a distinct membranebound nucleus and o ...
... Cell Terms Cell – a basic unit of structure and function in all organisms. Cell theory – states that all organisms are made up of one or more cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and all cells come from other cells Eukaryote – an organism whose cells have a distinct membranebound nucleus and o ...
Cell Growth & Reproduction II
... Interphase is a cell growth phase where the cell increases in size, carries on metabolism, and duplicates chromosomes prior to division. Interphase is divided into 3 parts: G1 – Cell grows & protein production is high. S – DNA Synthesis – the cell copies it’s chromosomes during this phase. G2 –A sec ...
... Interphase is a cell growth phase where the cell increases in size, carries on metabolism, and duplicates chromosomes prior to division. Interphase is divided into 3 parts: G1 – Cell grows & protein production is high. S – DNA Synthesis – the cell copies it’s chromosomes during this phase. G2 –A sec ...
Anatomy of Plants
... • Packages energy(proteins, carbohydrates, & hormones.) • Delivers packaged energy to different parts of the cell ...
... • Packages energy(proteins, carbohydrates, & hormones.) • Delivers packaged energy to different parts of the cell ...
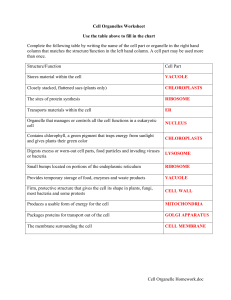
Cell Organelle Homework.doc Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Use the table above to fill in the chart Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function ...
... Use the table above to fill in the chart Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function ...
105110_Mitosis_Intro
... • Cell spends the majority of life in interphase – G1: Cells grow to mature size (growth phase) – S: Cell’s DNA is copied (synthesis phase) – G2: Cell prepares for division – G0: Cell exits cell cycle. Cells are not copying DNA or preparing to divide. (The vast majority of the body’s cells are in G0 ...
... • Cell spends the majority of life in interphase – G1: Cells grow to mature size (growth phase) – S: Cell’s DNA is copied (synthesis phase) – G2: Cell prepares for division – G0: Cell exits cell cycle. Cells are not copying DNA or preparing to divide. (The vast majority of the body’s cells are in G0 ...
Planet Earth and Its Environment A 5000
... The role of mitosis in multicellular organisms can be summarised as follows: Growth Repair of damaged tissue and replacement of worn out cells Genetic stability: mitosis ensures the precise and equal distribution of chromosomes to each daughter nucleus, so that all resulting cells contain the ...
... The role of mitosis in multicellular organisms can be summarised as follows: Growth Repair of damaged tissue and replacement of worn out cells Genetic stability: mitosis ensures the precise and equal distribution of chromosomes to each daughter nucleus, so that all resulting cells contain the ...
CELL CYCLE and THE LENGTH OF EACH PHASE
... A single fertilized human egg cell will divide to form two cells. These two cells will each divide into two cells. In time, trillions of cells are produced. The cycle of growth and division takes place in three major stages: 1. Interphase: The life and times of the cell (including growth and prep fo ...
... A single fertilized human egg cell will divide to form two cells. These two cells will each divide into two cells. In time, trillions of cells are produced. The cycle of growth and division takes place in three major stages: 1. Interphase: The life and times of the cell (including growth and prep fo ...