Lab: How long do Onion Cell spend in each stage of the Cell Cycle
... Name: _________________________________ Per ______ Lab: How long does an Onion Cell spend in each stage of the Cell Cycle? Information: It is hard to imagine that you can estimate how much time a cell spend in each phase of cell division from a slide of dead cells, yet this is precisely what you wil ...
... Name: _________________________________ Per ______ Lab: How long does an Onion Cell spend in each stage of the Cell Cycle? Information: It is hard to imagine that you can estimate how much time a cell spend in each phase of cell division from a slide of dead cells, yet this is precisely what you wil ...
Science Lesson Plan
... 1. The students will read as and class or in pairs pages 26 and 27 in the text book. 2. Teacher will discuss. 3. We will, as a class, review the definition of cell unicellular and multi cellular and define the parts of the cell: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuoles. (Notes) 4. Students wi ...
... 1. The students will read as and class or in pairs pages 26 and 27 in the text book. 2. Teacher will discuss. 3. We will, as a class, review the definition of cell unicellular and multi cellular and define the parts of the cell: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuoles. (Notes) 4. Students wi ...
Chapter 2 – Chemistry of Life and the Cell
... 2. High pH is basic and has more OHProkaryotic organisms are one celled and have no nucleus, bacteria is an example of this kind of cell. Eukaryotic organisms are made up of one or more nucleated cells that contain organelles that perform specific functions. An example of a eukaryote is the human. T ...
... 2. High pH is basic and has more OHProkaryotic organisms are one celled and have no nucleus, bacteria is an example of this kind of cell. Eukaryotic organisms are made up of one or more nucleated cells that contain organelles that perform specific functions. An example of a eukaryote is the human. T ...
2-1,2-2 Cell Division - Cell Structures
... Cytoplasm – This is the fluid that contains all of the organelles in the cell. The cytoplasm also contains a network of microtubules that act like a rail system and skeleton for the cell. During cell division a segment of the microtubules, called the centrioles, help the cell divide evenly in half. ...
... Cytoplasm – This is the fluid that contains all of the organelles in the cell. The cytoplasm also contains a network of microtubules that act like a rail system and skeleton for the cell. During cell division a segment of the microtubules, called the centrioles, help the cell divide evenly in half. ...
2.3 note full - Grade 8A/B Science
... Amoeba are unicellular and they will live for 2 days Human brain cells can live for 120 days Skin cells live for 20 days This reflects on how quickly those cells can accumulate errors The average human body will have about 3 billion cells die every day Cells can die through programmed ce ...
... Amoeba are unicellular and they will live for 2 days Human brain cells can live for 120 days Skin cells live for 20 days This reflects on how quickly those cells can accumulate errors The average human body will have about 3 billion cells die every day Cells can die through programmed ce ...
Biology 12
... C. spherical protozoans use more energy D. irregular protozoans have a greater surface area to volume ratio ...
... C. spherical protozoans use more energy D. irregular protozoans have a greater surface area to volume ratio ...
Cell Wall
... Where are organelles found? Organelles are found in the cytoplasm of Eukaryotic cells…plant and animal cells. ...
... Where are organelles found? Organelles are found in the cytoplasm of Eukaryotic cells…plant and animal cells. ...
Cells Alive! - Harrison High School
... Cell History 1. The invention of microscope led to the study of cells 2. Notable Scientists a. Robert Hooke: 1st to describe the cell b. Schleiden: Plants are composed of cells c. Schwann: Animals are composed of cells ...
... Cell History 1. The invention of microscope led to the study of cells 2. Notable Scientists a. Robert Hooke: 1st to describe the cell b. Schleiden: Plants are composed of cells c. Schwann: Animals are composed of cells ...
Section 10–2 Cell Division (pages 244–249)
... 10. What happens during the S phase? Chromosomes are replicated and the synthesis of DNA molecules takes place. Also, key proteins associated with the chromosomes are synthesized. ...
... 10. What happens during the S phase? Chromosomes are replicated and the synthesis of DNA molecules takes place. Also, key proteins associated with the chromosomes are synthesized. ...
TheHumanCheekCellANSWERKEY
... 5. The light microscope used in the lab is not powerful enough to view other organelles in the cheek cell. What parts of the cell are visible? Nucleus and cell membrane. 6. List two organelles that were NOT visible but should have been in the cheek cell. Mitochondria or lysosome or endoplasmic retic ...
... 5. The light microscope used in the lab is not powerful enough to view other organelles in the cheek cell. What parts of the cell are visible? Nucleus and cell membrane. 6. List two organelles that were NOT visible but should have been in the cheek cell. Mitochondria or lysosome or endoplasmic retic ...
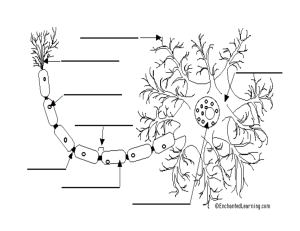
axon diagram
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
Bio 12-Diagram of Mi.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Mitosis is the duplication and division of a eukaryotic cell's nucleus and nuclear material (DNA). The stages of mitosis are: [interphase (the cell when not undergoing mitosis, but the DNA is replicated)], prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. ...
... Mitosis is the duplication and division of a eukaryotic cell's nucleus and nuclear material (DNA). The stages of mitosis are: [interphase (the cell when not undergoing mitosis, but the DNA is replicated)], prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. ...
Mitosis (cell division)
... • Cell spends the majority of life in interphase – G1: Cells grow to mature size (growth phase) – S: Cell’s DNA is copied (synthesis phase) – G2: Cell prepares for division – G0: Cell exits cell cycle. Cells are not copying DNA or preparing to divide. (The vast majority of the body’s cells are in G0 ...
... • Cell spends the majority of life in interphase – G1: Cells grow to mature size (growth phase) – S: Cell’s DNA is copied (synthesis phase) – G2: Cell prepares for division – G0: Cell exits cell cycle. Cells are not copying DNA or preparing to divide. (The vast majority of the body’s cells are in G0 ...
Chapter 4 : Cells - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... energy by cellular respiration. Has many folds called cristae that increases the surface area. 11. Chloroplasts – plastids that hold chlorophyll (green pigment used for making food in plants) ...
... energy by cellular respiration. Has many folds called cristae that increases the surface area. 11. Chloroplasts – plastids that hold chlorophyll (green pigment used for making food in plants) ...
A1 Cell Structure Notes
... An organelle is a specialised membrane-bound compartment within a cell that has a specific function. ...
... An organelle is a specialised membrane-bound compartment within a cell that has a specific function. ...
Review Puzzle
... Write the correct term in the spaces besides each definition. The boxed letters should spell a familiar term. SPELLING COUNTS. ...
... Write the correct term in the spaces besides each definition. The boxed letters should spell a familiar term. SPELLING COUNTS. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Cells that lack internal structures surrounded by membranes. Cells with no defined nucleus. The DNA is a circular strand. ...
... Cells that lack internal structures surrounded by membranes. Cells with no defined nucleus. The DNA is a circular strand. ...
Cell Organelles
... Site of protein synthesis (where proteins are made!) Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cell Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus ...
... Site of protein synthesis (where proteins are made!) Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cell Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus ...
MAIN IDEAS
... •Nucleus – controls many of the functions of the cell contains DNA •Mitochondria – “powerhouse” of the cell where food is burned and energy is released. •Golgi bodies – packages proteins and carbohydrates into vessels for export from the cell. •ER – a network of membranes – acts like a packaging sys ...
... •Nucleus – controls many of the functions of the cell contains DNA •Mitochondria – “powerhouse” of the cell where food is burned and energy is released. •Golgi bodies – packages proteins and carbohydrates into vessels for export from the cell. •ER – a network of membranes – acts like a packaging sys ...