Cell Analogy Webquest
... Objective: Students will use the internet to research the functions of cell organelles. Students will be able to define the term analogy. Students will work in groups to create an analogy using the cell and one of the following suggestions: * City * Factory * Pizza Parlor * Automobile * Airplane and ...
... Objective: Students will use the internet to research the functions of cell organelles. Students will be able to define the term analogy. Students will work in groups to create an analogy using the cell and one of the following suggestions: * City * Factory * Pizza Parlor * Automobile * Airplane and ...
Prokaryotic Cell Diagram Homework Assignment
... that are not associated with eukaryotic organisms. In addition, all Archaea are also prokaryotic. As is the case for bacteria, it is unknown how many Archaean cells are on Earth, but the number is sure to be astronomical. In all, eukaryotic cells make up only a very small fraction of the total numbe ...
... that are not associated with eukaryotic organisms. In addition, all Archaea are also prokaryotic. As is the case for bacteria, it is unknown how many Archaean cells are on Earth, but the number is sure to be astronomical. In all, eukaryotic cells make up only a very small fraction of the total numbe ...
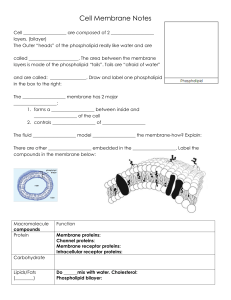
Cell Defense Build a membrane: The membrane of the cell is
... The membrane of the cell is selectively permeable meaning that only some substances are allowed to enter and leave the cell. The membrane is organized into a lipid bilayer. Each layer is made up of macromolecules called phospholipids (a phosphate head and 2 fatty acid tails). The heads are hydroph ...
... The membrane of the cell is selectively permeable meaning that only some substances are allowed to enter and leave the cell. The membrane is organized into a lipid bilayer. Each layer is made up of macromolecules called phospholipids (a phosphate head and 2 fatty acid tails). The heads are hydroph ...
A Project about Cells
... Label all parts of the cell correctly. Explain why it is important to know about cells. Explain the jobs of each part of the cell correctly. Explain simply why the cell is good at its job. Ext. State the approximate size of the cell. Do this in more than 2 units (one being cm, N.B. it is likely to b ...
... Label all parts of the cell correctly. Explain why it is important to know about cells. Explain the jobs of each part of the cell correctly. Explain simply why the cell is good at its job. Ext. State the approximate size of the cell. Do this in more than 2 units (one being cm, N.B. it is likely to b ...
The Discovery and Basic Cell Theory
... 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic living units within organism, and the chemical reactions of life take place within cells. 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
... 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic living units within organism, and the chemical reactions of life take place within cells. 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
The Living World - Chapter 4
... • Johannes Purkinji – Coined the word protoplasm to describe the content of the cell ...
... • Johannes Purkinji – Coined the word protoplasm to describe the content of the cell ...
brief overview of the 5 kingdoms
... (e.g. swim, fly, run). Some move by beating of cilia or flagella, or oozing like an amoeba. Others like corals and oysters do not move from place to place. Respiration – The process of respiration in body cells involves conversion of sugar and oxygen to ENERGY, carbon dioxide and water. Sensitiv ...
... (e.g. swim, fly, run). Some move by beating of cilia or flagella, or oozing like an amoeba. Others like corals and oysters do not move from place to place. Respiration – The process of respiration in body cells involves conversion of sugar and oxygen to ENERGY, carbon dioxide and water. Sensitiv ...
Unit 3 Exploration Guide SOL: LS.2, LS.3, LS.5, and 6.5 Previous
... compounds. 20. Describe the structure and function of water. 21. Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane. 22. Compare and contrast passive and active transport. 23. Explain what happens to a cell put into an environment with more, less, or equal amounts of water than is inside the c ...
... compounds. 20. Describe the structure and function of water. 21. Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane. 22. Compare and contrast passive and active transport. 23. Explain what happens to a cell put into an environment with more, less, or equal amounts of water than is inside the c ...
Two Kinds of Cells
... I find it interesting that if we look at every cell on earth from trees to humans to bacteria (yes, bacteria are a cell), we can categorize them into just two types. Before we get to their official names though, we have to figure out what makes them different. Inside each cell are a variety of d ...
... I find it interesting that if we look at every cell on earth from trees to humans to bacteria (yes, bacteria are a cell), we can categorize them into just two types. Before we get to their official names though, we have to figure out what makes them different. Inside each cell are a variety of d ...
Movement through the Membrane
... Cell Membrane One of the most important functions of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of molecules from one side of the membrane to the other. The cell membrane is selectively permeable (it doesn’t let just everything through; it is selective). ...
... Cell Membrane One of the most important functions of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of molecules from one side of the membrane to the other. The cell membrane is selectively permeable (it doesn’t let just everything through; it is selective). ...
CYTOSKELETON
... nerve fibers. They are found in the cytoplasmic matrix of all eukaryotic cells. They are also present in structures like centrioles, basal bodies, cilia or flagella, sensory hair, spindle apparatus, chromosome fibres, nerve processes, sperm tail etc. They are absent in prokaryotic cells. Microtubule ...
... nerve fibers. They are found in the cytoplasmic matrix of all eukaryotic cells. They are also present in structures like centrioles, basal bodies, cilia or flagella, sensory hair, spindle apparatus, chromosome fibres, nerve processes, sperm tail etc. They are absent in prokaryotic cells. Microtubule ...
Jeopardy—Biology The Cell Rules: - answers do not have to be in
... 26. The model that represents how proteins, phospholipids, and other cell membrane components are able to move around within the cell membrane is ...
... 26. The model that represents how proteins, phospholipids, and other cell membrane components are able to move around within the cell membrane is ...
The Incredible Edible Cell
... The cell nucleus is the largest organelle found in the cell. The nucleus is spherical in shape and separated from the cytoplasm by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope isolates and protects a cell's DNA from various molecules that could accidentally damage its structur ...
... The cell nucleus is the largest organelle found in the cell. The nucleus is spherical in shape and separated from the cytoplasm by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope isolates and protects a cell's DNA from various molecules that could accidentally damage its structur ...
Cell Defense App Guide Sheet Build a membrane: Diffusion
... meaning that only some substances are allowed to enter and leave the cell. The membrane is organized into a lipid bilayer. Each layer is made up of macromolecules called phospholipids (a phosphate head and 2 fatty acid tails). ...
... meaning that only some substances are allowed to enter and leave the cell. The membrane is organized into a lipid bilayer. Each layer is made up of macromolecules called phospholipids (a phosphate head and 2 fatty acid tails). ...
Methods of Cell Transport, Such As Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active
... • Tonicity: the movement of water into and out of cells in response to the water concentration on the outside of the cell. Water moves from where it is in high concentration to where it is in low concentration until an equilibrium of the water concentration is reached. ...
... • Tonicity: the movement of water into and out of cells in response to the water concentration on the outside of the cell. Water moves from where it is in high concentration to where it is in low concentration until an equilibrium of the water concentration is reached. ...
THE ORGANELLLE/ORGAN SHOW
... these structures are used during cellular reproduction, pulling the chromosomes to daughter cells during Anaphase and Telophase. ...
... these structures are used during cellular reproduction, pulling the chromosomes to daughter cells during Anaphase and Telophase. ...
File
... Color and label the central vacuole purple. Color vacuoles purple. Mitochondria are spherical to rodshaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections called cristae. The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP ...
... Color and label the central vacuole purple. Color vacuoles purple. Mitochondria are spherical to rodshaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections called cristae. The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP ...
Problem: How do animal and plant cells differ? Materiars fu IEt
... 4. What parts are found in plant cells that ar absent in animal cells? ...
... 4. What parts are found in plant cells that ar absent in animal cells? ...
Cell organelles
... ”And there shall in no wise enter into it anything that defileth, or worketh abomination, or maketh a lie: but they which are written in the Lamb’s book of life” - Revelation 21:27 ...
... ”And there shall in no wise enter into it anything that defileth, or worketh abomination, or maketh a lie: but they which are written in the Lamb’s book of life” - Revelation 21:27 ...
CONNECT! - Thousand Islands CSD / Homepage
... Name some specific molecules that can’t. Explain diffusion in the lung. Explain diffusion in the digestive tract. ...
... Name some specific molecules that can’t. Explain diffusion in the lung. Explain diffusion in the digestive tract. ...
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
... • Plants can have cell walls that are multiple layers – _____________ cell wall develops in young plants – A ______________ cell wall can develop in more mature plants • Wood is an example of a secondary cell wall ...
... • Plants can have cell walls that are multiple layers – _____________ cell wall develops in young plants – A ______________ cell wall can develop in more mature plants • Wood is an example of a secondary cell wall ...
View pdf
... From the very first cell from which they all came: the fertilized egg cell in the mother’s womb. When the egg cell divides over and over again to become an embryo, all new cells get an identical copy of the genome, and always the same double set. Egg cells are very special. The cells that divide to ...
... From the very first cell from which they all came: the fertilized egg cell in the mother’s womb. When the egg cell divides over and over again to become an embryo, all new cells get an identical copy of the genome, and always the same double set. Egg cells are very special. The cells that divide to ...