Cell Structure and Function Note Guide
... All living things are made up of one or more _____________. Single celled or _________________ organisms do many of the same things as multicellular organisms. Describe the two basic types of cells: Prokaryotes: Eukaryotes: List the structures that help single-celled organisms move: ...
... All living things are made up of one or more _____________. Single celled or _________________ organisms do many of the same things as multicellular organisms. Describe the two basic types of cells: Prokaryotes: Eukaryotes: List the structures that help single-celled organisms move: ...
The Cell Theory
... Modern Cell Theory contains 4 statements, in addition to the original Cell Theory: ...
... Modern Cell Theory contains 4 statements, in addition to the original Cell Theory: ...
Gundry Rachel Gundry Bio Lab 1615 April 3, 2012 Summary of
... have been attacked and have damage done to the cell. Necrosis causes swelling and may help to cure cancer if learned to be controlled. The author of this article said that this type of cell destruction is the most unknown and scientists still have a lot to learn about this and the role it plays in o ...
... have been attacked and have damage done to the cell. Necrosis causes swelling and may help to cure cancer if learned to be controlled. The author of this article said that this type of cell destruction is the most unknown and scientists still have a lot to learn about this and the role it plays in o ...
The Cell
... Cell Theory All things are made up of at least one cell Cells carry on life processes (RENT…) Come from “old” cells Exceptions? Where did the 1st one come from? Viruses aren’t cells ...
... Cell Theory All things are made up of at least one cell Cells carry on life processes (RENT…) Come from “old” cells Exceptions? Where did the 1st one come from? Viruses aren’t cells ...
Structure and Function of Cells
... If you drag an organelle or structure into the cell you are building and it is not part of that cell type, you will get an error message stating that this organelle or structure is not part of this type of cell. When your cell is complete, you will get a message stating that it is complete. 1. Af ...
... If you drag an organelle or structure into the cell you are building and it is not part of that cell type, you will get an error message stating that this organelle or structure is not part of this type of cell. When your cell is complete, you will get a message stating that it is complete. 1. Af ...
Normal and Neoplastic Stem Cell
... Irving Weissman, Stanford University School of Medicine, Ca. USA Self renewal is the principal property that distinguishes stem cells from their daughter cells; when stem cells divide they give rise to stem cells (by self-renewal) and progenitors (by differentiation). The balance between self-renewa ...
... Irving Weissman, Stanford University School of Medicine, Ca. USA Self renewal is the principal property that distinguishes stem cells from their daughter cells; when stem cells divide they give rise to stem cells (by self-renewal) and progenitors (by differentiation). The balance between self-renewa ...
Mitosis Questions and Answers
... Called Gap 1 or First Growth phase; cell grows and maintains normal functions. Cells make RNA and proteins during this phase. ...
... Called Gap 1 or First Growth phase; cell grows and maintains normal functions. Cells make RNA and proteins during this phase. ...
The Cell Cycle KEY
... Called Gap 1 or First Growth phase; cell grows and maintains normal functions. Cells make RNA and proteins during this phase. ...
... Called Gap 1 or First Growth phase; cell grows and maintains normal functions. Cells make RNA and proteins during this phase. ...
Cells Study Guide - Mrs. Pruitt`s 5th Grade Science
... Be able to identify the parts of a plant cell and animal cell diagram. Be careful! Chloroplasts look like vacuoles in a plant. You know they aren’t because the vacuole in a plant is usually larger than the nucleus. Also, chloroplasts look a lot like mitochondria. Mitochondria usually have a squiggly ...
... Be able to identify the parts of a plant cell and animal cell diagram. Be careful! Chloroplasts look like vacuoles in a plant. You know they aren’t because the vacuole in a plant is usually larger than the nucleus. Also, chloroplasts look a lot like mitochondria. Mitochondria usually have a squiggly ...
Collect-a-Cell! - Partnerships for Environmental Education and Rural
... o Understand that all organisms are composed of one or more cells o Recognize that the presence of a nucleus determines whether a cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. 7.12 - Organisms and environments. The student knows that living systems at all levels of organization demonstrate the complementary na ...
... o Understand that all organisms are composed of one or more cells o Recognize that the presence of a nucleus determines whether a cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. 7.12 - Organisms and environments. The student knows that living systems at all levels of organization demonstrate the complementary na ...
Mitochondrion
... Passive Transport-materials do not need energy to move from higher concentration to lower to a lower concentration Active Transport-materials need energy to move from a higher concentration to lower concentration Osmosis-water moving from higher concentration to a lower concentration ...
... Passive Transport-materials do not need energy to move from higher concentration to lower to a lower concentration Active Transport-materials need energy to move from a higher concentration to lower concentration Osmosis-water moving from higher concentration to a lower concentration ...
IHS-9.1_The Structure outline_JM
... Pinocytic vesicles – pocetlike folds in the cell membrane. The folds capture and hold protein & fats, folds then form vacuoles or bubbles and enter into the cell. Cell Reproduction – Mitosis – form of asexual reproduction. o Skin, blood forming & intestinal tract cells reproduce continuously. o Musc ...
... Pinocytic vesicles – pocetlike folds in the cell membrane. The folds capture and hold protein & fats, folds then form vacuoles or bubbles and enter into the cell. Cell Reproduction – Mitosis – form of asexual reproduction. o Skin, blood forming & intestinal tract cells reproduce continuously. o Musc ...
Unit 1 and 7 Study Cards You enter the classroom and you see a
... that you do not disrupt the natural setting, would you environment. remove plants from the environment or carefully observe only? Why? Students were asked to observe pond organisms in a Petri dish. At the end of class, how would you clean up after this observation? ...
... that you do not disrupt the natural setting, would you environment. remove plants from the environment or carefully observe only? Why? Students were asked to observe pond organisms in a Petri dish. At the end of class, how would you clean up after this observation? ...
CELL BIOLOGY TECHNIQUES
... • Phase Contrast microscopy – Thin layers of cells but not thick tissues ...
... • Phase Contrast microscopy – Thin layers of cells but not thick tissues ...
$doc.title
... Cancer cells divide out of control. They are not governed by the chemical messages that control the cell cycle. Sometimes, mutations cause the loss of expression of the p53 or guardian angel gene/protein which protects the individual by destroying cancerous cells. If this is then followed by a mutat ...
... Cancer cells divide out of control. They are not governed by the chemical messages that control the cell cycle. Sometimes, mutations cause the loss of expression of the p53 or guardian angel gene/protein which protects the individual by destroying cancerous cells. If this is then followed by a mutat ...
Lesson Plan
... Instructor: Patrick Hogan Date: 23 October 2013 Ohio Academic Content Standards 1. Grade 10, Life Sciences, indicator 2 a. Compare the structure, function and interrelatedness of cell organelles in eukaryotic cells (e.g. nucleus, chromosome, mitochondria, cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplasts, cili ...
... Instructor: Patrick Hogan Date: 23 October 2013 Ohio Academic Content Standards 1. Grade 10, Life Sciences, indicator 2 a. Compare the structure, function and interrelatedness of cell organelles in eukaryotic cells (e.g. nucleus, chromosome, mitochondria, cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplasts, cili ...
Human Transforming Growth Factor - beta 1
... carcinogenesis, cellular differentiation and tissue remodeling. They are highly stable molecules and are expressed by almost all cell types in small quantities. They also regulate cell proliferation, growth, differentiation and motility as well as synthesis and deposition of the extracellular matrix ...
... carcinogenesis, cellular differentiation and tissue remodeling. They are highly stable molecules and are expressed by almost all cell types in small quantities. They also regulate cell proliferation, growth, differentiation and motility as well as synthesis and deposition of the extracellular matrix ...
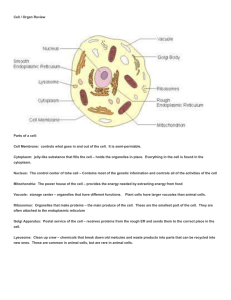
Cell / Organ Review Parts of a cell: Cell Membrane: controls what
... Groups of tissue that carry on a specific job in a living organism. ...
... Groups of tissue that carry on a specific job in a living organism. ...
REVIEW of CELL PARTS AND FUNCTION:
... CELL MEMBRANE…..boundary setting structure that retains the contents of the cell; serves as a selectively permeable barrier to the environment and regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell. NUCLEAR MEMBRANE: the double membrane that encloses the nucleus of the cell. Regulates move ...
... CELL MEMBRANE…..boundary setting structure that retains the contents of the cell; serves as a selectively permeable barrier to the environment and regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell. NUCLEAR MEMBRANE: the double membrane that encloses the nucleus of the cell. Regulates move ...
Chapter 12 notes
... Regulation of the cell cycle • kinase – enzyme that catalyzes transfer of PO4 from ATP to a target protein to activate or inactivate it Cdk’s – cyclin-dependent kinases (active only when attached to a particular cyclin) ex: MPF (maturation promoting factor) • cyclins – concentrations change cyclic ...
... Regulation of the cell cycle • kinase – enzyme that catalyzes transfer of PO4 from ATP to a target protein to activate or inactivate it Cdk’s – cyclin-dependent kinases (active only when attached to a particular cyclin) ex: MPF (maturation promoting factor) • cyclins – concentrations change cyclic ...
Cell Theory and Diversity
... between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Describe the anatomy & physiology of all cell components. ...
... between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Describe the anatomy & physiology of all cell components. ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.