7-2.1 Science Notes
... 7-2.1 Summarize the structures and functions of the major components of plant and animal cells (including the cell wall, the cell membrane, the nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles). It is essential for students to know that a cell is the smallest unit of life that conducts all life fun ...
... 7-2.1 Summarize the structures and functions of the major components of plant and animal cells (including the cell wall, the cell membrane, the nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles). It is essential for students to know that a cell is the smallest unit of life that conducts all life fun ...
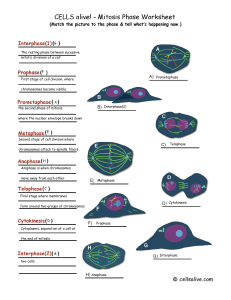
Interphase: Chromosomes are doubled
... Nuclear membrane breaks down Spindle fibers appear Centrioles pulled to opposite ends of cell Crossing over ...
... Nuclear membrane breaks down Spindle fibers appear Centrioles pulled to opposite ends of cell Crossing over ...
Activity 8 Information Sheet - The Road to Cancer What is cancer
... Our cells grow and multiply by a process called mitosis. Cell growth and multiplication is part of a continual process called the cell cycle. To move through the different stages of the cell cycle each cell has to go through a series of checkpoints. These checkpoints act a bit like traffic lights an ...
... Our cells grow and multiply by a process called mitosis. Cell growth and multiplication is part of a continual process called the cell cycle. To move through the different stages of the cell cycle each cell has to go through a series of checkpoints. These checkpoints act a bit like traffic lights an ...
Cell Project
... Due:____1/29/2016_______ Make a 3 dimensional model of either a plant or animal cell Cell model must contain the following organelles: o Nucleus o cytoplasm o mitochondria o vacuole o cell membrane o chloroplast (plant only) o Chlorophyll (plant only) o cell wall (plant only) Materials for the ...
... Due:____1/29/2016_______ Make a 3 dimensional model of either a plant or animal cell Cell model must contain the following organelles: o Nucleus o cytoplasm o mitochondria o vacuole o cell membrane o chloroplast (plant only) o Chlorophyll (plant only) o cell wall (plant only) Materials for the ...
The Cell
... 1. In 1665, Robert Hooke used a simple microscope to view thin slices of cork from plants. This was one of the first viewings of the cell. 2. Cells are the basic unit of life. 3. Anton van Leeuwenhoek was one of the first people to identify and observe that there were life forms found in water. 4. T ...
... 1. In 1665, Robert Hooke used a simple microscope to view thin slices of cork from plants. This was one of the first viewings of the cell. 2. Cells are the basic unit of life. 3. Anton van Leeuwenhoek was one of the first people to identify and observe that there were life forms found in water. 4. T ...
PowerPoint
... Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell & Culture System CEFO’s products are research cells & culture system such as medium, enzyme etc. and also cosmetic ingredient. Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) is useful cell source due to its clinical applicability for regeneration of organ and for in vitro testing such as ...
... Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell & Culture System CEFO’s products are research cells & culture system such as medium, enzyme etc. and also cosmetic ingredient. Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) is useful cell source due to its clinical applicability for regeneration of organ and for in vitro testing such as ...
7 Story Impressions
... Cells share common structural features, including an outer boundary called the cell membrane. The cell membrane encloses the cell and separates the cell interior, called the cytoplasm, from its surroundings. The cell membrane also regulates what enters and leaves a cell – including gases, nutrients, ...
... Cells share common structural features, including an outer boundary called the cell membrane. The cell membrane encloses the cell and separates the cell interior, called the cytoplasm, from its surroundings. The cell membrane also regulates what enters and leaves a cell – including gases, nutrients, ...
Cells A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living
... A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living organisms. Cells arise from pre-existing cells. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. Unicellular Organisms ...
... A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living organisms. Cells arise from pre-existing cells. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. Unicellular Organisms ...
Document
... Where are embryonic stem cells found? How does their ability to differentiate change ...
... Where are embryonic stem cells found? How does their ability to differentiate change ...
Story Impressions
... Cells share common structural features, including an outer boundary called the cell membrane. The cell membrane encloses the cell and separates the cell interior, called the cytoplasm, from its surroundings. The cell membrane also regulates what enters and leaves a cell – including gases, nutrients, ...
... Cells share common structural features, including an outer boundary called the cell membrane. The cell membrane encloses the cell and separates the cell interior, called the cytoplasm, from its surroundings. The cell membrane also regulates what enters and leaves a cell – including gases, nutrients, ...
8.2 Cell Growth and Reproduction
... DNA coils up into chromosomes just before cell divides Chromatin – uncoiled DNA ...
... DNA coils up into chromosomes just before cell divides Chromatin – uncoiled DNA ...
Chap 7 HW Biology Due Date: Please compl
... 4. You examine an unknown cell under a microscope and discover that the cell contains chloroplasts. From what type of organism does the cell likely come? 5. Why is the cell membrane sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic? What part of the membrane acts like a fluid? What makes it a mosaic? ...
... 4. You examine an unknown cell under a microscope and discover that the cell contains chloroplasts. From what type of organism does the cell likely come? 5. Why is the cell membrane sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic? What part of the membrane acts like a fluid? What makes it a mosaic? ...
Cell Structure and Function
... throughout the cytoplasm- plays a major role in organizing the structure and activities of the cells. • Motor Proteins- allows for cell movement. ...
... throughout the cytoplasm- plays a major role in organizing the structure and activities of the cells. • Motor Proteins- allows for cell movement. ...
How are Plant and Animal Cells Different Similar.indd
... 1. What does the plant cell have that the animal cell doesn’t? ____________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. How are these “additions” to the plant cell important ...
... 1. What does the plant cell have that the animal cell doesn’t? ____________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. How are these “additions” to the plant cell important ...
Structure and function of the cell
... “Selectively permeable”: decides what comes in or out of the cell “Membrane proteins”: receptors for hormones and protein channels ...
... “Selectively permeable”: decides what comes in or out of the cell “Membrane proteins”: receptors for hormones and protein channels ...
File
... Highly organized cells Have membrane bound nucleus and organelles Perform cellular functions Are found in animals, plants, protests, fungi Most are multi-cellular, but there are a limited number of unicellular eukaryotic organisms such as amoeba, paramecium and yeast. Complex cells because ...
... Highly organized cells Have membrane bound nucleus and organelles Perform cellular functions Are found in animals, plants, protests, fungi Most are multi-cellular, but there are a limited number of unicellular eukaryotic organisms such as amoeba, paramecium and yeast. Complex cells because ...
Electrochemical cells
... recharged There are two basic types of primary cells The primary wet cell and... The primary dry cell ...
... recharged There are two basic types of primary cells The primary wet cell and... The primary dry cell ...
Cell Organelle Summarizer Match the organelles below to their
... Name ____________________ Date ______ Period ___ ...
... Name ____________________ Date ______ Period ___ ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.